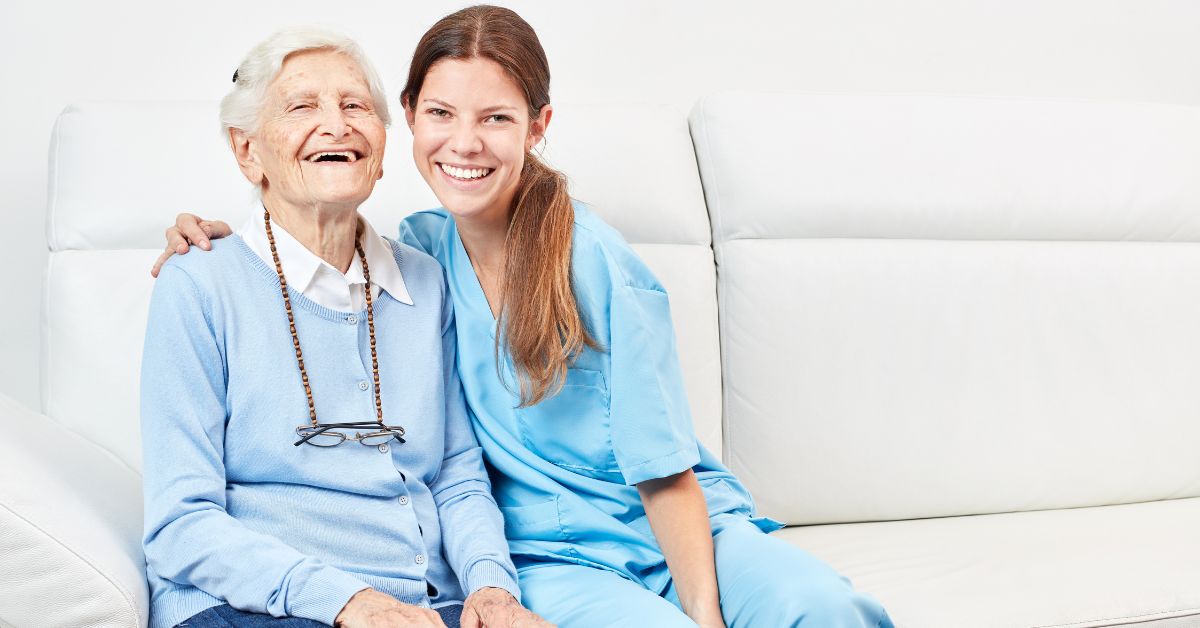
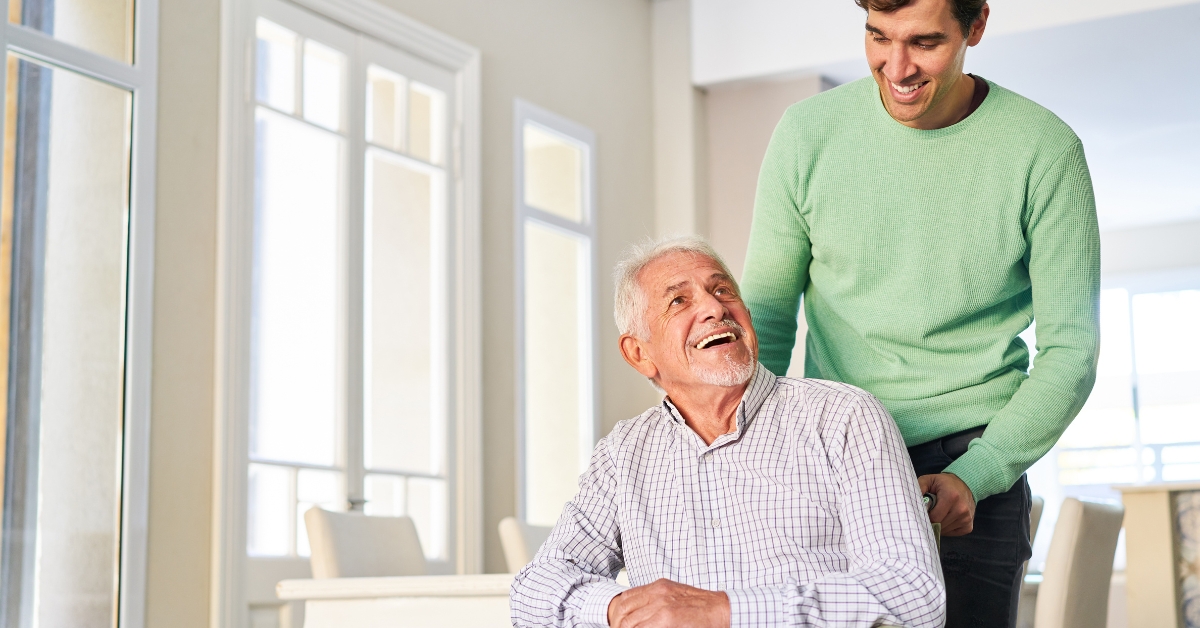
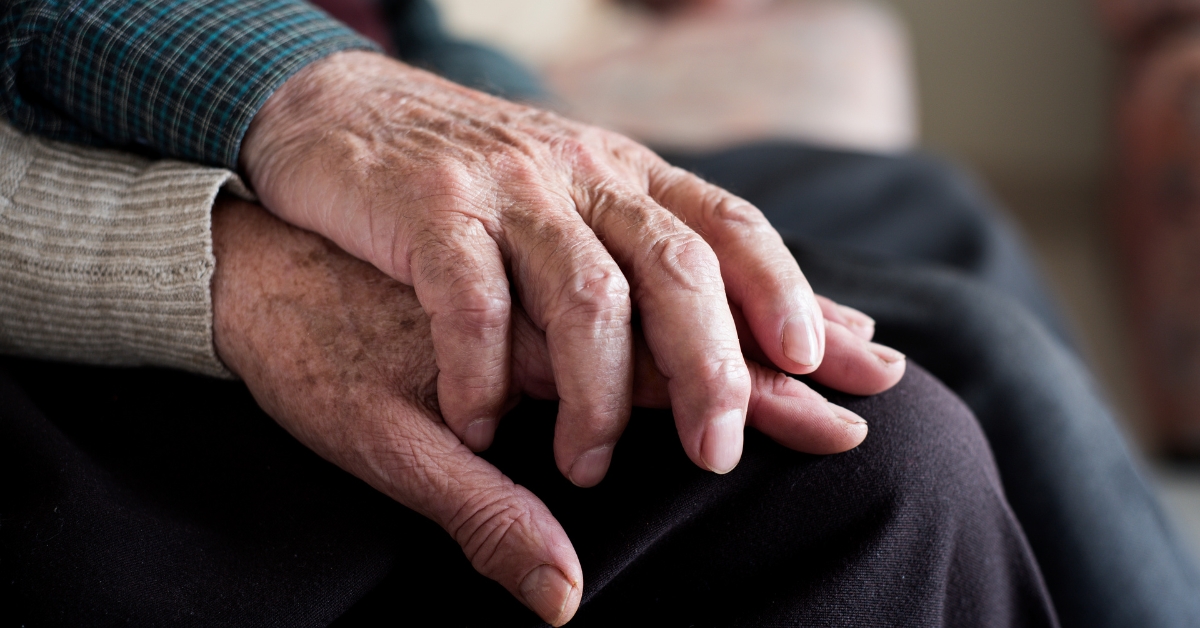
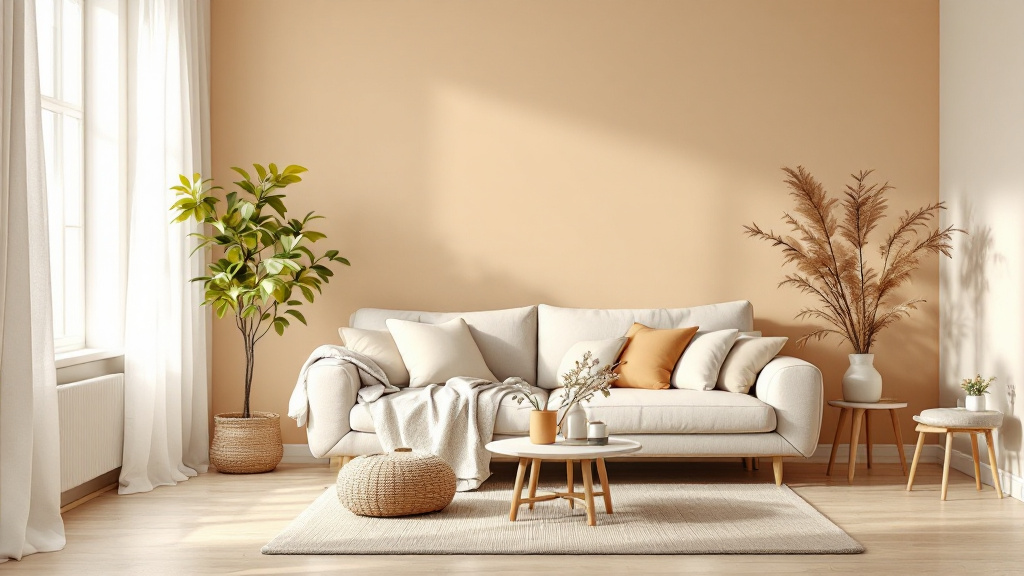
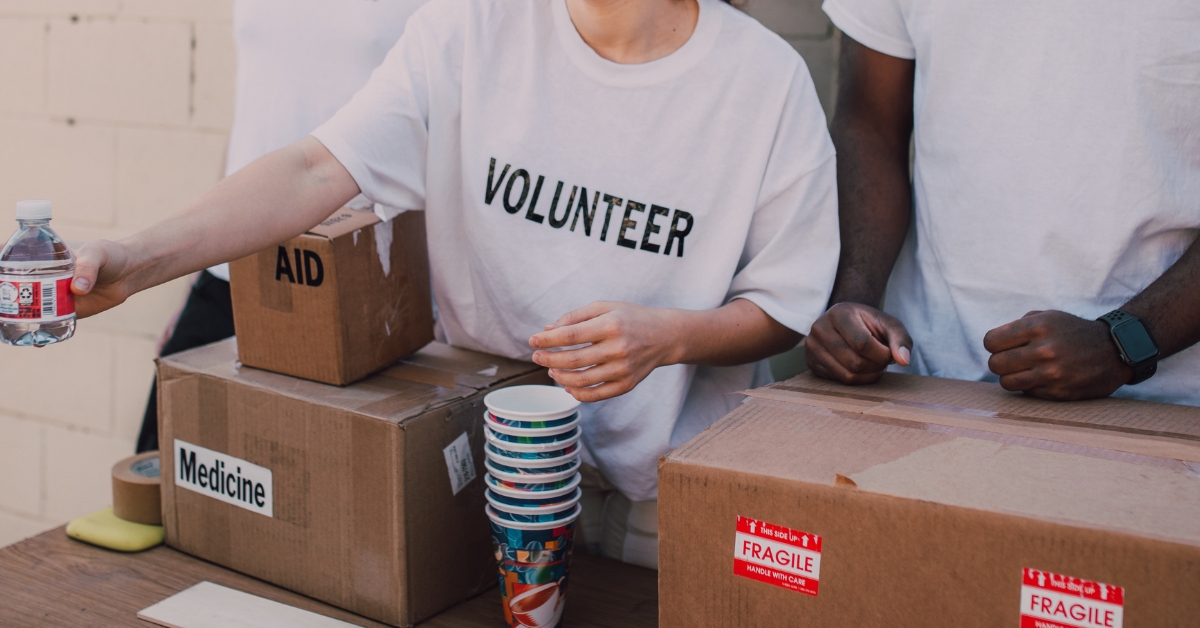
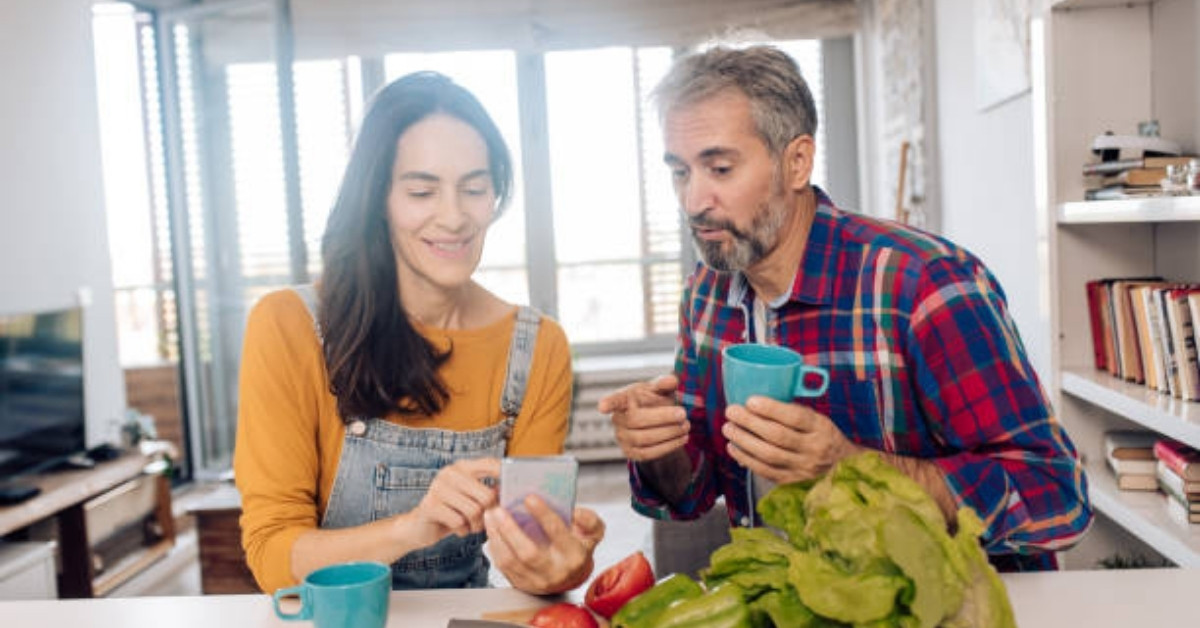
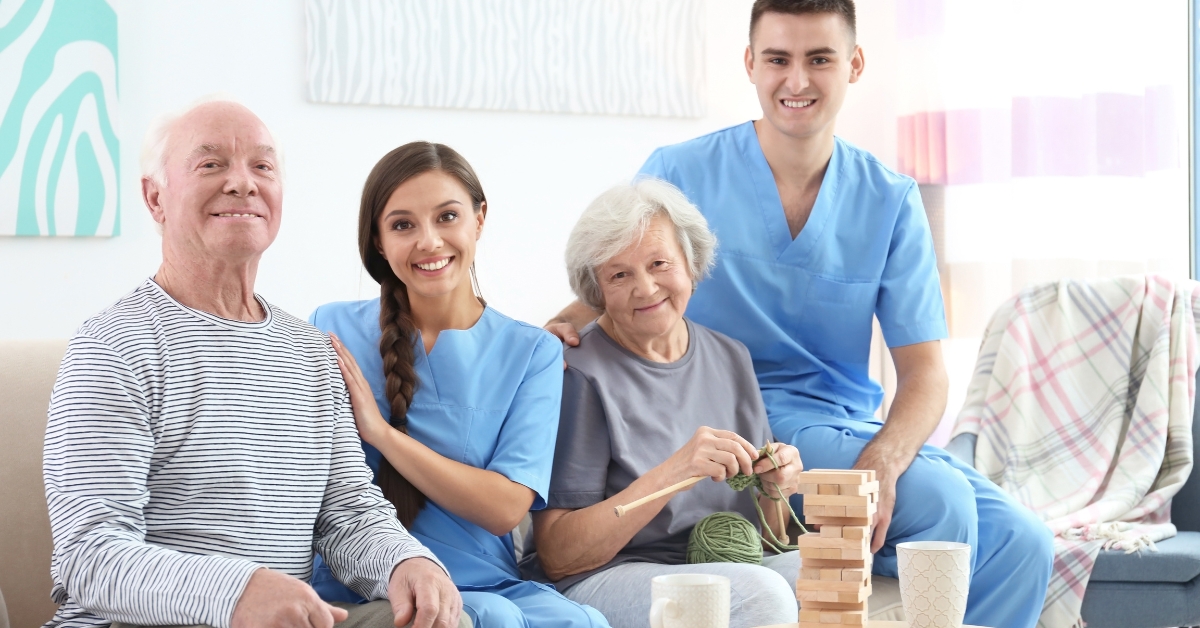
How to Build Resilience in Aging Loved Ones at Home
Empowering Seniors to Thrive at Home

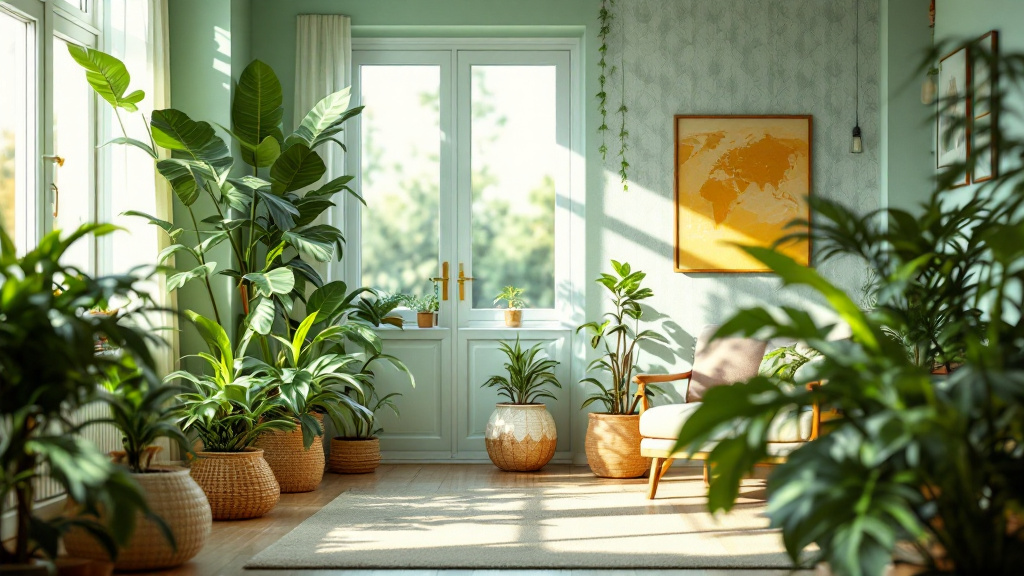
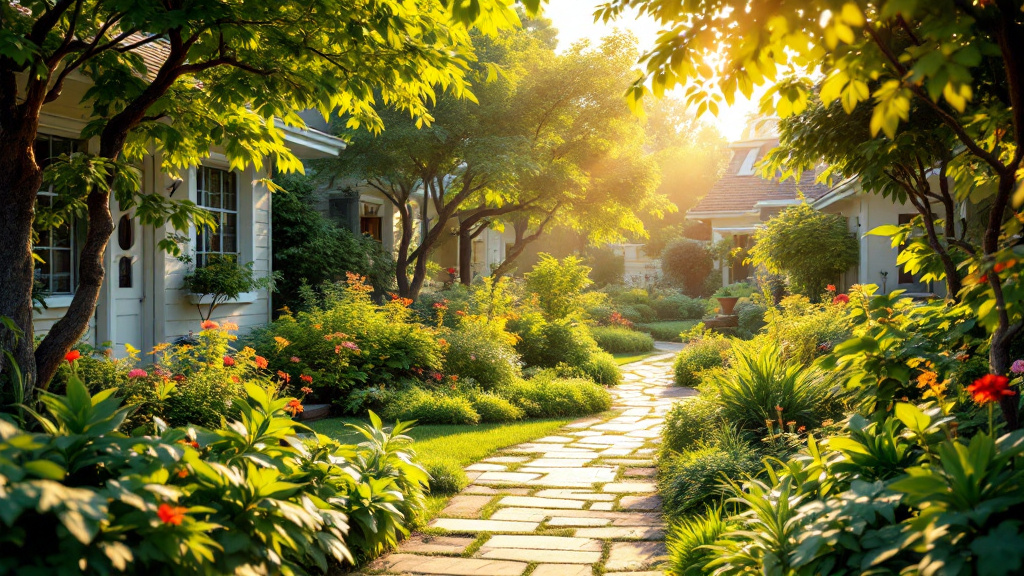
Understanding the Concept of Aging in Place
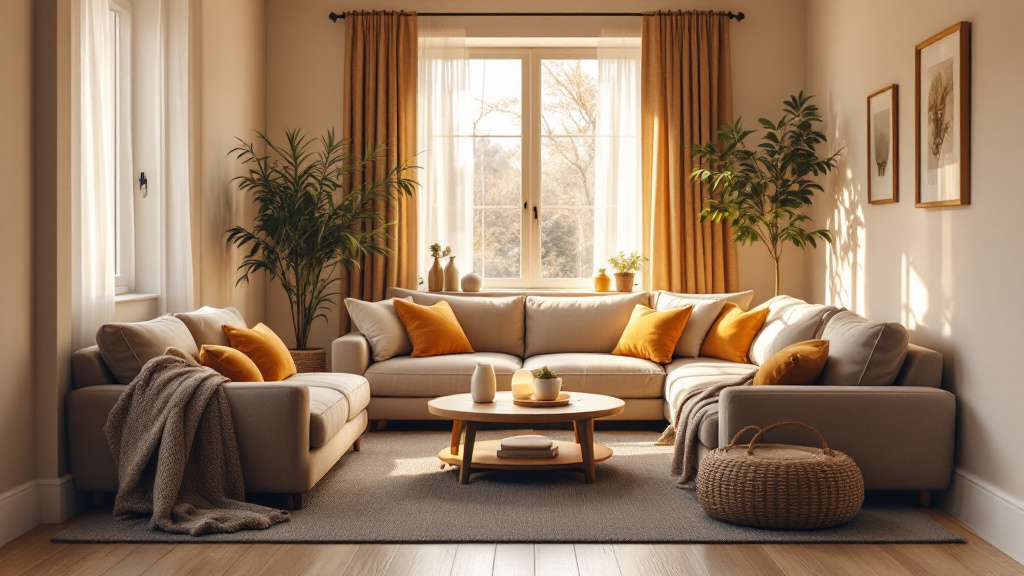
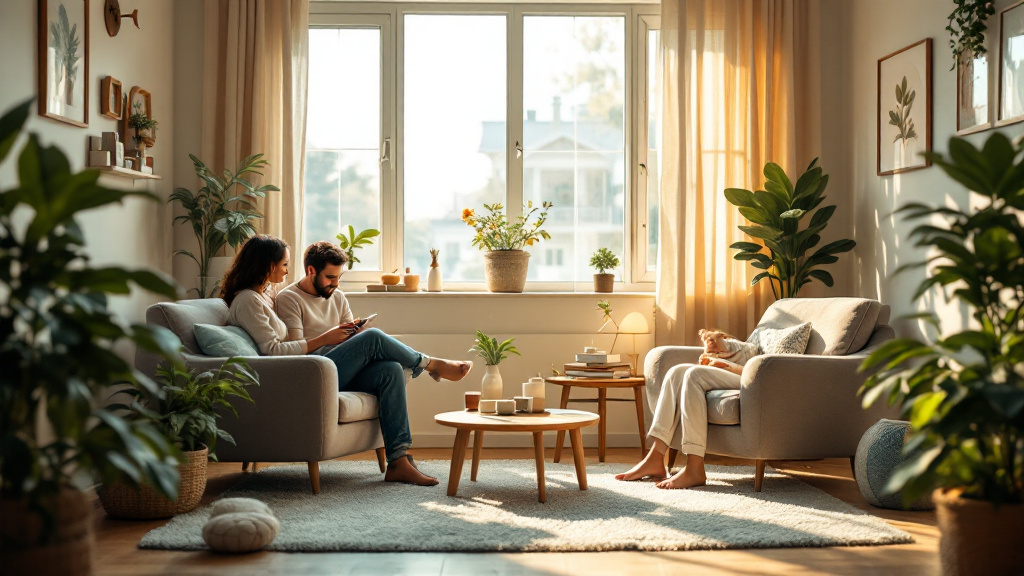
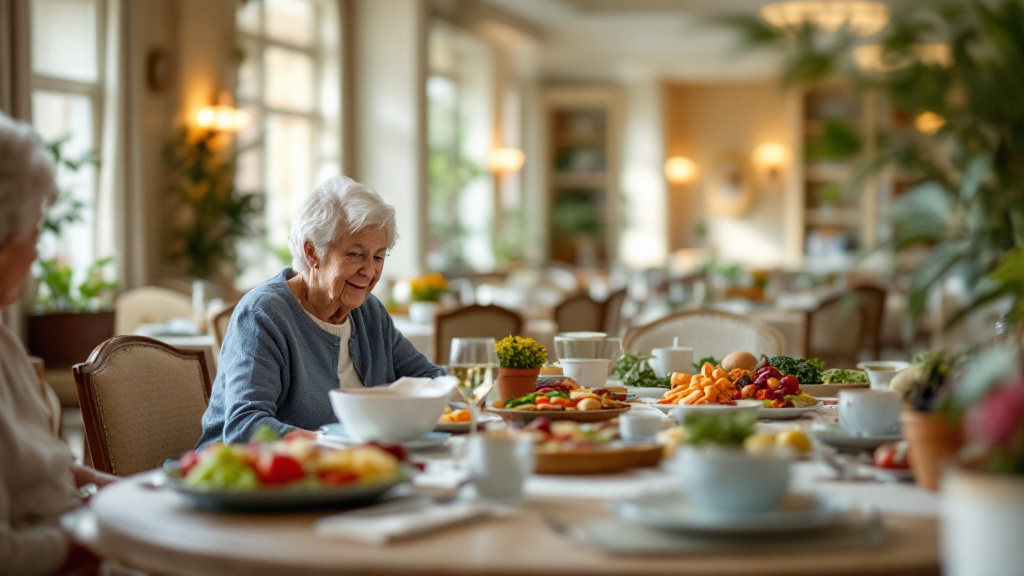
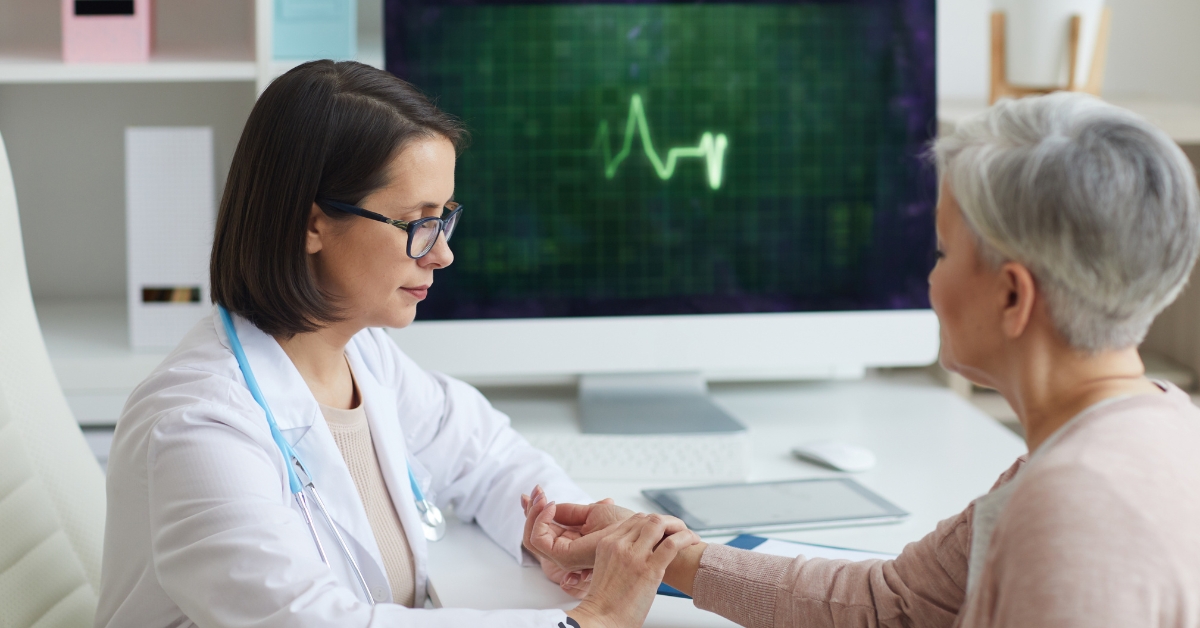
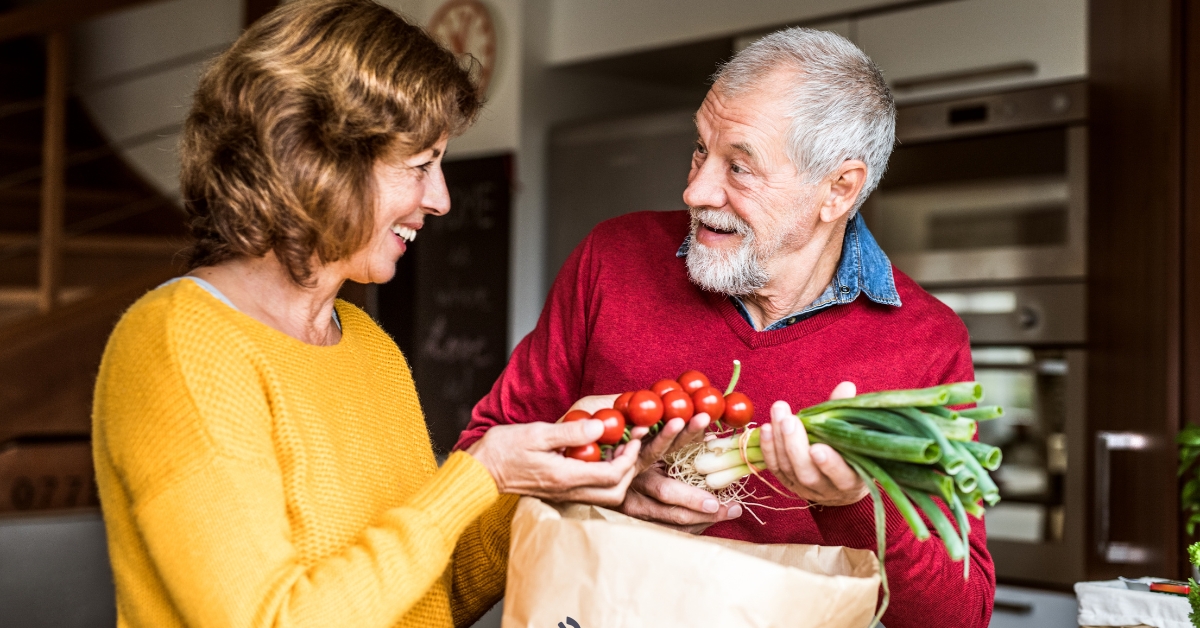
With the majority of adults over 50 expressing a strong desire to remain in their homes as they age, the concept of 'aging in place' takes on crucial significance. This approach emphasizes maintaining independence while receiving necessary support from family, friends, and community resources. Balancing safety, emotional well-being, and a sense of purpose at home can significantly bolster resilience in older adults, ensuring a high quality of life.
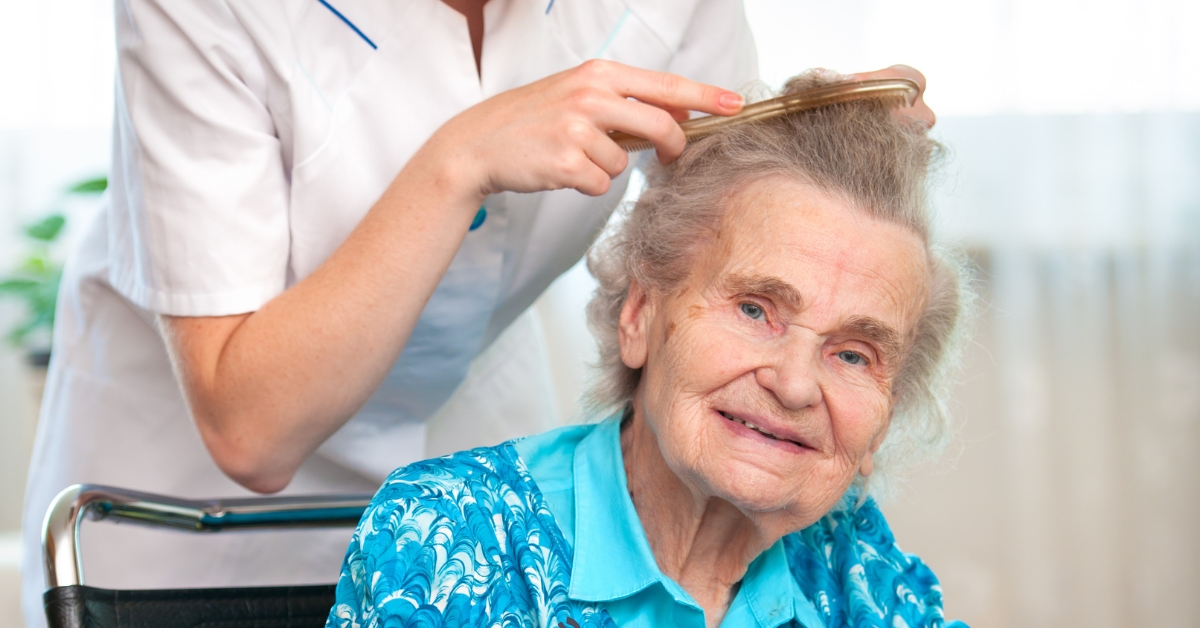
Fostering a Supportive Home Environment

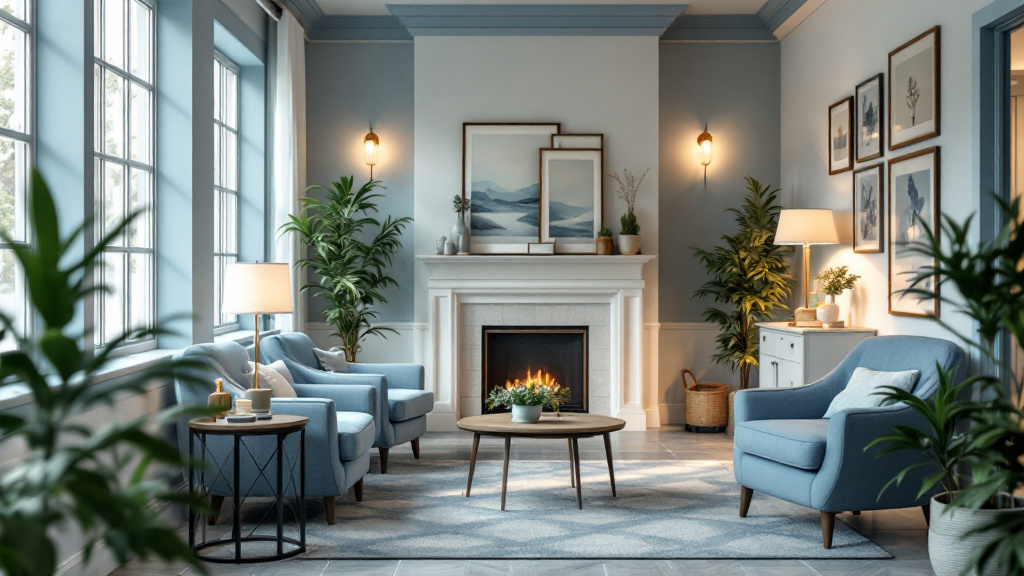
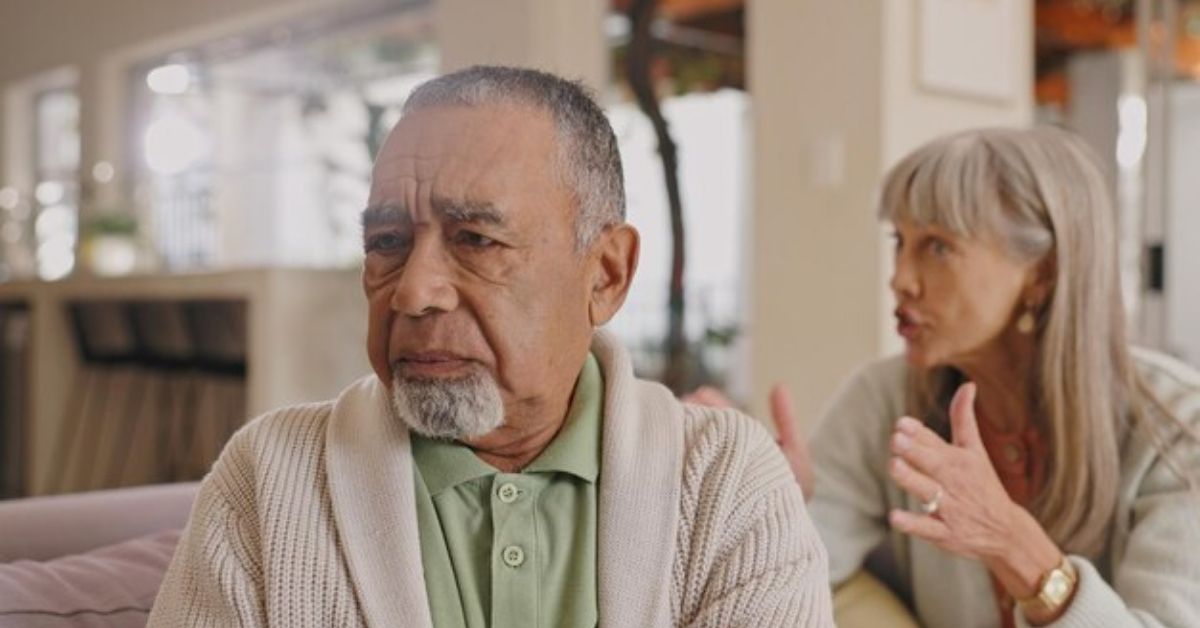
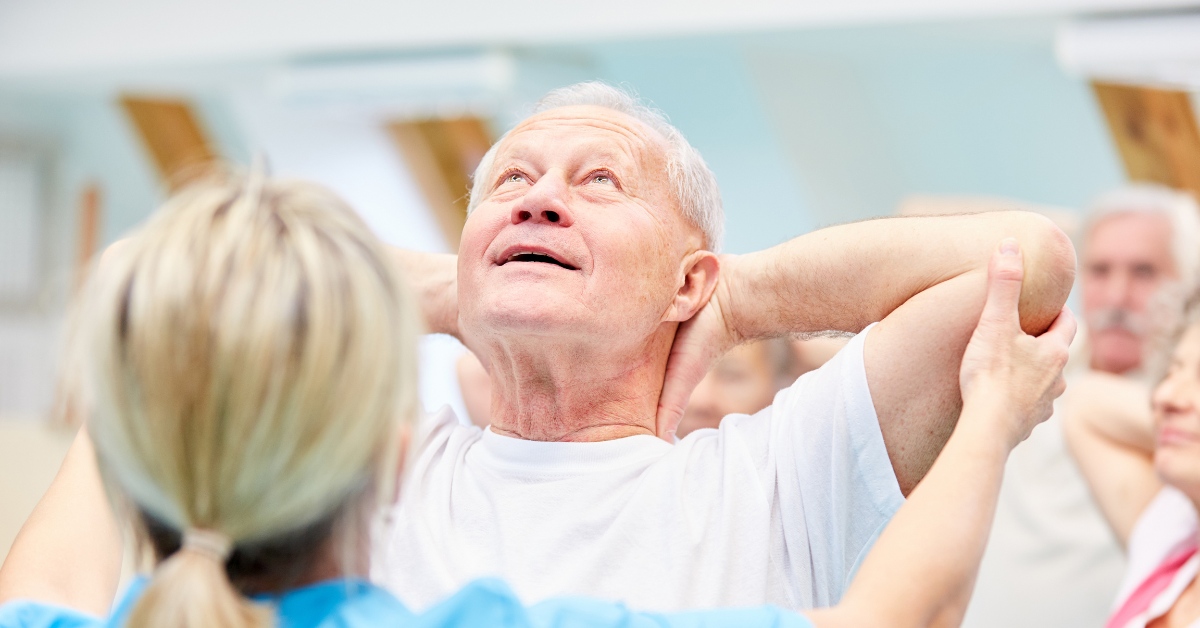
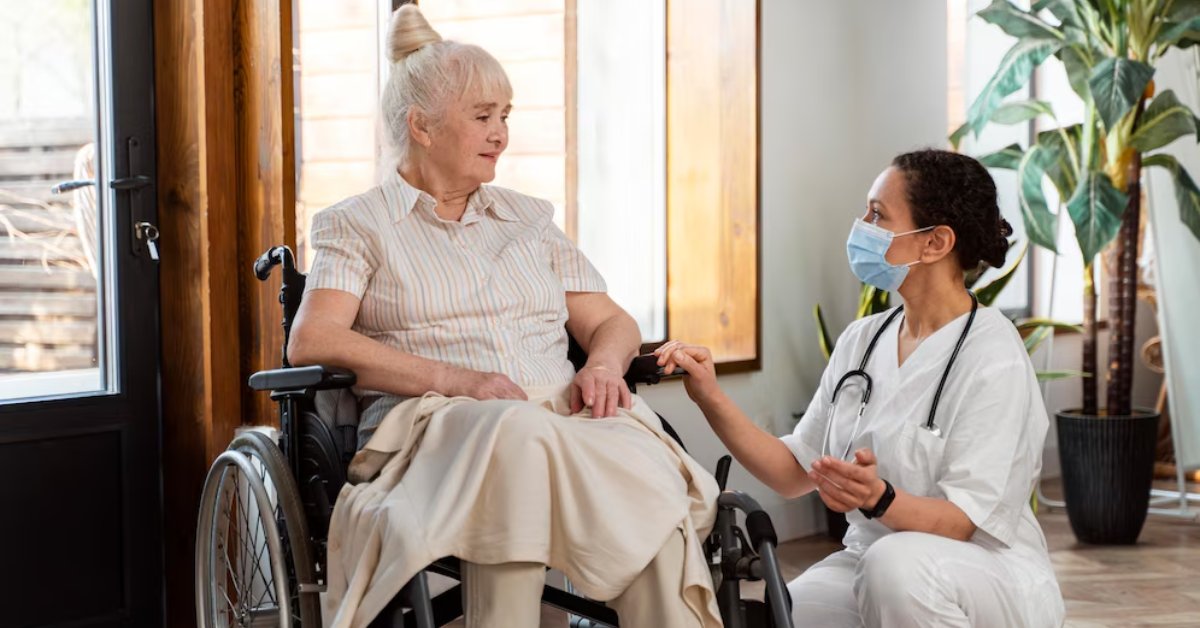
What are practical tips for senior-proofing a home?
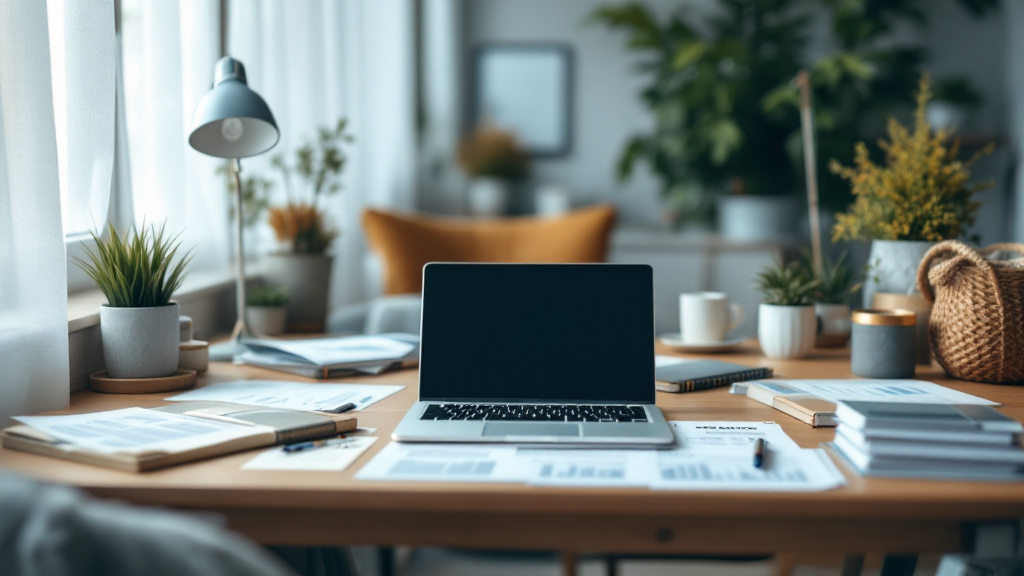
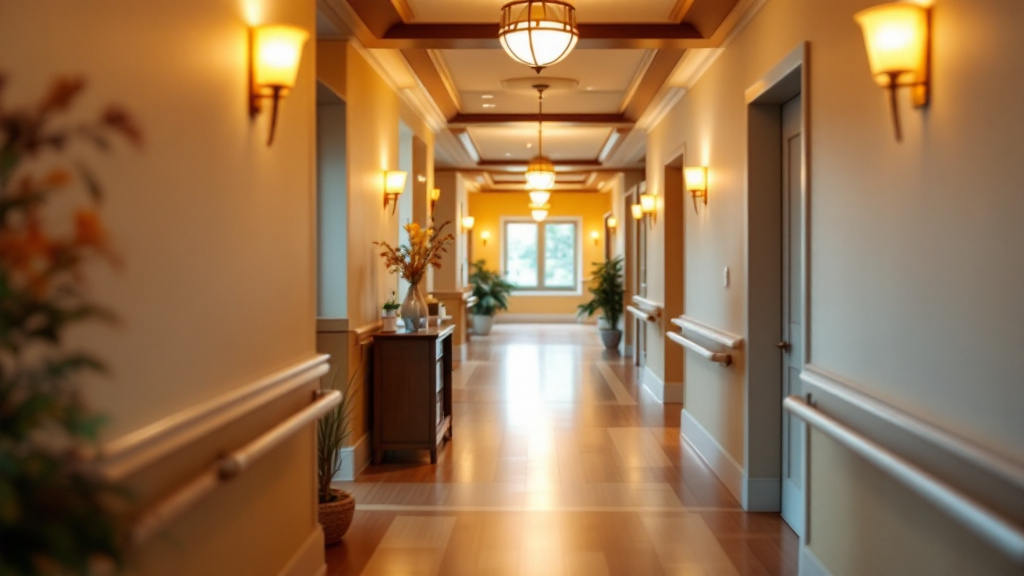
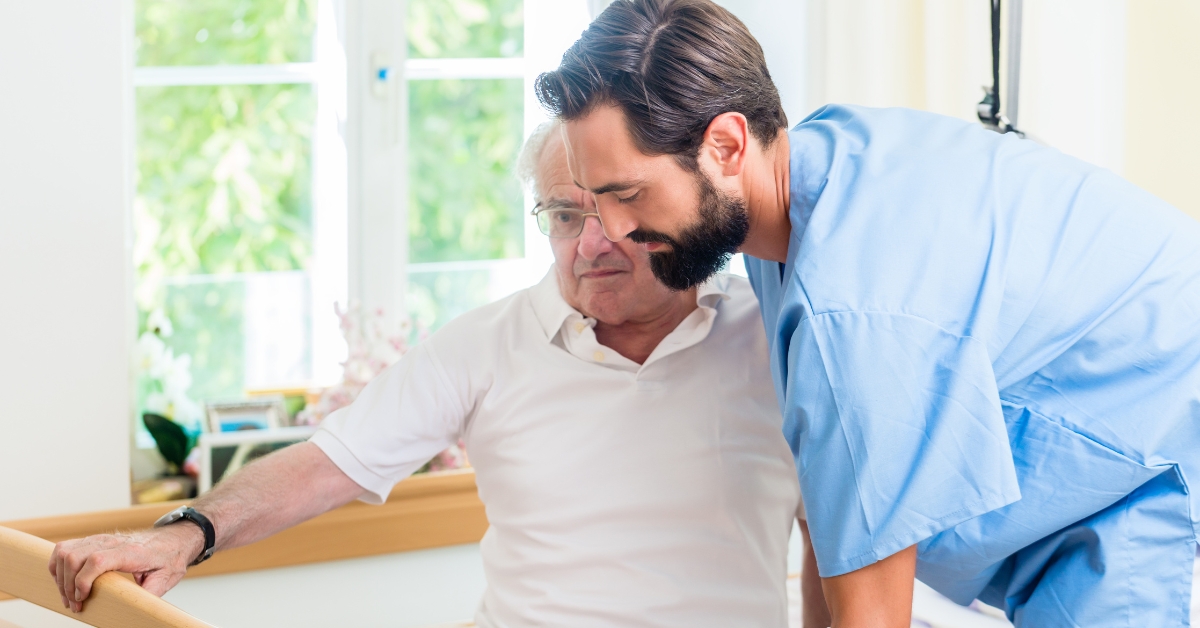
To senior-proof a home, start with essential safety modifications. Ensuring that all hallways, stairs, and paths are well lit is crucial. Utilizing bright, energy-efficient bulbs can significantly improve visibility. It’s important to remove tripping hazards such as loose rugs or furniture that obstructs walkways.
Installing grab bars in bathrooms and around the home is vital for enhancing stability. These should particularly be placed in areas prone to moisture, such as showers and beside toilets. Additionally, keep areas free of clutter to maintain clear paths.
Fire safety measures are equally essential. Make sure smoke detectors are fitted and functioning, while also keeping heaters away from flammable materials. Ensure that elderly residents are familiar with escape routes and have a plan in case of an emergency.
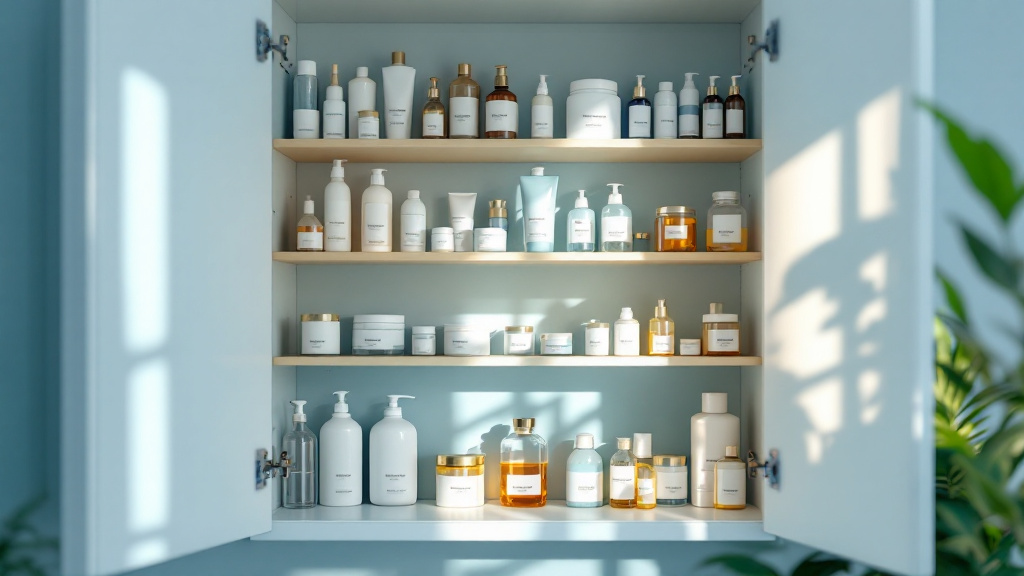
Preventing poisoning should also be a priority. Use carbon monoxide detectors to guard against gas leaks, and manage medications vigilantly—store them in their original containers marked with large-print labels to avoid confusion.
Finally, have emergency numbers easily accessible throughout the house. Consider providing personal alarms that alert caregivers or family members for immediate assistance in the event of falls or other emergencies.
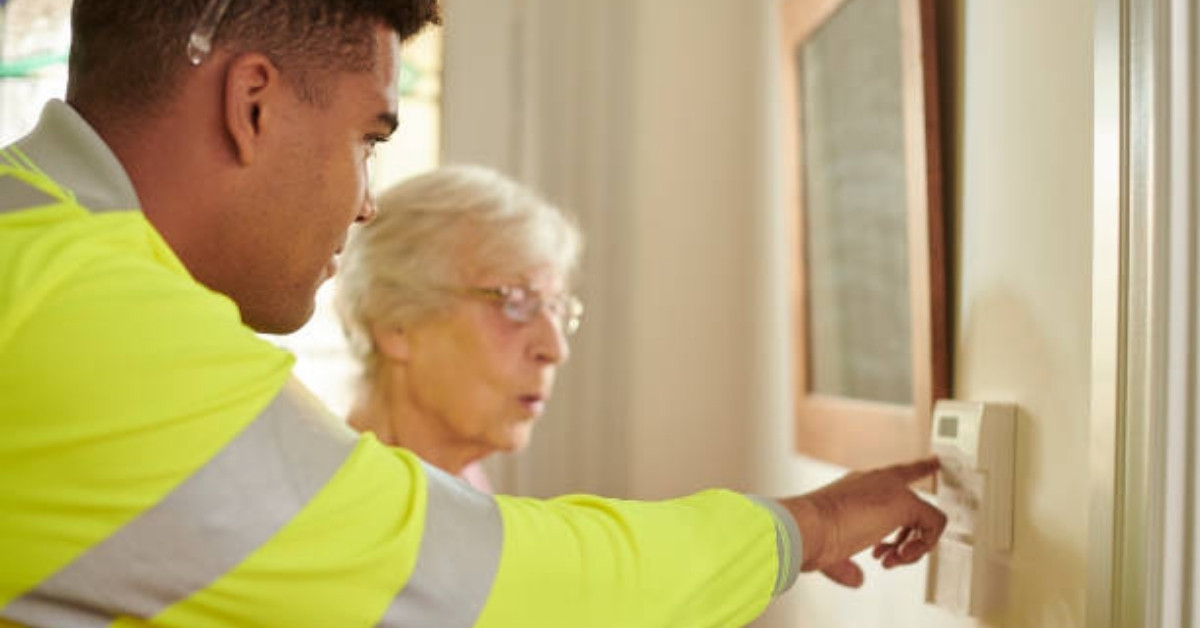
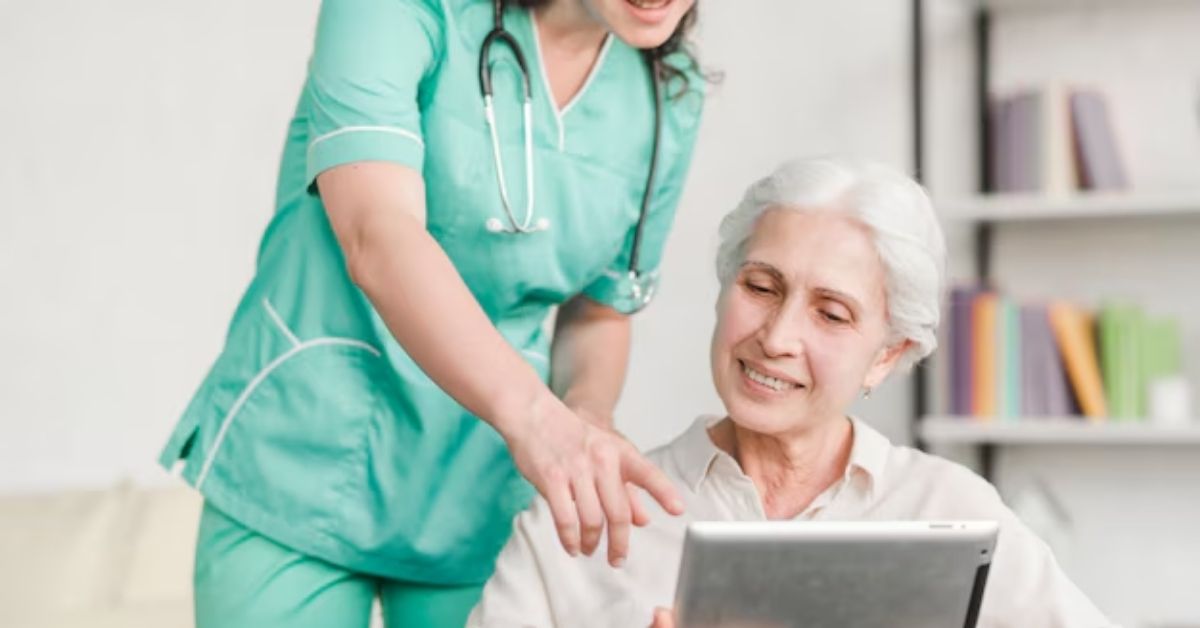
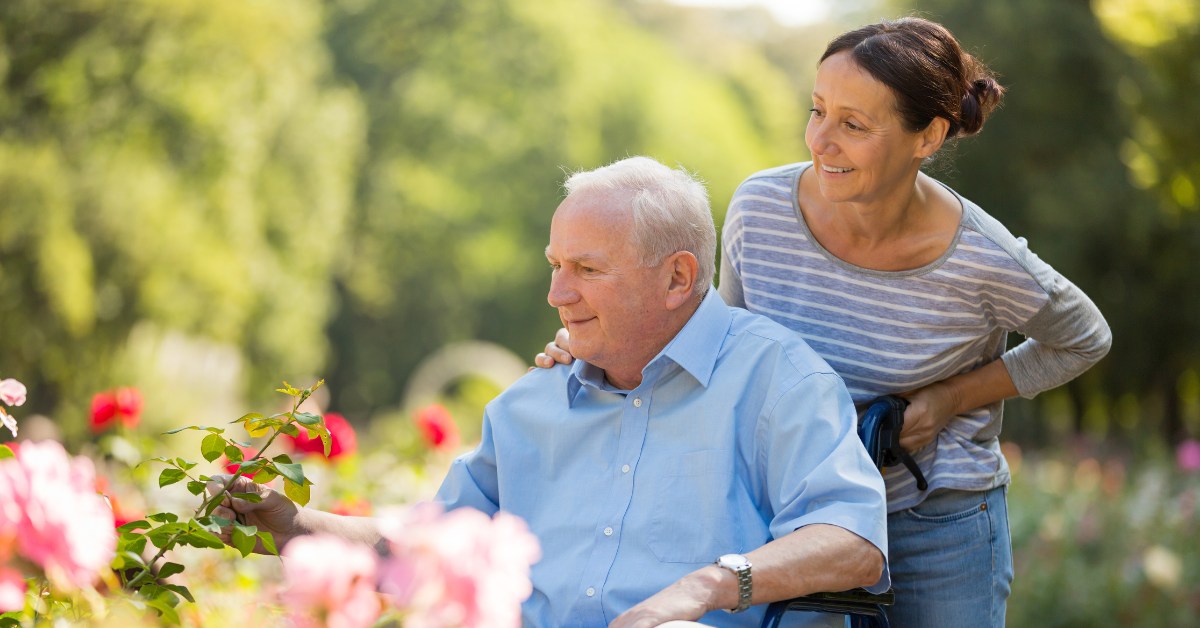
Engaging community and technological resources
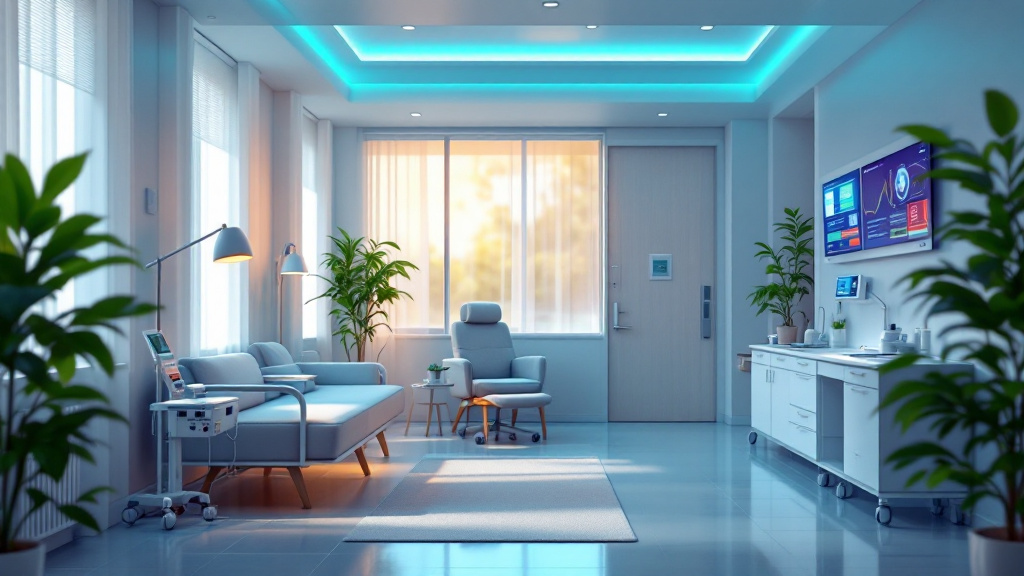
Support for seniors aging in place extends beyond home modifications. Engaging local community resources can provide valuable assistance, such as meal delivery or transportation services. Leverage technology by integrating medical alert systems and health monitoring tools to enhance communication with caregivers and healthcare providers.
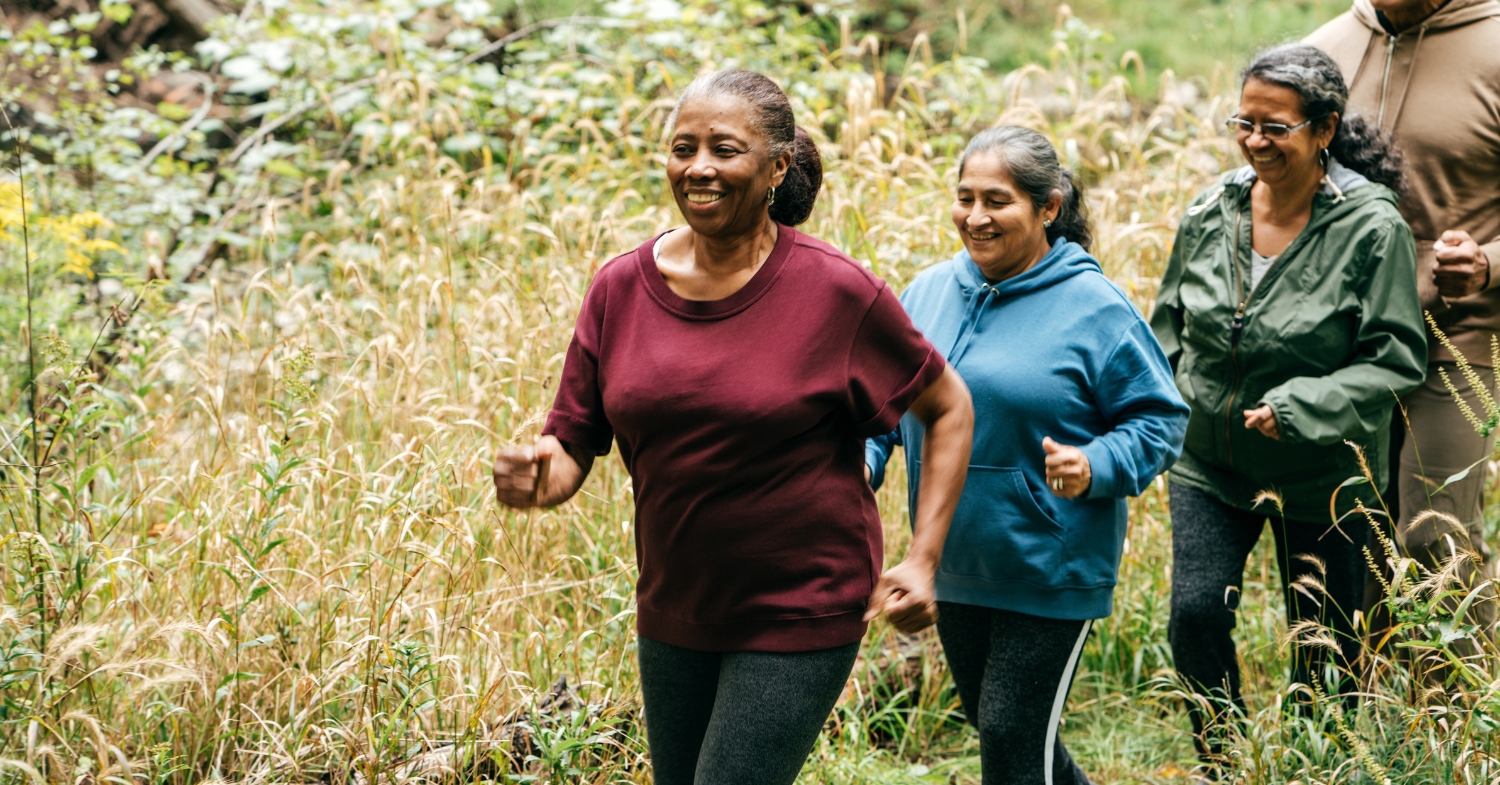
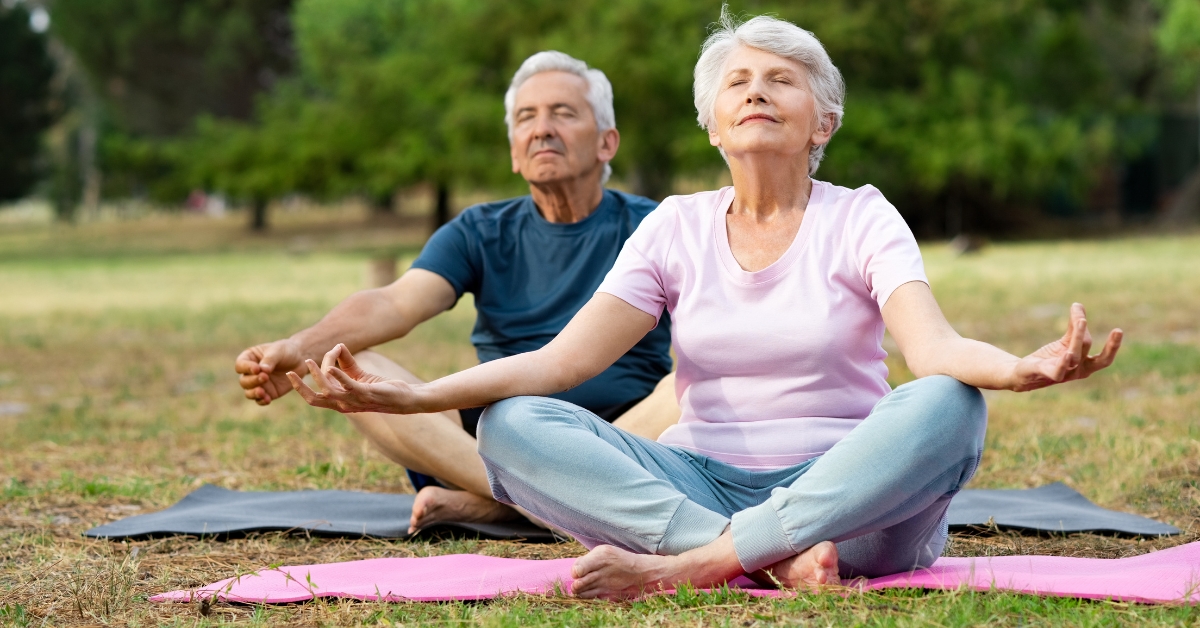
Physical activity and lifestyle adjustments
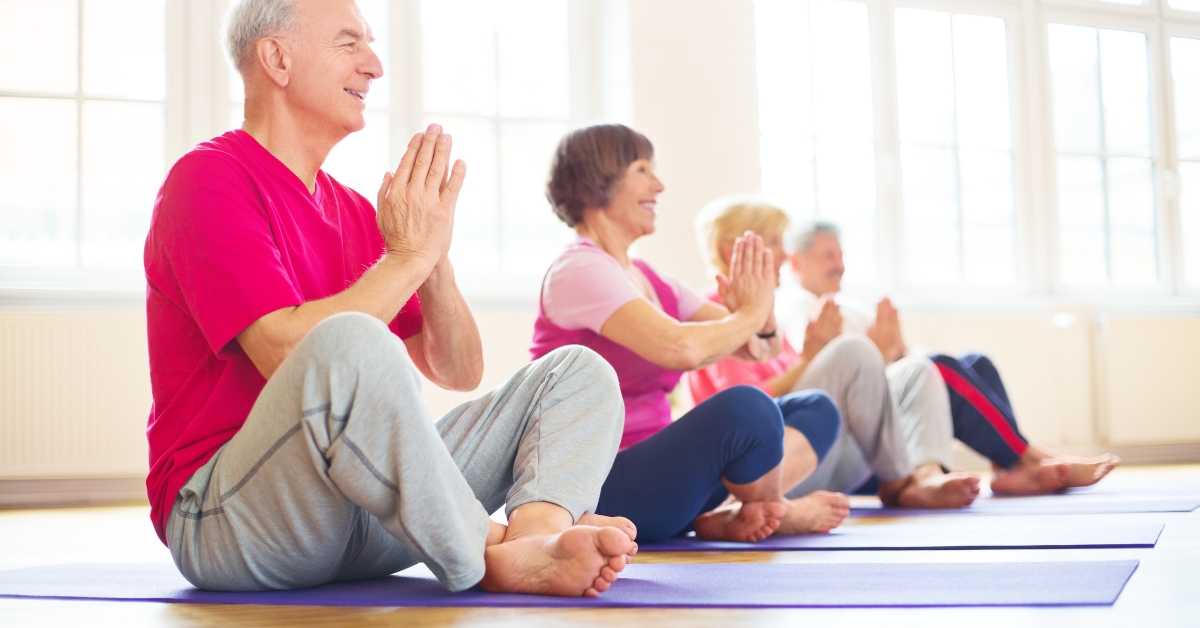
Promoting ongoing physical activity is essential for both safety and well-being. Simple exercises tailored to seniors—like walking, stretching, or joining a local exercise class—can greatly improve mobility and resilience. Encouraging healthy lifestyle choices, such as balanced nutrition and regular sleep, further supports both mental and physical health. By creating a safe and supportive home environment, caregivers can significantly contribute to the quality of life for older adults.
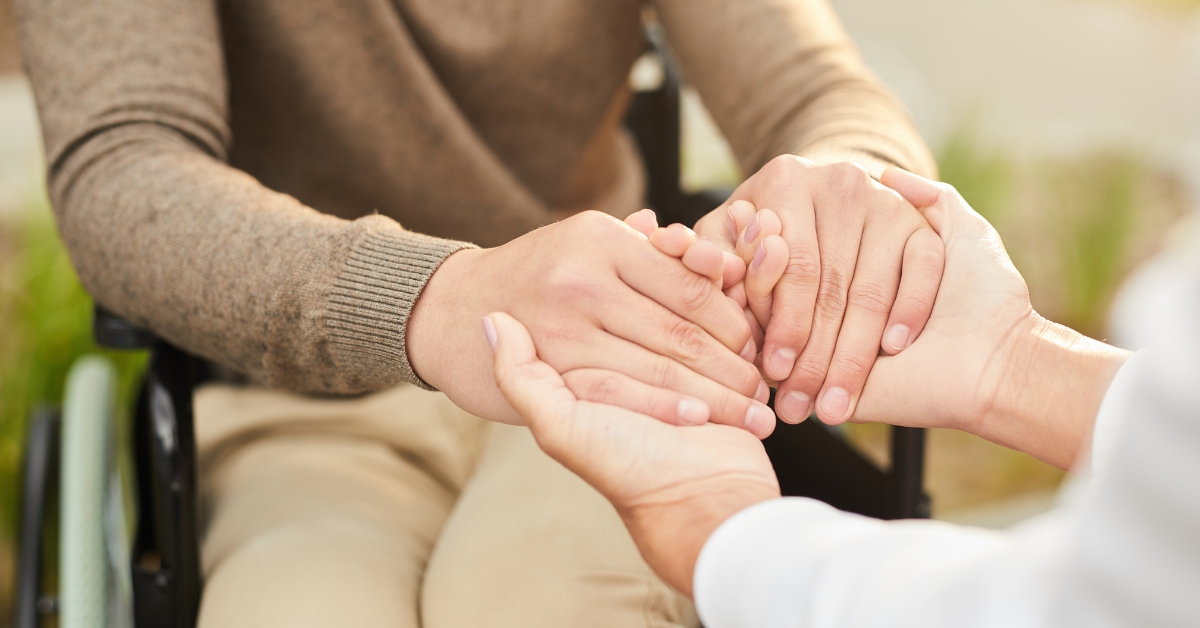
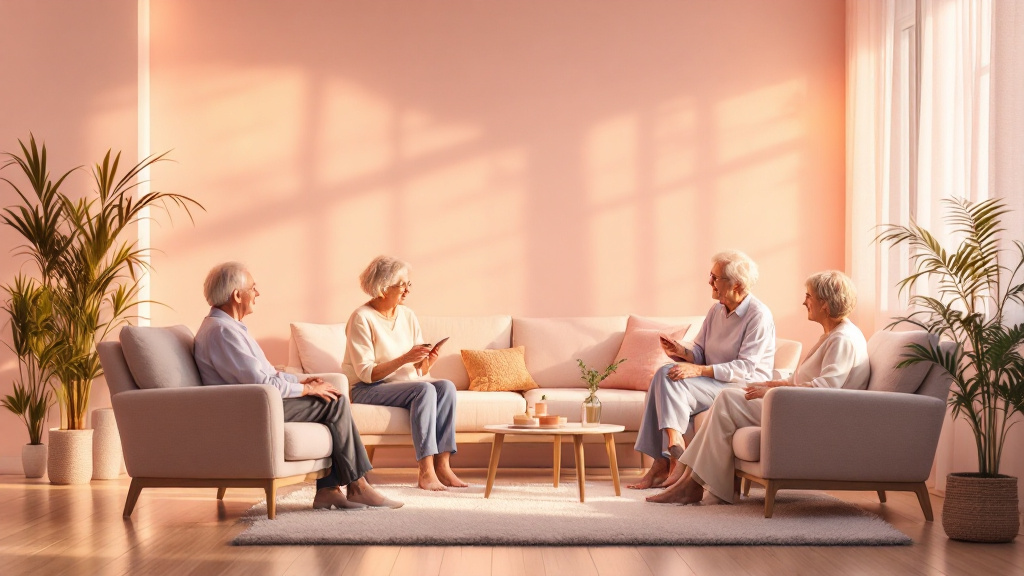
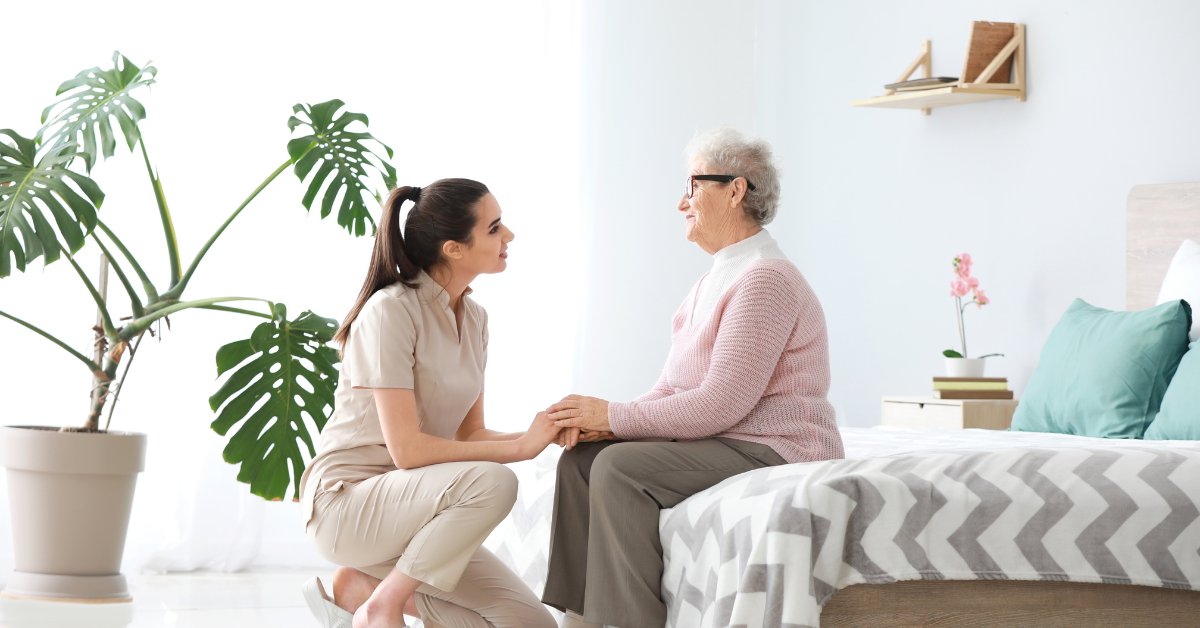
Building Emotional Resilience and Social Connections

Importance of Social Relationships
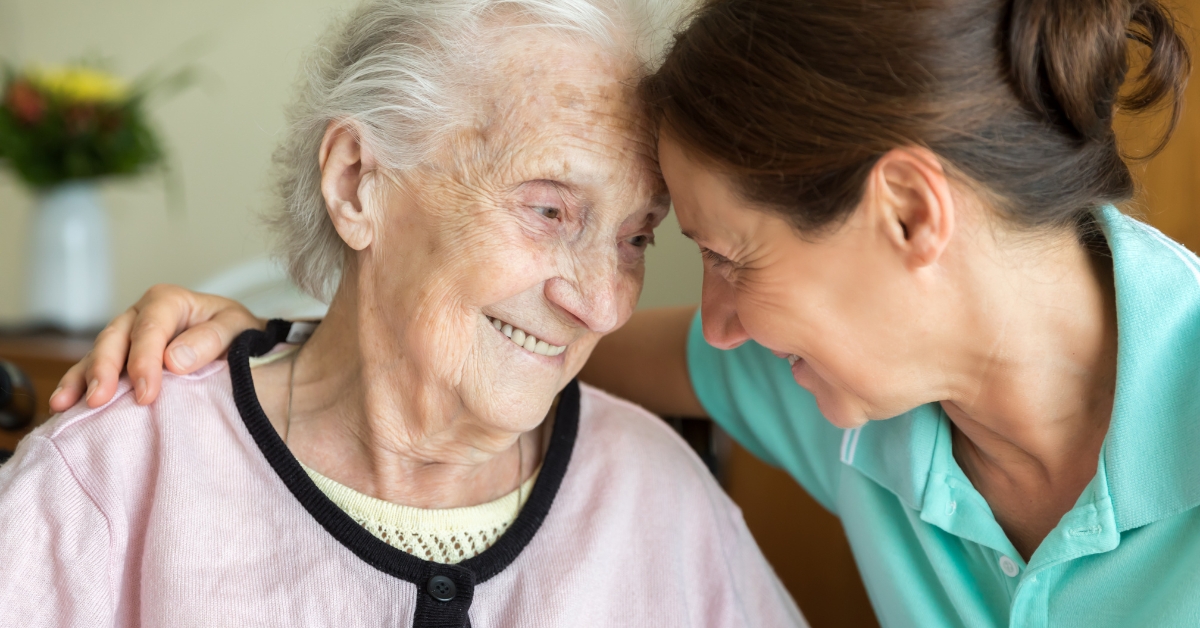
Maintaining strong social relationships is crucial for the mental and emotional health of older adults. Research shows that connection with family and friends can significantly reduce feelings of isolation and depression. For seniors, regular interactions foster self-confidence and motivation, resulting in better self-care and overall well-being.
Overcoming Isolation
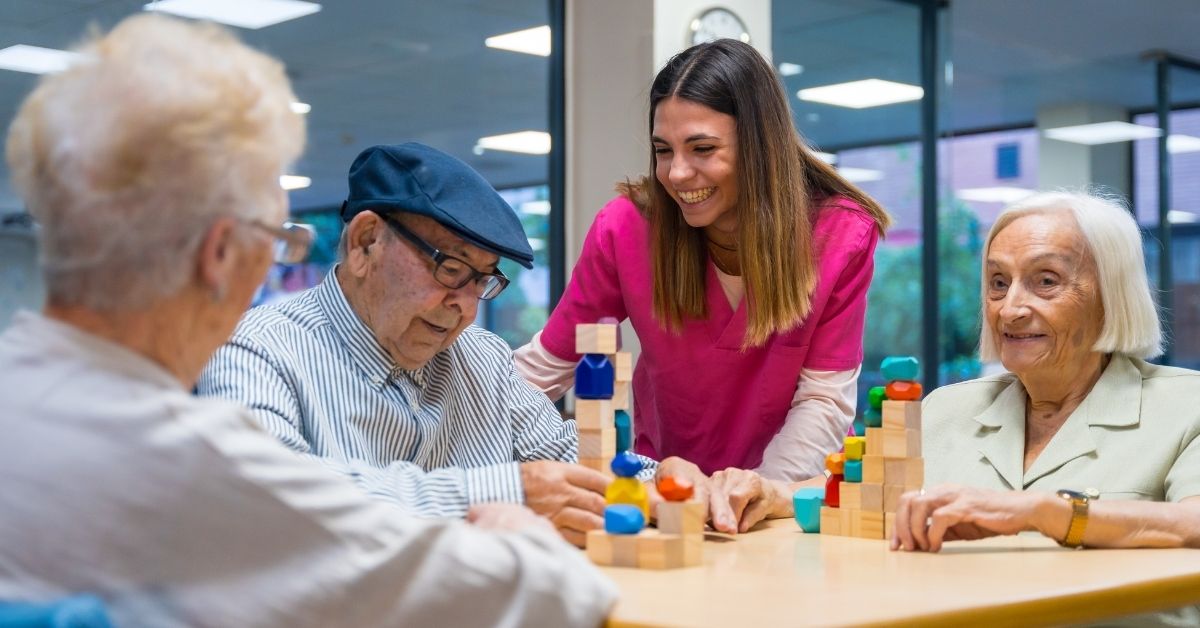
Caregivers play a vital role in encouraging seniors to maintain social ties. Organizing family visits, planning outings, and helping seniors engage in community activities can combat loneliness. Examples include volunteering, joining local clubs, or attending community classes, all of which can expand their social networks and provide a sense of belonging.
Finding Purpose and Fostering Positivity
Cultivating a sense of purpose is essential for resilient aging. Engaging in hobbies or new activities contributes to a more positive outlook on life. It’s important to emphasize enjoyable daily activities and set achievable goals, fostering a daily sense of accomplishment. This practice, alongside mindfulness and maintaining a hopeful perspective, can greatly enhance the emotional well-being of seniors, helping them navigate the challenges of aging while thriving at home.
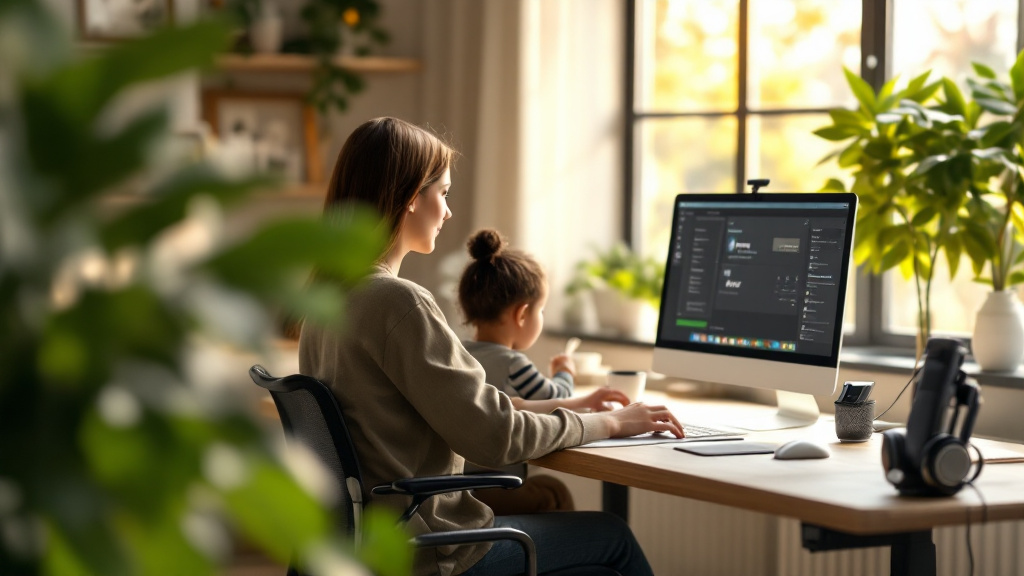
Proactive Caregiver Strategies

How can caregivers effectively cope with aging loved ones?
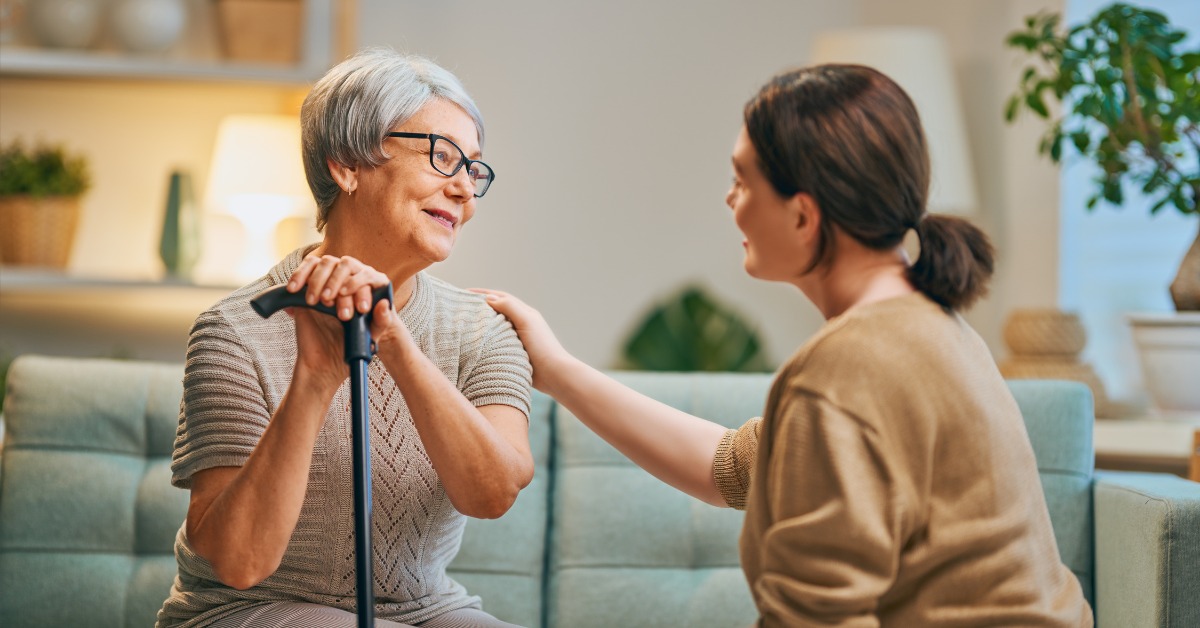
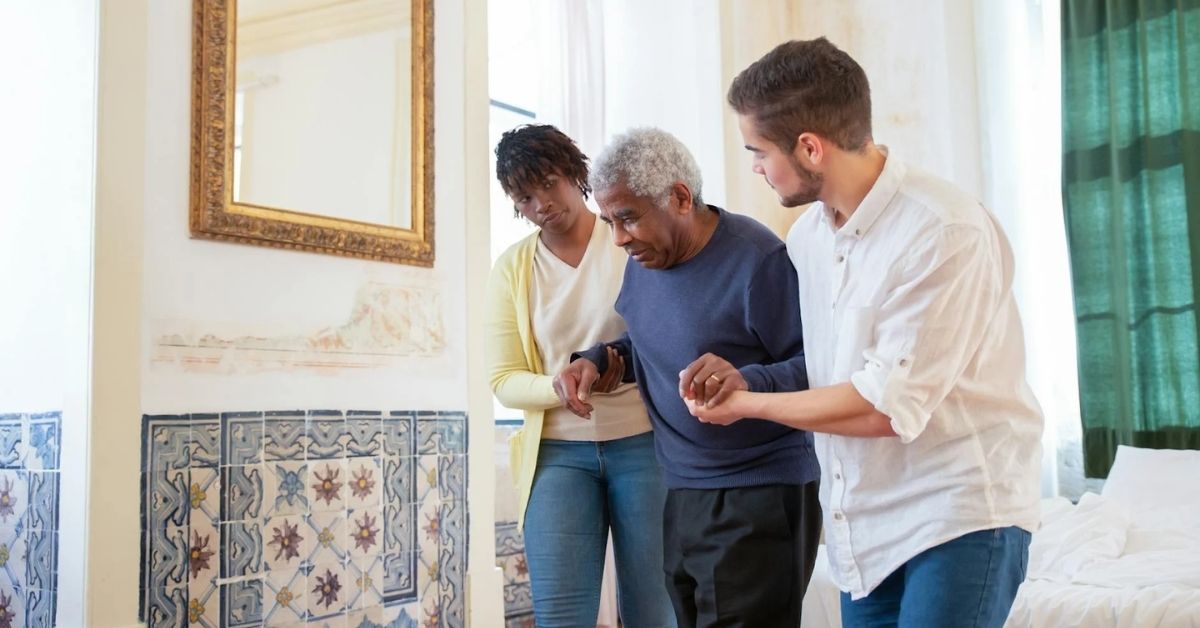
Caregivers play a critical role in the lives of aging loved ones, and coping effectively involves several essential strategies.
- Open Communication: Involving older adults in discussions about their care creates an atmosphere of respect and encourages empowerment. Listening to their wishes can promote a cooperative spirit and reduce anxiety.
- Empathy and Understanding: Caregivers should approach their loved ones' behaviors with empathy, recognizing that they may stem from personal struggles such as illness or emotional distress.
- Setting Boundaries: It’s vital for caregivers to establish clear boundaries regarding their availability and emotional space. This helps sustain their well-being and mitigates feelings of exhaustion.
- Encouraging Engagement: Caregivers should motivate elderly loved ones to stay active—both physically and socially. Engaging in enjoyable activities together can foster connections and enhance mental health.
- Finding Stress Outlets: Caregivers should prioritize their own mental health. Having support systems, such as friends or professional counseling, allows caregivers to share burdens and strategies.
What resources exist for external support?
Caregivers should not hesitate to seek external support when needed. Local agencies offer a wealth of resources to ease the caregiving process:
- In-Home Care Services: These services can manage daily tasks, allowing caregivers to focus on emotional connections.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide invaluable peer support and coping strategies.
- Community Programs: Programs like adult day care can offer socialization opportunities for elderly individuals, helping to reduce caregivers’ workloads.
How can caregivers communicate their needs?
It’s crucial for caregivers to communicate their own needs and feelings. Techniques include:
- Regular Check-Ins: Routine discussions with family can provide a support network and help avoid misunderstandings.
- Expressing Feelings: Sharing emotions and challenges is essential for mental health, whether through journaling or open dialogues with trusted friends.
- Setting Up Assistance: Clearly stating when extra help is required can be a proactive step toward maintaining a balanced caregiving role.
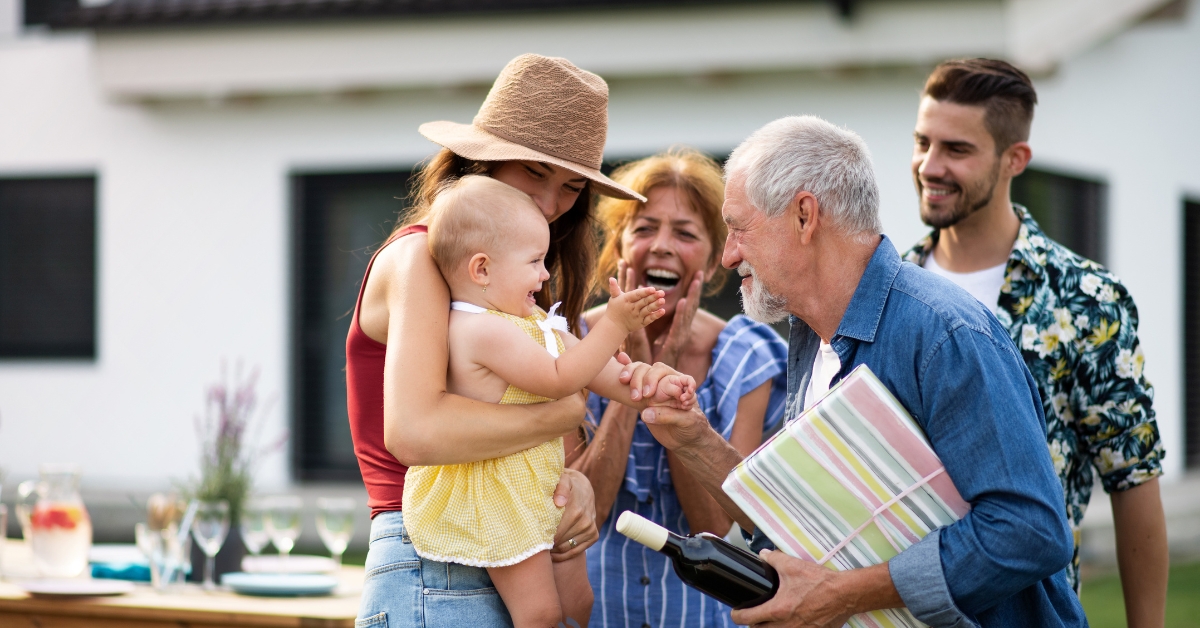
Community Services and Resources

Community as a Support System
Older adults often prefer to remain independent by aging in place, which makes community support essential. Networks of family and friends provide informal assistance, while formal community services offer structured support, creating a balanced safety net for seniors.
Role of Local Agencies and Services
Local agencies on aging, religious organizations, and geriatric care managers play a vital role in this ecosystem. They help navigate available resources, connecting seniors to services such as healthcare, meal programs, and transportation. For example, many communities offer meal delivery options or transportation services to medical appointments, significantly impacting an older adult's quality of life.
Engagement in Volunteer Activities
Engaging in volunteer activities allows older adults to expand their social networks, prevent feelings of isolation, and maintain a sense of purpose. Many community centers are ripe with opportunities, from assisting at local food banks to mentoring youth, fostering connections that are essential for emotional well-being.
Utilizing Technology and Home Modifications

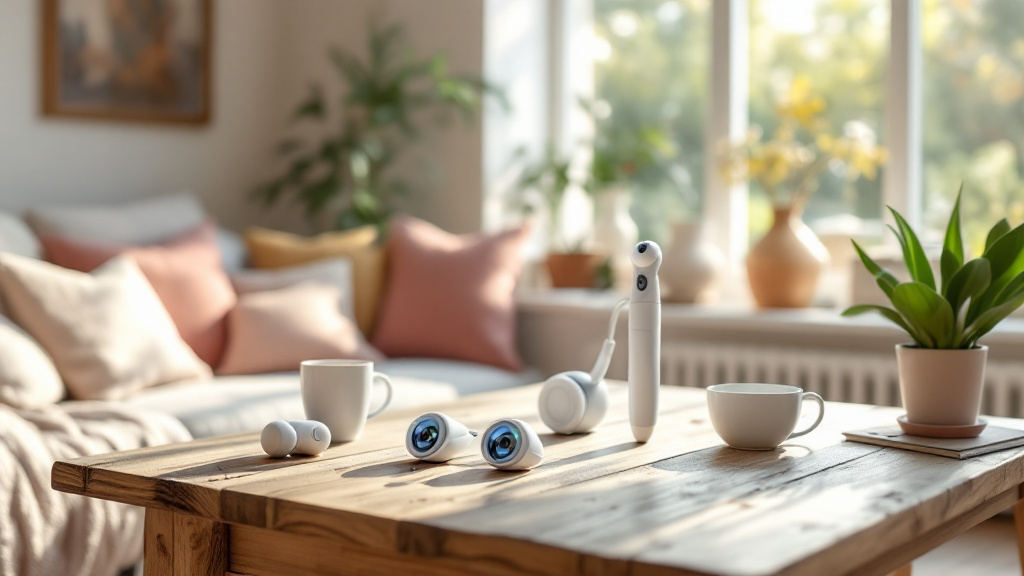
Role of technology in aging care
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing care for older adults at home. Medical alert systems provide immediate assistance during emergencies, while health tracking tools help monitor daily health metrics. Caregiving apps facilitate communication between family members and professional caregivers, ensuring optimal support is provided.
Practical home modifications
Home modifications can greatly improve safety for aging individuals. Some effective changes include:
- Installing grab bars in bathrooms and hallways to prevent falls.
- Creating no-step entries for easier accessibility.
- Improving lighting to enhance visibility and reduce hazards.
- Walk-in showers and raised toilet seats for enhanced convenience. These modifications create a safer living environment that fosters dignity and independence.
Financial assistance for modifications
Financial support is available to help with home modifications. Local and state programs, along with Medicare Advantage plans, often offer benefits for aging-in-place improvements. Nonprofits such as Habitat for Humanity also assist low-income families in making necessary home adaptations, ensuring that more seniors can live safely in their homes.
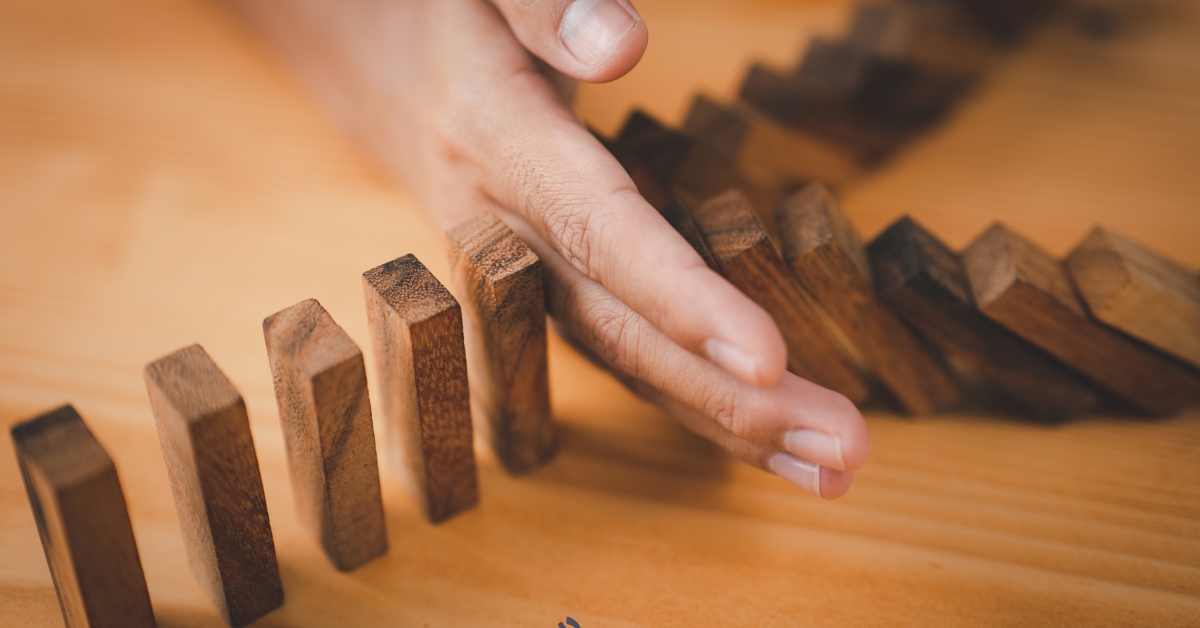
Nurturing Caregiver Resilience
Importance of caregiver well-being
The emotional and physical well-being of caregivers is essential, not only for their own health but also for the quality of care they provide to aging loved ones. A well-supported caregiver can better manage stressors, leading to improved outcomes for both themselves and the individuals they care for. Resilience in caregivers has been linked to lower levels of depression and feelings of loneliness, which highlights the importance of nurturing one’s own mental and emotional health.
How can caregivers build their own resilience?
Caregivers can build their resilience by practicing several strategies:
- Setting Boundaries: Learning to say no helps manage overload and prioritize personal well-being.
- Acceptance: Embracing the reality of their situation can reduce stress and improve acceptance of imperfections.
- Emotional Support Networks: Maintaining social connections through friends and support groups can diminish feelings of isolation. Family interactions and engagement in community activities provide vital emotional support during challenging times.
- Self-Care: Regularly engaging in enjoyable activities, ensuring proper nutrition, sleep, and exercise are crucial components of maintaining personal health.
Practices to build caregiver resilience
- Self-Awareness: Recognizing personal feelings and stress signals enables caregivers to address issues before they escalate.
- Maintaining a Positive Outlook: Focusing on the positive aspects of caregiving and the joys in life can foster emotional resilience.
- Personal Interests: Allocating time for hobbies or relaxation is critical for avoiding burnout and sustaining joy in caregiving roles.
Through these practices, caregivers not only enhance their resilience but also secure better care for their loved ones, ultimately fostering a healthier caregiving environment.
Creating a Holistic Care Strategy
Fostering resilience in aging loved ones is not just about the physical adjustments made to their living spaces but also about creating an emotional and social environment that supports their growth and independence. By integrating these strategies, you can help your loved ones lead purposeful, happy lives while ensuring that caregivers themselves remain resilient and fulfilled. Equip yourself and your family with the right resources, and remember that building strong community ties and utilizing modern technological solutions can make a world of difference in achieving these goals.
References
- Aging in Place: Growing Older at Home
- How to Encourage Your Aging Loved One's Social Relationships to ...
- Resources, Gadgets and Tools to Care for an Older Adult at Home
- Resilience: Build skills to endure hardship - Mayo Clinic
- Ways to Improve Your Elderly Loved Ones Chances of Living In ...
- Caring for Elderly Parents Requires Resilience. These Tips Can Help.
- Home Safety Tips for Caregivers to Protect Older Adults - AARP
- Supporting caregivers with resilience and sense-of-purpose
- Taking Care of Elderly Parents Requires Resilience. Here's How to ...
- Building Up Emotional Resilience: The Key to Recovery

How In-Home Care Services Help Manage Hypertension

How Home Team Services Provide Post-Discharge Care Plans

Advantages of Self-Directed Home Health Care

Promoting Social Engagement with In-Home Care Services

The importance of fading prompts to encourage independence

The Role of Caregivers in Enhancing Senior Well-being

Maximizing Home Team Services for Optimal Health Outcomes

Maintaining a Clean Home: Bathroom Cleaning Services for Seniors

How In-Home Care Services Assist Seniors with Communication Challenges

The Importance of Community Engagement for Seniors Receiving Home Care

Assisting with Bill Payments and Correspondence: Financial Management Support

How to encourage participation in family activities

The Importance of Regular Health Monitoring for Seniors
.jpg)
Finding the Best Dermatologist Near You That Accept Medicaid
.jpg)
Who Qualifies for Emergency Medicaid in NY?
.jpg)
How to Access Endocrinologist that Accepts Medicaid?
.jpg)
Best Exercises for Bat Wings Over 60
.jpg)
Where to Find Eye Doctors that Take Medicaid?
.jpg)
What Are Food Stamp Bills?
.jpg)
How to Get Paid to Care for Family Member NY?
.jpg)
Highest Paying CDPAP Agencies
.jpg)
Exploring Home Care Covered by Aetna
.jpg)
Understanding Home Care Covered by Cigna
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits Of Home Care Covered by Humana

Home Care vs Palliative Care
.jpg)
How Long Does it Take for Food Stamps to Get on the Card After Being Approved?
.jpg)
How Much Does AmeriBest Home Care Pay?
.jpg)
How to Find Neurologist Near You That take Medicaid?
.jpg)
How to Tighten Arms?
.jpg)
What is In-Home Care for the Elderly?
.jpg)
What are the Types of In-Home Care Solutions?
.jpg)
A Complete Guide on Lunch Ideas for Seniors
.jpg)
What is Medicaid Copay?

A Complete Guide to Narrow Walks for Seniors
.jpg)
Benefits on Having a New York State Medicaid Card
.jpg)
How to Get NYS Disability Eligibility?
.jpg)
A Complete Guide to Old People Food
.jpg)
Private Pay Home Care Agencies in New York
.jpg)
How to Find Psychiatrists Near You That Accept Medicaid?
.jpg)
Top 3 Quotes About Caregiving
.jpg)
In-Depth Guide on Choosing Reclining Chairs for Seniors

Risk for Fall Care Plans for the Elderly

Top 5 Challenges Faced by the Sandwich Generation
.jpg)
Best 3 Types of Senior Housing in New York

The 10 Services That Medicaid Will Pay For

Top 3 Strategies For Dealing Sick Spouse Stress
.jpg)
A Complete Guide to Social Security for Caregiver

What is Social Security Caregiver Pay?

Top 3 Essential Skills for Special Needs Caregiver

Spending Down Assets to Qualify for Medicaid in NY

6 Effective Stress Management for a CDPAP Caregiver

6 Benefits of Stroke Care Plan for CDPAP Caregivers

What Is the Suffolk County Social Services?

Taking Care of Elderly Patients with Muscle Weakness
Taking Care of Elderly With Diabetes
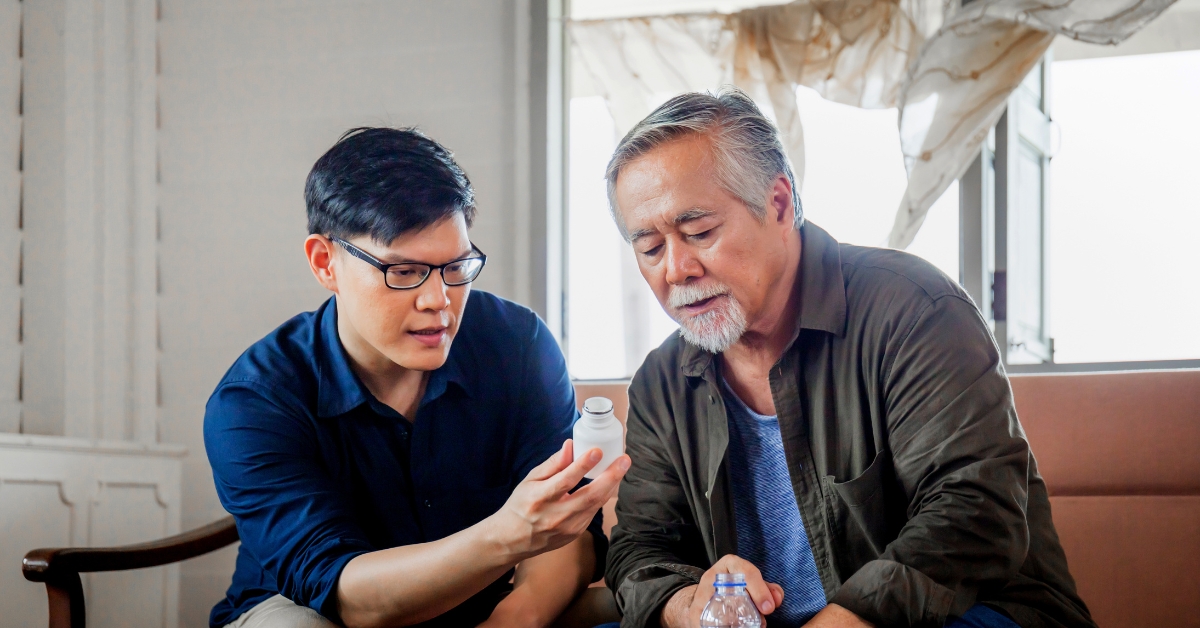

Taking Care of Sick Parents

The 7 Stages of Alzheimer’s

The Consumer Directed Personal Assistance Association of New York State (CDPAANYS)
The Signs of Patient Abuse

Things Happy Seniors Do

Things to Do in Ithaca NY

Things to Know Before Starting CDPAP

Tips to Stay Independent as You Get Older

Tools To Help With Urinary Incontinence
4 Factors Contributing to Treating Kidney Stones In the Elderly

The Complete Guide for Unemployment in NY

The Ultimate Massage Guide
Best 3 Urinary Incontinence Devices for the Elderly

Urinary Infection Symptoms in Elderly

A Complete Guide of Using a Cane

A Guide for Using the Elderly Mobility Scale (EMS) to Assess Mobility

Top 5 Benefits of Vaccines for the Elderly

4 Top Benefits of Velcro Clothing for Seniors

Volunteer Opportunities in Albany, NY

A Guide on Ways to Earn a Living While on CDPAP

Top Ways to Get Paid While Taking Care of a Family Member
.jpg)
What are Considered Utilities for Food Stamps?

What are the Medical Power of Attorney Laws in Nevada?

What Assisted Living Facilities Accept Medicaid?

What Do Old People Do?
.jpg)
What Do Old People Like To Do?

What is a CNA?

What is a Fiscal Intermediary?

What is CDPAANYS?
.jpg)
What is HPD Housing?

What is Immediate Need CDPAP and How to Apply?

What is Multiple Sclerosis?
.jpg)
What is Polypharmacy?
.jpg)
What Is Poverty Level Income For A One Person?

What is Retroactive Medicaid?

What is Seasonal Affective Disorder?

What is the American Caregiver Association?

What Is The Hardest Part of A Caregiver?

What is the New York City Department of Youth and Community Development?
.jpg)
What It Means to Be an Elderly Caregiver?
.jpg)
What Kind of Hearing Aids Does Medicaid Cover?
.jpg)
What Should an Elderly Person with Diarrhea Eat?
.jpg)
What to Look for When Hiring a Caregiver?
.jpg)
What You Need to Know About In-Home Physical Therapy?
.jpg)
When Will I Get my Food Stamp Card in the Mail?
.jpg)
Who is Legally Responsible for Elderly Parents?
.jpg)
Who Qualifies for CDPAP?
.jpg)
Why Are Advance Directives Important?
.jpg)
Why Should Senior Citizens Perform Balance Exercises?
.jpg)
Work-from-Home Jobs for the Disabled
.jpg)
Top Worst Dog Breeds for Seniors

The Importance of Consistent Therapy Sessions in Home Care

The Role of In-Home Care Services in Preventing Social Isolation
.jpg)
Who Can Benefit from 24 Hour In-Home Care?
.jpg)
What is 24 Hour Nursing Care at Home?
.jpg)
Understanding Adaptive Fashion for Seniors

Advocating for Home Care Rights
.jpg)
How to Apply for Social Security Caregiver Benefits?
.jpg)
Are Caregivers Supposed To Clean The House?
.jpg)
Can Dehydration Cause Tremors?
.jpg)
3 Types of Caregiver Respite Options
.jpg)
What Are The Causes of Diarrhea in Elderly Woman?

CDPAP vs Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Does Home Health Care Include Physical Therapy?
.jpg)
Best Exercises for Flabby Arms
.jpg)
Friends & Family Home Care CDPAP Services
.jpg)
What is a Home Accessibility Audits?
.jpg)
Understanding Home Care Aide Registry
.jpg)
Home Care and Family Support Grant is it Legit?

How Home Team Ensures the Highest Standards in In-Home Care
.jpg)
How Much Does a CDPAP Get Paid?
.jpg)
How to Become a Home Care Provider for a Family Member?
.jpg)
Is A Homemaker A Caregiver?
.jpg)
Understanding Pain Management Techniques in Home Health
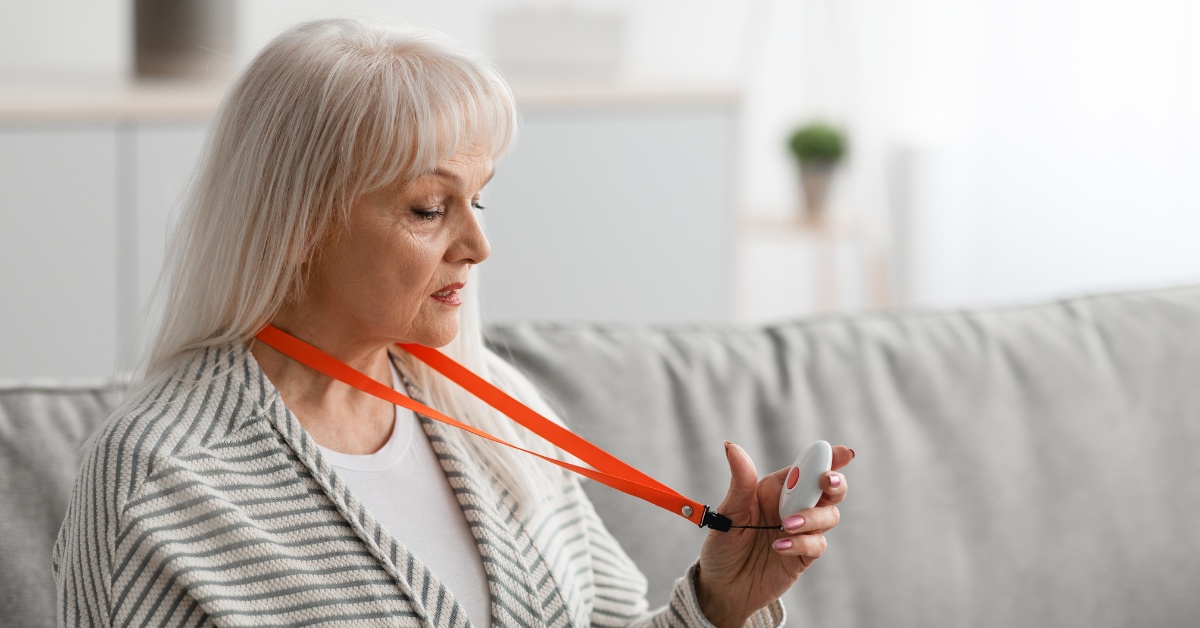

3 Best Types Of Personal Alarms for the Elderly
.jpg)
Starting Physical Therapy Home Exercise Program
.jpg)
How Remote Monitoring Works in Home Care?

Who Qualifies for SSI Caregiver Allowance?
.jpg)
Top 6 Benefits of Tailored Support for Disabilities in Home Care
.jpg)
Best Taking Care of Elderly Parents Quotes

The Importance of Reliable Caregivers in Maintaining Independence
.jpg)
What Are Transitional Care Programs?

Understanding Autism In Older Adults
.jpg)
What Does a Home Health Physical Therapist Do?
.jpg)
What Does HHA mean in Medical Terms?

What is A Personal Caregiver Called?
.jpg)
Will Medicare Pay for Home Health Care by Family Member?

The Importance of Cognitive Stimulation in In-Home Care

Navigating Payroll and Taxes in Consumer Directed Care

The Role of Occupational Therapy in Senior Home Care

How to handle holidays and special occasions with children with autism

The benefits of community-based activities in ABA therapy

The benefits of community-based activities in ABA therapy
.jpg)
How To Find Adult Day Care Centers Near You?
.jpg)
What is Aging in Place?
.jpg)
A Complete Guide for Alzheimer's Caregivers
.jpg)
Top 6 Benefits of Arm Exercises for Women Over 60
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits of Back Exercises for Seniors
.jpg)
3 Benefits of Aging in Place
.jpg)
Best Exercise for Arm Flab
.jpg)
Can a Disabled Person be a Caregiver?
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits of Care Coordination Agencies
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits of Care Coordination Services
.jpg)
The Ultimate Guide for Caregiver Training
.jpg)
How to Find Chair Yoga for Seniors Near You?

5 Benefits of Chronic Illness Home Care
.jpg)
Cognitive Exercises for Seniors
.jpg)
What Are Comfort Keepers?
.jpg)
What are the Types of Community-Based Service?
.jpg)
Does Health Insurance Cover Home Health Care?
.jpg)
Does Medicaid Cover Hospital Stays?

Top 5 Benefits of Elder Financial Planning
.jpg)
Top 4 Benefits of Eldercare Locator
.jpg)
3 Types of Elderly Care Services at Home
.jpg)
Elderly Caregiver Hourly Rate
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits of Elderly Caregiver Quotes
.jpg)
How Much Does Elderly Day Care Cost?
.jpg)
How to Choose an Elderly Rehabilitation Center Near You?
.jpg)
5 Benifits of Engaging Fun Activities for Elderly in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Home Health Care for Disabled Adults
.jpg)
Top 4 Benefits of Home PT
.jpg)
How Long Does Stage 7 Alzheimer's Last?
.jpg)
How Much Does 24/7 in Home Care Cost per Month?
.jpg)
How Much Does Home Health Care Cost?
.jpg)
How to Avoid Loneliness in Old Age?
.jpg)
How to Get a Handicap Parking Permit in NY?
.jpg)
How to Get Handicap Placard in NY?
.jpg)
How to Get In-Home Care for Disabled?
.jpg)
How to Protect Assets from Medicaid?
.jpg)
6 Benefits of Independent Living Communities for Seniors
.jpg)
Is Palliative Care End of Life Care?
.jpg)
Is There a Copay with Medicaid?

How to Transition to In-Home Care Smoothly

The importance of promoting inclusion in community settings

How CDS Providers Assist with Managing Anxiety and Stress

How to adapt ABA therapy for older children and adolescents

Staying Connected: Transportation Services for Seniors
.jpg)
3 Types of Medicaid Providers in New York
.jpg)
6 Benefits of Memory Exercises for Seniors

Types of Mobility Assistance Devices Available
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits of Personalized Care Plans
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits of Post-Surgery Home Care

What is a Private Duty Caregiver?
.jpg)
Nutritious and Easy-to-Make Recipes for Seniors
.jpg)
Replace Your NY Medicaid Card: A Step-by-Step Guide
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits of Senior Advocacy
.jpg)
A Complete Guide To Senior Fall Prevention
.jpg)
The Complete Guide to Senior Safety
.jpg)
A Complete Guide to Finding Senior Volunteer Opportunities
.jpg)
Top 6 Benefits of Prioritizing Senior Wellness
.jpg)
Who Qualifies for Social Security Disability Caregiver Pay?
.jpg)
Types of Supportive Housing Options
.jpg)
Temporary Handicap Parking Permit NY
.jpg)
The Benefits of Music Therapy in Nursing Homes

The Benefits of Physical Assistance for Individuals with Limited Mobility
.jpg)
What are the Advantages of Home Health Care?
.jpg)
What are the Things for Old People to do?
.jpg)
What do Old People Like?
.jpg)
What Home Health Care is Covered by Medicare?
.jpg)
What is Assisted Living for Seniors?
.jpg)
What is Chronic Disease Management?
.jpg)
What is Exempt from Medicaid Spend Down?
.jpg)
What is the Average Cost of Senior Independent Living?
.jpg)
When Should Dementia Patients Go Into Care?
.jpg)
Why Do Seniors Want to Stay in Their Homes?
.jpg)
Why Palliative Care is Bad?

How CDS Providers Assist Seniors in Managing Digestive Health

The Importance of Regular Health Monitoring in Home Care

How a CDS Provider Can Support Post-Surgery Recovery

How to address sensory sensitivities in children with autism

How Local CDS Providers Support Family Caregivers

Top Home Health Aide Do’s and Dont’s
.jpg)
What are Age-Friendly Communities?
.jpg)
A Comprehensive Guide to Alzheimer’s Treatment
.jpg)
What Is Community Home Health Care?
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits of Core Exercises for Seniors with Back Pain
.jpg)
Does Aetna Pay for Home Health Care?
.jpg)
Does Medicaid Cover Hearing Aids for Seniors?
.jpg)
Top 11 Targeted Exercises for Upper Arm Flab
.jpg)
How to Find Senior Yoga Classes Near You?
.jpg)
The Best Lower Back Exercises for Seniors
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits of Medicaid Dermatology
.jpg)
The Ultimate Medicaid Spend Down Ideas
.jpg)
Creating Personalized Rehabilitation Plans for Seniors

What Causes Uncontrollable Diarrhea in Elderly?
.jpg)
What to Do with Seniors?
.jpg)
Why is Geriatric Care in High Demand?
The Role of CDS Providers in Reducing Emergency Room Visits

How CDS Providers Support Adults with Disabilities

Top Signs Your Loved One May Need In-Home Care Services

Addressing Dementia Symptoms with In-Home Care Services

How to Manage Medication with In-Home Care Services

How In-Home Care Services Promote Better Sleep Habits

How In-Home Care Services Reduce Fall Risks at Home

How CDS Providers Support Seniors During Family Visits

How In-Home Care Services Improve Communication with Healthcare Providers

Caring for Seniors with Arthritis Through In-Home Care

How In-Home Care Services Help Seniors Adjust to Vision Loss

The Role of In-Home Care Services in Managing PTSD Symptoms

How In-Home Care Services Improve Quality of Life for Seniors

The Benefits of In-Home Physical Therapy with a CDS Provider

How CDS Providers Can Support Seniors in Recreational Activities

Creating a Daily Routine with In-Home Care Services

How a Local CDS Provider Supports Family Caregiver Burnout

The Importance of Personalized Care in In-Home Services

Creating a Customized Care Plan with a Local CDS Provider

How CDS Providers Help Seniors Manage Finances and Bills

How CDS Providers Help Seniors Stay Connected to Their Communities

How In-Home Care Services Provide Support for Veterans

The Role of a Local CDS Provider in Enhancing Independent Living

The Role of In-Home Care Services in Enhancing Memory Skills

The Benefits of Personalized Activity Plans with CDS Providers

The Benefits of Personalized Activity Plans with CDS Providers

The Role of In-Home Care Services in Managing Chronic Fatigue

How CDS Providers Help Reduce Caregiver Stress

How In-Home Care Services Assist with Dressing and Clothing Choices

How In-Home Care Services Support Wound Care and Healing

How CDS Providers Help Manage Chronic Pain at Home

How CDS Providers Assist Seniors with Managing Technology

How In-Home Care Services Improve Cognitive Function

Managing Diabetes with In-Home Care Services

The Benefits of Companionship in In-Home Care Services

How a Local CDS Provider Can Help with Meal Preparation

How In-Home Care Services Assist Seniors with Dental Hygiene

How In-Home Care Services Support Palliative Care Needs

How In-Home Care Services Help Prevent Hospital Readmissions

Enhancing Mobility: Safe Transfer Techniques in Home Care

Medication Management: Support in Home Care Settings

How to Build a Routine for Consistent In-Home Therapy

Transportation Services: Facilitating Social Connections

Transportation Services: Facilitating Social Connections

How to Support Cognitive Rehabilitation in the Home Environment

How Home Team Services Use Data to Enhance Patient Outcomes

The importance of maintaining a balanced routine for children with autism

How to Transition from Rehab Facility to Home-Based Care

The Psychological Benefits of Aging at Home

The role of family involvement in successful ABA therapy

Housekeeping's Impact on Senior Health and Safety

The Process of Hiring Friends or Family Members as Caregivers

How Home Team Services Address Social Isolation in Patients

The importance of teaching time management and organizational skills

The Role of Home Health Aides in Senior Care

The importance of collaboration between therapists and families

The role of reinforcement in shaping positive behaviors

The benefits of natural environment teaching in in-home therapy

How to Integrate Wellness Activities into Home Healthcare

Financial Assistance: Managing Bills and Correspondence

Understanding the Role of Spiritual Care in Senior Home Services

How to address sensory-seeking behaviors during therapy

How to address sensory-seeking behaviors during therapy

How Respite Services Can Prevent Caregiver Burnout

The Importance of Ongoing Training for Home Health Professionals

How Home Team Services Support End-of-Life Care Needs

Financial Management: Assisting with Bills and Correspondence

Exploring Respite Care Services for Family Caregivers

How to Get Paid for Caring for a Loved One Through CDS

How to address toileting challenges in children with autism

Trash Removal: Maintaining a Sanitary Living Environment

Engaging Seniors: The Importance of Recreational Activities

Understanding and Preventing Caregiver Burnout

Family Caregivers as Paid Providers: Pros and Cons

HomeTeam's Support in Self-Directed Care Management

Applying for Consumer Directed Services: What to Know

Dietary Support: Meal Prep and Nutritional Planning

Meal Planning: Addressing Nutritional Needs in Seniors

Laundry Services: Ensuring Clean and Comfortable Living for Seniors

Physical Health: The Role of Passive Range of Motion Exercises

Assisting with Medications: Ensuring Compliance and Safety

Hiring Family Members as Caregivers: Benefits and Considerations

Activities of Daily Living: What They Are and Why They Matter

The Importance of Housekeeping in Elderly Health

Applying for CDS in Missouri: A Step-by-Step Guide

Preventing Burnout: The Role of Respite Services

Keeping the Kitchen Clean: Essential for Senior Health
.jpg)
What Are Supportive Housing Programs?
.jpg)
Services Offered by Special Needs Care Providers
.jpg)
What Are Retirement Statistics?
.jpg)
Top Missouri Home Health Care Regulations You Need to Know

What Are Long-Term Care Statistics?
.jpg)
How to Implement Person-Centered Care in Nursing Homes

How to Implement a Resident Safety Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Implement a Pain Management Strategy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Apply for Low-Income Senior Housing in Missouri?
.jpg)
How Long Will Medicare Pay for Home Health Care?

How do i become a paid caregiver for a family member?

How Caregivers Help Manage Chronic Pain for Seniors
.jpg)
How To Find Home Health Care Physical Therapy Near You?
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits Of Home Health Care Physical Therapy

Main Differences Between Home Care vs Health Home
.jpg)
Ultimate Guide on Home Care for Special Needs Children
.jpg)
The Family’s Essential Role in Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
4 End of Life Symptoms in the Elderly

Top 3 Easy Meals for Elderly to Reheat
.jpg)
Effective Cognitive Decline Prevention Programs for Seniors

Best Medicaid Plans IN Missouri
.jpg)
Best Home Care Companies in Missouri
.jpg)
Create the Perfect At Home St. Louis Retreat for Relaxation

Comprehensive Alzheimer's Home Care Missouri for Your Loved Ones

Dusting and Vacuuming: Reducing Allergens in the Home

Ironing and Mending: Keeping Wardrobes in Top Shape

Grooming and Dressing: Essential Personal Care Services for Seniors
.jpg)
Top 9 Benefits of Social Connections for Seniors

The Effects of Sundown Syndrome
.jpg)
What Is In-Home Senior Care?
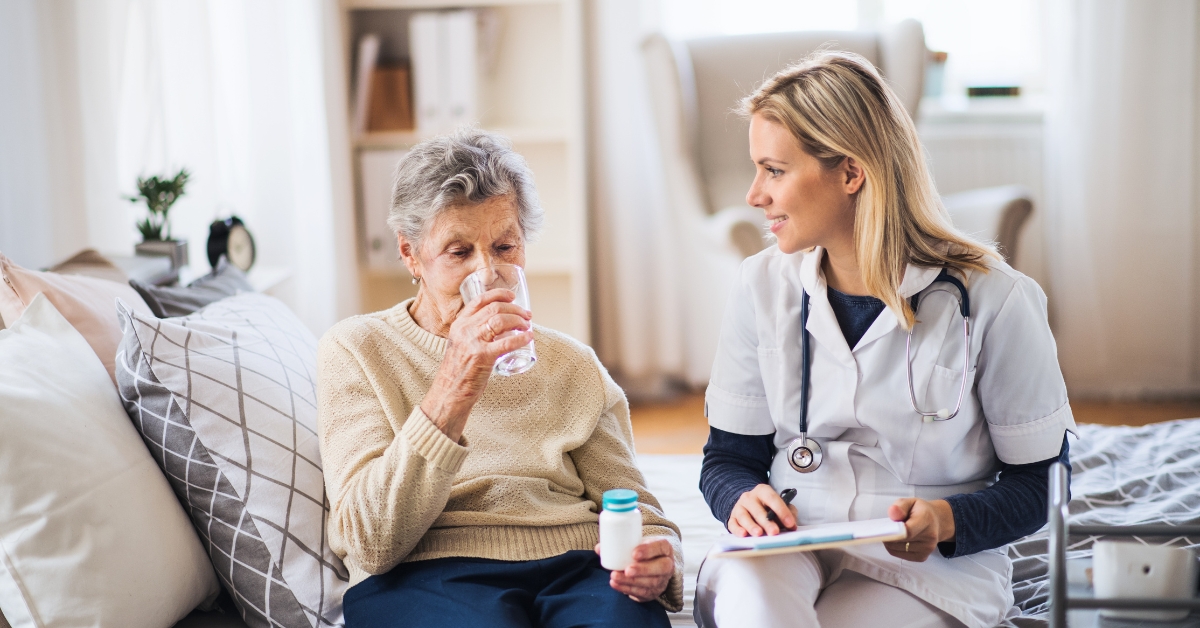

A Complete Guide to Caregivers for Taking Care Of A Relative With Cancer
.jpg)
Top 3 Types of Alternative Medicine in Home Care
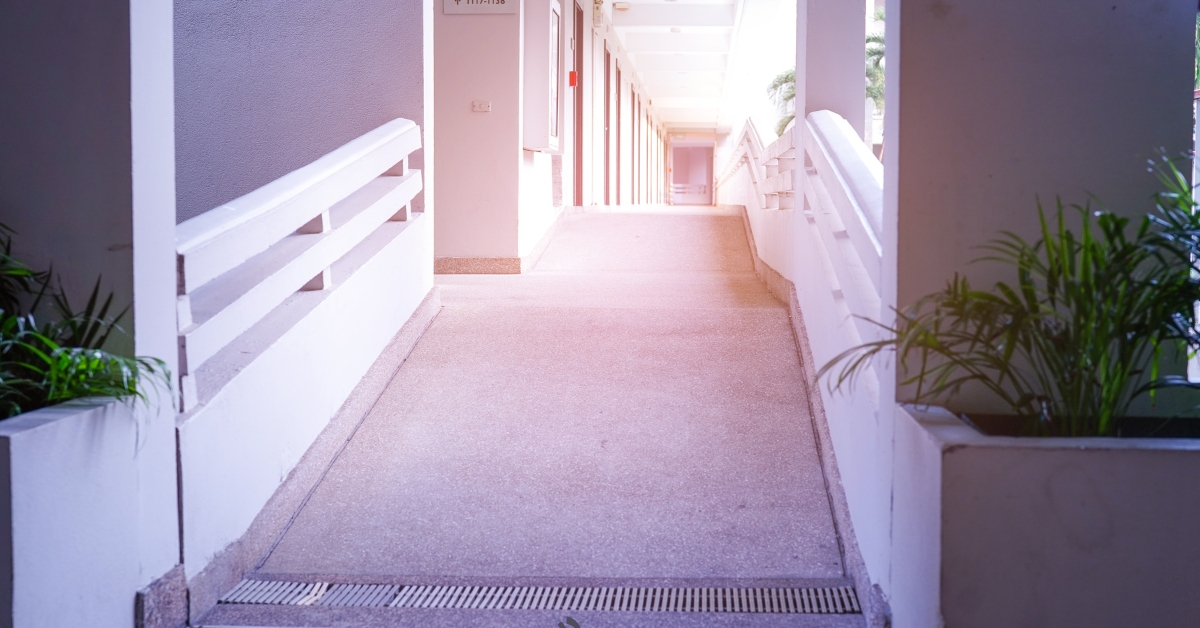

3 Types of Ramps for Stairs for Elderly
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits of Art and Music Therapy in Home Care
.jpg)
Dignity and Independence with Care

A Comprehensive Guide to Vital Signs
What Causes Purple Bruising in Elderly?
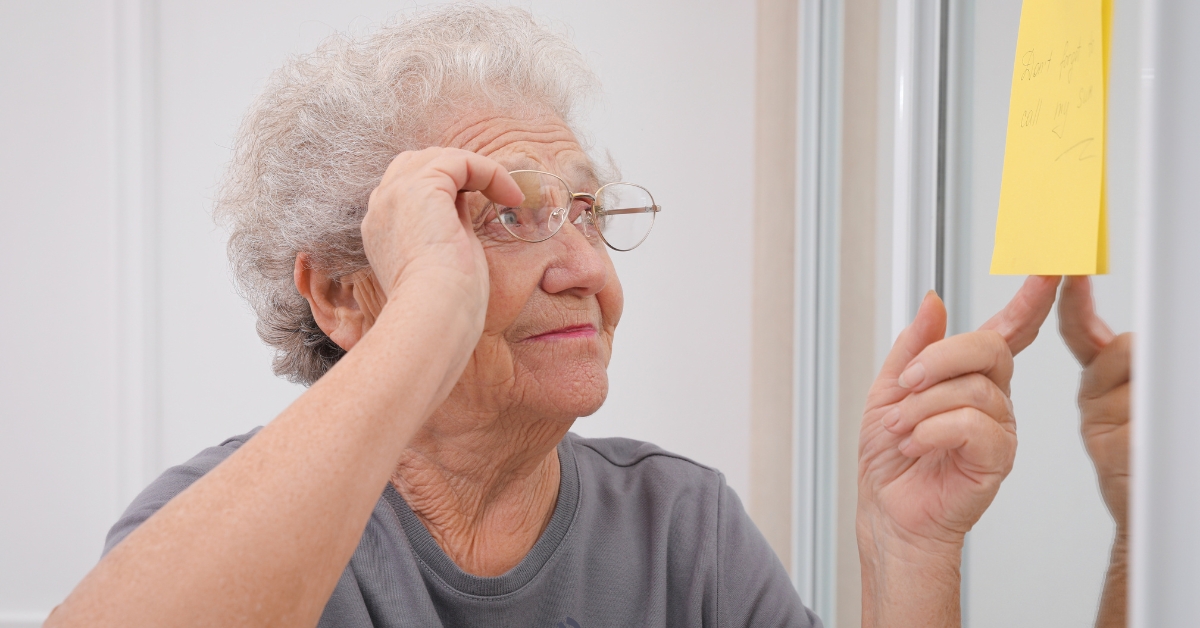

Forgetfulness vs Dementia
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits of Gardening Therapy for Seniors
.jpg)
Ultimate Guide on Addressing Spiritual Needs
.jpg)
Top 3 Nutrition Tips for Seniors in Home Care
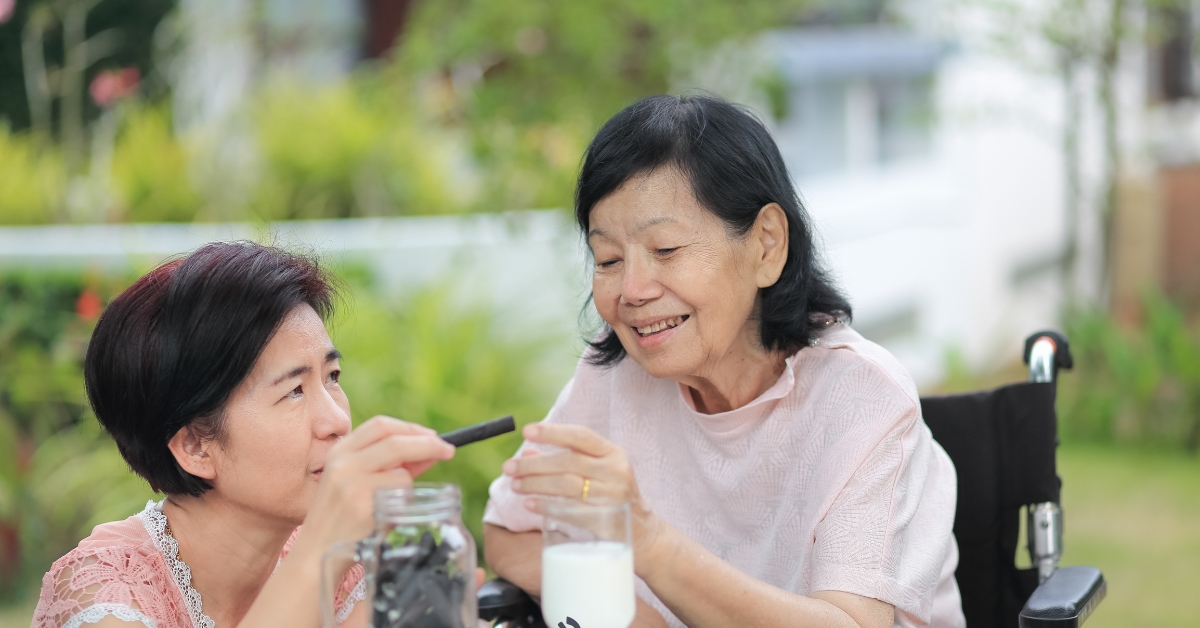

Essential Tips for Caring for an Elderly Parent
.jpg)
The 4 Triggers of Paranoia in Elderly
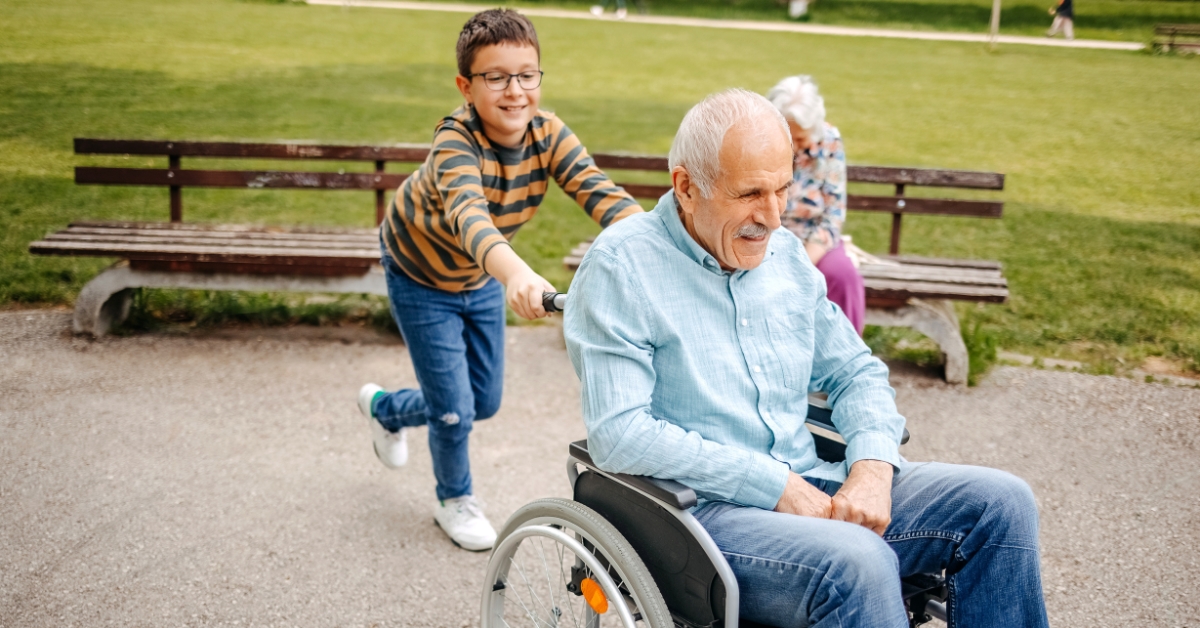

The Importance of Taking Care of Grandparents
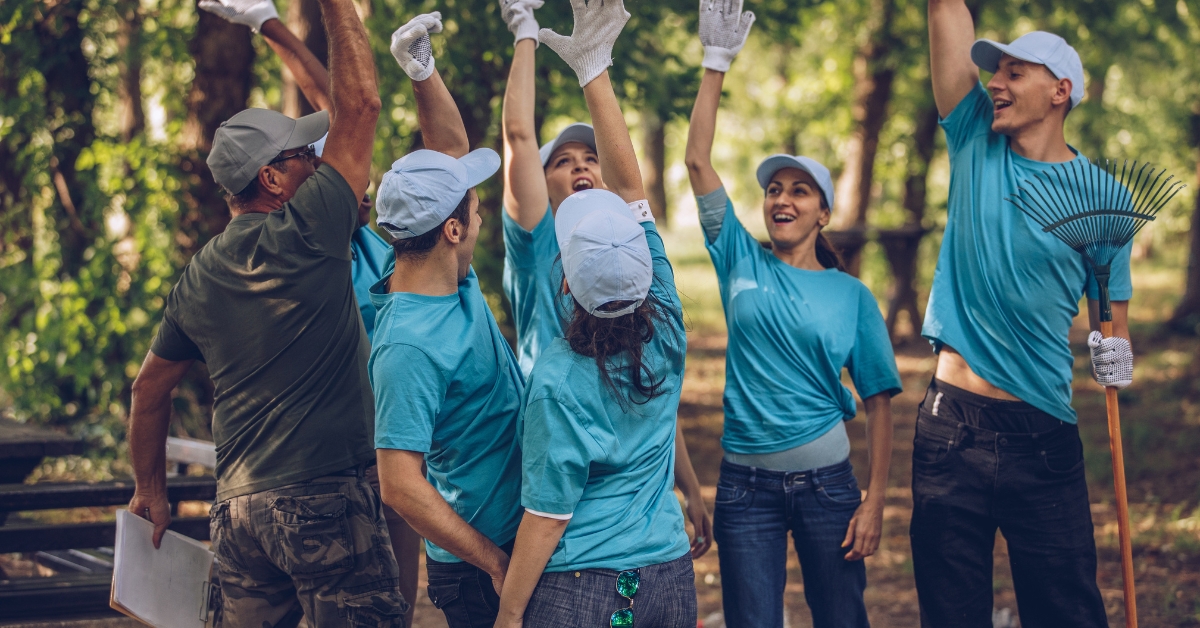

How to Find Volunteer Opportunities in Rochester?
.jpg)
Why Doesn’t Medicare Cover CDPAP?
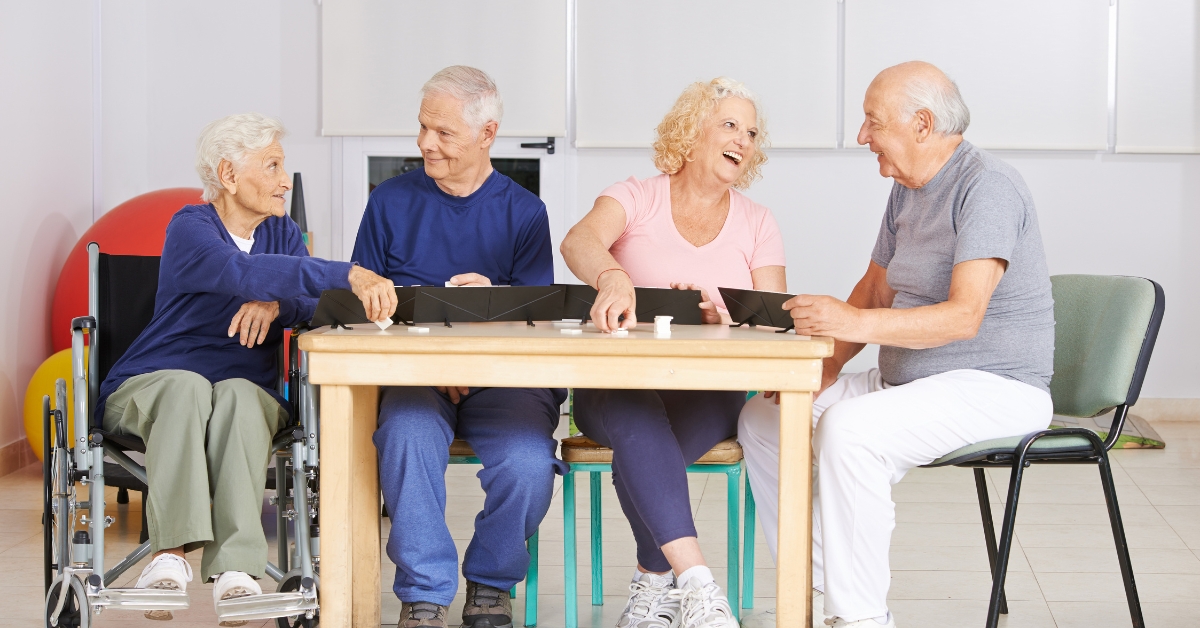

Support Groups for People with Disabilities
.jpg)
Understanding Private Pay Home Care Rates
.jpg)
What are the Role of Social Workers?
.jpg)
What is Disability Law Information?
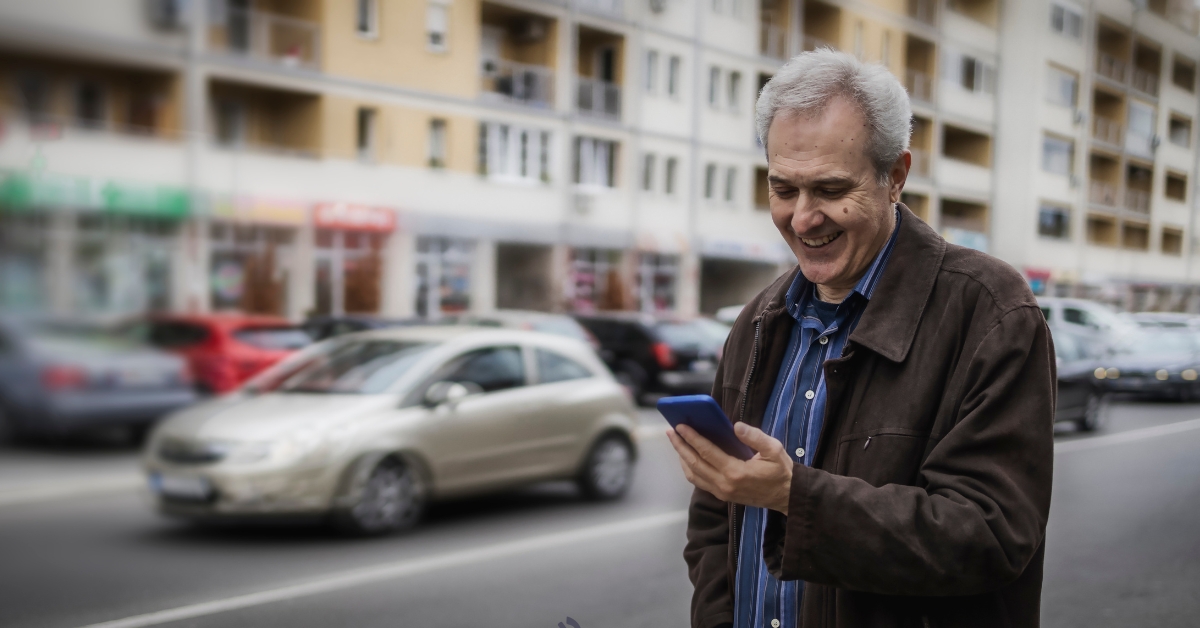

Top 5 Benefits of Uber for Seniors

How Much Does CDPAP Pay in NY?

Top Benefits of the Free Food Card for Seniors
.jpg)
What is the Role of Home Health Aides?
.jpg)
Top 3 Free Hoarding Help for Seniors
.jpg)
A Guide on Creating an Emergency Preparedness in Home Care

The 3 Types of Veteran Benefits NY

Who Qualifies for Veterans Home Care?

Volunteer Opportunities For The Elderly Population In Missouri

The Importance of Community Activities for Nursing Home Residents

How to Support Residents with Chronic Pain in Nursing Homes

The Role of Pain Management in Enhancing Nursing Home Care
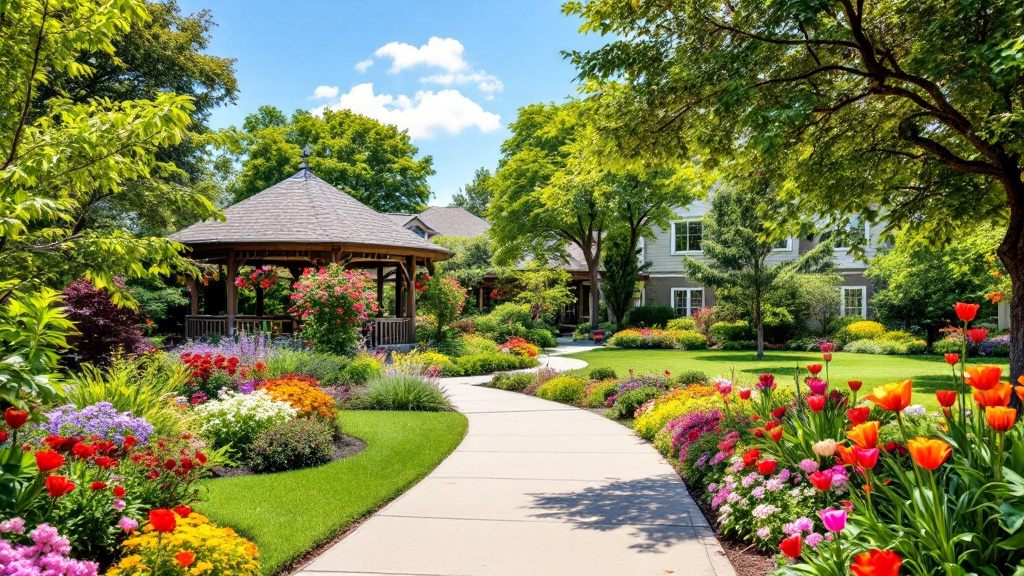

How to Support Residents with Limited Mobility in Nursing Homes

How to Address Depression in Nursing Home Residents
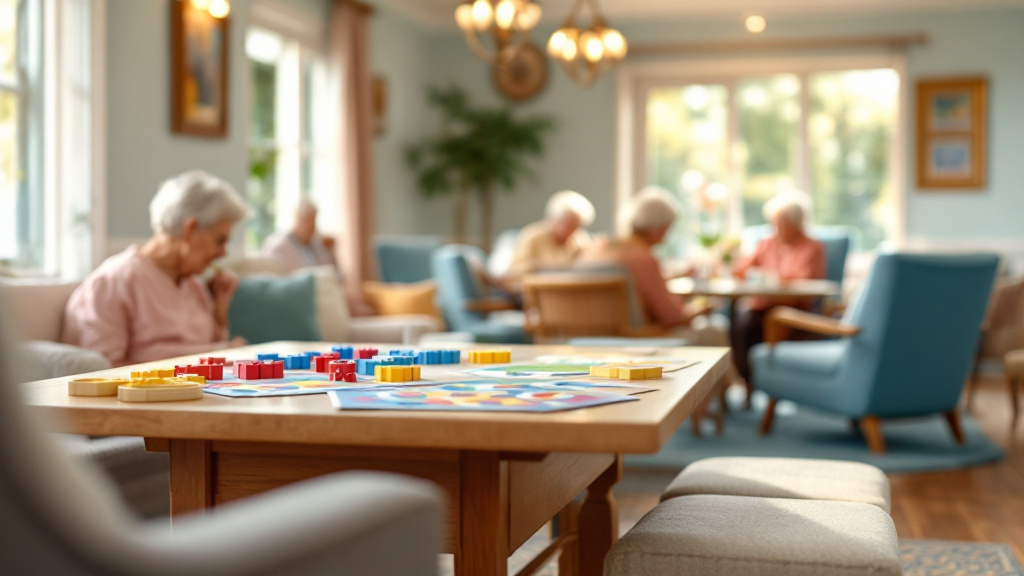

The Importance of Cognitive Stimulation for Nursing Home Residents

The Benefits of Occupational Therapy for Nursing Home Residents

How to Address Nutritional Needs in Nursing Home Residents

How to Implement a Fall Prevention Program in Nursing Homes

The Role of Health Information Technology in Enhancing Nursing Home Care

How to Develop a Resident Satisfaction Program in Nursing Homes

Explore Nutritional Programs for Senior Health and Wellness

The Benefits of Music Therapy for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Impact of Technology Use in Elderly Communities Explained
.jpg)
Effective Caregiver Support Programs for Staff in Senior Care

The Role of Pain Management in Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
The Importance of Advanced Vaccination Plans for Seniors
.jpg)
How to Recognize and Address Depression in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
Effective Pain Management in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Top Benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Mental Wellness
.jpg)
Why Advance Care Planning for Seniors is Essential for Care
.jpg)
Comprehensive Substance Abuse Solutions for Residents' Recovery

The Benefits of Group Therapy for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
Exploring the Benefits of Group Therapy for Seniors in Care

The Importance of Community Engagement for Nursing Home Residents

How to Develop a Chronic Disease Management Program in Nursing Homes

The Role of Care Coordination in Enhancing Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
A Guide to Addressing Elderly Sexuality Concerns with Care

How to Address Substance Use Disorders in Nursing Home Residents

The Benefits of Cognitive Stimulation for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Importance of Volunteer Programs in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Top Benefits of Promoting Hobbies for Nursing Home Residents

The Importance of Social Support for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Importance of Oral Health in Senior Care Explained

How to Address Malnutrition in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
Top Social Isolation Solutions for Seniors: Enhancing Quality of Life
.jpg)
The Power of Dance Therapy for Seniors: Enhancing Well-being

The Benefits of Physical Activity for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
Supporting Residents with Addiction Issues in Senior Communities
.jpg)
Top Strategies for Boosting Resident Satisfaction in Senior Homes
.jpg)
The Importance of Regular Health Check-Ups for Seniors

The Benefits of Social Support for Nursing Home Residents

The Role of Social Work in Enhancing Nursing Home Care

How to Support Residents with Substance Use Disorders in Nursing Homes

How to Develop a Chronic Disease Management Strategy in Nursing Homes

The Importance of Routine Vaccinations for Nursing Home Residents
The Role of Health Information Technology in Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
Why Comprehensive Health Checks Are Crucial for Seniors
.jpg)
Routine Vaccines for Elderly Health: Essential Immunizations
.jpg)
Top Social Activities for Elderly Residents to Boost Well-Being

The Role of Care Coordination in Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
Top Strategies for Fighting Malnutrition in Nursing Homes

How to Implement Technology in Elderly Care for Better Outcomes
.jpg)
Top Approaches to Chronic Illness Care for Nursing Home Staff

How to Implement a Health Promotion Program in Nursing Homes

How to Develop a Health Promotion Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Top Fun Activities for Nursing Home Residents to Stay Engaged
.jpg)
The Role of Palliative Care Development in Homes for Seniors
.jpg)
Effective Sleep Apnea Support for Elderly Residents’ Health

How to Address Mental Health Issues in Nursing Home Residents

How to Support Residents with Chronic Illnesses in Nursing Homes

The Benefits of Physical Therapy for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
Top Nutrition Tips for Nursing Home Residents to Boost Health
.jpg)
Top Strategies for Building Resident Independence in Homes
.jpg)
Treating Sleep Disorders in Nursing Homes: Improving Resident Health
.jpg)
Top Strategies for Enhancing Social Life in Nursing Homes

How to Implement a Fall Prevention Strategy in Nursing Homes

The Importance of Routine Health Screenings for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
Effective Hydration Strategies for Elderly Care and Wellness

How to Implement a Rehabilitation Program in Nursing Homes

The Benefits of Group Activities for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
Effective Communication Strategies for People with Hearing Loss

How to Develop a Rehabilitation Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Best Physical Fitness Programs for Seniors

How to Develop a Resident Satisfaction Strategy in Nursing Homes

How to Develop a Health Promotion Strategy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Top Tips for Supporting Nutritional Health in Elderly Care

The Role of Physical Activity in Nursing Home Care

How to Support Residents with Vision Impairments in Nursing Homes

The Importance of Regular Exercise for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
Effective Smoking Cessation for Elderly Residents Explained
.jpg)
The Power of Aromatherapy for Senior Residents Explained
.jpg)
The Power of Music Therapy in Senior Communities Explained

How to Address Behavioral Health Issues in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Importance of Psychiatric Care for Elderly Residents
.jpg)
Creating Comprehensive Health Strategies for Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Evolution of Pharmacy Services in Missouri
.jpg)
Physical Therapy Benefits for Seniors: Improving Mobility and Health

Home Health Care Cape Girardeau Mo

How to Develop a Rehabilitation Strategy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Top Home Health Care Services in Florissant, Missouri
.jpg)
Top Vision Support Strategies for Senior Residents in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
What are Aging Population Trends?
.jpg)
The Importance of Hospice Care Support in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Managing Chronic Diseases Effectively: Top Tips & Strategies
.jpg)
Personalized Home Health Care in Cape Girardeau, MO
.jpg)
The Importance of Mental Health in Senior Communities
.jpg)
Effective Coordination of Care for Seniors: A Guide

The Benefits of Art Programs for Nursing Home Residents

Top Home Health Care Agencies for Seniors in St. Louis
.jpg)
How to Address Nutritional Needs in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How to Address Chronic Pain in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Benefits of Music Therapy for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Benefits of Mindfulness for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Benefits of Cognitive Stimulation for Nursing Home Residents

The Importance of Regular Health Assessments in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Develop a Rehabilitation Strategy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Benefits of Group Activities for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Role of Care Coordination in Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
The Role of Music in Enhancing Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
The Benefits of Aromatheray for Nursing Home Residents

The Crucial Role of Respiratory Therapists in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Empowering Elderly Care: Essential Importance of Oral Health in Nursing Homes

Understanding Home Care for Disabilities
.jpg)
The Importance of Routine Health Screenings in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Support Residents with Psychiatric Disorders in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Address Hydration Needs in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Heartwarming Benefits of Recreational Activities for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How to Implement a Resident Safety Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
7 Best Tips To Prevent Bowel Infections in the Elderly
.jpg)
How to Address Nutritional Deficiencies in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Benefits of Social Support for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How to Implement a Smoking Policy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Address Sleep Disorders in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Importance of Mental Health Services in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Benefits of Occupational Therapy Serves Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Address Depression in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How to Develop a Chronic Disease Management Strategy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Address Behavioral Health Issues in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How to Address Hearing Loss in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How to Support Residents with Chronic Illnesses in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Importance of Regular Health Screenings in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Address Substance Abuse in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Telehealth Transformation: Enhancing Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
The Benefits of Physical Activity for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How to Implement an Infection Control Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Benefits of Art Programs for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Role of Exercise in Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
The Importance of Routine Vaccinations in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Address Anxiety in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How to Address Hearing Impairments in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Benefits of Pet Therapy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Importance of Regular Exercise in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Top-Rated Home Care Providers in Bridgeton
.jpg)
The Role of Social Work in Enhancing Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
The Benefits of Crafts and Hobbies for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Role of Dietitians in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Implement a Health Promotion Strategy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Role of Family Caregivers in Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
How to Navigate the Nursing Home Admission Process
.jpg)
How to Support Residents with Substance Abuse Issues in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Develop a Resident Satisfaction Strategy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Address Sleep Apnea in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Critical Role of Nutrition in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Exploring the Benefits of Dance Therapy for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Benefits of Community Activities for Nursing Home Residents

How to Implement a Smoking Cessation Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Role of Pet Therapy in Improving Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
How to Implement a Caregiver Support Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Implement a Rehabilitation Prgram in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Support Residents With Mental Health Issues in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Benefits of Horticultural Therapy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Support Residents with Visual Impairments in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Role of Physical Activity in Nursing Home Care

How to Implement a Respite Care Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Implement a Resident Satisfaction Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Impact of Social Isolation on Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How to Address Sexuality and Intimacy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Role of Speech Therapy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Role of Health Information Technology Transforms Nursing Home
.jpg)
The Importance of Community Engagement in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Benefits of Physical Therapy for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
Splashing Away Limitations: Aquatic Therapy Benefits for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How to Address Medication Adherence in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How to Develop a Recreation Therapy Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Develop a Chronic Disease Management Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Develop a Palliative Care Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Develop a Health Promotion Program in Nursing Homes
How long can I use my food stamp balance after benefits end?
.jpg)
The Importance of Regular Physical Activity in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Paving the Path to Relief: The Essential Position of Pain Management Specialists in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Address Substance Use Disorders in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How to Address Weight Management in Nursing Home Residents

3 Proven Tips For Enjoying Card Games for Seniors
.jpg)
How Often Should You Visit Elderly Parents?
.jpg)
What Bills Count For Food Stamps?
.jpg)
The Role of Social Activities in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Critical Role of Emergency Preparedness in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Benefits of Group Therapy in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How to Implement a Hospice Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Harmonizing Health: Meditations Positive Effects on Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
Top 3 Safety Tips With Narrow Walkers for Seniors
.jpg)
How to Address Sensory Impairments in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Benefits of Art Therapy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Role of Recreational Therapy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Importance of Continuing Education for Nursing Home Staff
.jpg)
How to Address Polypharmacy in Nursing Home Residents

How to Address Behavioral Issues in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Address Multimorbidity in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How to Develop a Wellness Program for Nursing Home Staff
.jpg)
Rejuvenate and Renew: The Healing Power of Yoga for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How to Develop a Technology Training Program for Nursing Home Staff
.jpg)
Navigating Loneliness: How Peer Support Groups Transform Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Healing Touch: Pharmacists Vital Contribution to Nursing Homes

Optimize Your Workflow: Must-Have Assisted Living Facility Software Features
.jpg)
How to Address Cognitive Decline in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Develop a Dementia Care Plan in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Benefits of Memory Care Units in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Create a Homelike Environment in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Address Substance Use in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Benefits of Reminiscence Therapy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Address Malnutrition in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
How To Bathe Elderly: A Step-by-Step Guide
.jpg)
The Role of Nutritionists in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Handle Conflict Resolution in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Incorporate Exercise Programs in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Support Caregivers of Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Impact of Climate Change on Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
The Benefits of Tai Chi for Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Role of Nutrition in Managing Chronic Diseases in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Develop a Disaster Preparedness Plan in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Develop a Volunteer Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Importance of Advance Care Planning in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Advocate for a Loved One in a Nursing Home
.jpg)
How to Foster Independence in Nursing Home Residents
.jpg)
The Importance of Resident Satisfaction Surveys in Nursing Homes

15 Things Old People Do for Fun
.jpg)
What are the Roles of Occupational Therapy Assistant?
.jpg)
The Benefits of Gardening Programs in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Importance of Personal Hygiene in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Failure to Thrive Elderly Life Expectancy Statistics
.jpg)
How to Ensure Compliance with Nursing Home Standards
.jpg)
The Benefits of Intergenerational Programs in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Navigate End-of-Life Decisions in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Role of Community Partnerships in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Importance of Family Involvement in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Finding the Best Home Health Care in Kansas City MO
.jpg)
The Role of Ethics Committees in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Develop a Health and wellness Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Role of Spiritual Care in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Assisted Living vs Skilled Nursing
.jpg)
How to Support Residents with Mobility Issues in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Role of Financial Planning in Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
How to Develop a Pet Policy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Address Loneliness and Isolation in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Most Effective Hip Flexor Exercises for Seniors

Home Care Industry Statistics and Facts

Top 5 Benefits Of Back Strengthening Exercises for Seniors
.jpg)
How to Develop a Sleep Hygiene Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Develop a Pain Management Plan in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How Much Does A Home Health Aide Make?
.jpg)
The Benefits of Animal Assisted Therapy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Handle Medical Emergencies in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Building Stronger Support: Hospital Readmissions and Nursing Home Care Interplay
.jpg)
The Role of Palliative Care in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Impact of Staffing Levels on Nursing Home Care

Top 3 Benefits Of Long Term Care for Seniors with Dementia
.jpg)
The Role of Physical Therapy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Handle Medication Management in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
Top Respite Care at Home Missouri Services

How to Support Emotional Well-being in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Transition from Home Care to a Nursing Home?
.jpg)
The Crucial Role of Volunteers in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Technology Advancements in Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
The Role of Rehabilitation Services in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Fund Nursing Home Care with Limited Resources

The Importance of Cultural Competency in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Discover Phoenix Home Care in Springfield, Missouri
.jpg)
Integrity Home Care Services in Lees Summit, Missouri
.jpg)
Missouri Care vs. Home State Health: A Comprehensive Comparison
.jpg)
Virtual Tours of Nursing Homes: What to Look For
.jpg)
The Best Home Health Care In Missouri
.jpg)
Why Choose Phoenix Home Care in Missouri?
.jpg)
Integrity Home Care and Hospice Services in Springfield, MO
.jpg)
Quality Home Health Care Options in West Plains, Missouri
.jpg)
How to Navigate Nursing Home Regulations?
.jpg)
Top Services at Willow Care Nursing Home Hannibal Missouri
.jpg)
Discover Integrity Home Care Springfield Missouri Services
.jpg)
Innovations in Nursing Home Architecture and Design
.jpg)
Comprehensive Missouri Home Health Care for Seniors
.jpg)
How to Obtain a Home Health Care License in Missouri
.jpg)
Top Features of Missouri Home Care Software Solutions
.jpg)
Genesis Home Care Services in Poplar Bluff, Missouri
.jpg)
Reliable Missouri Baptist Home Health Care Solutions
.jpg)
The Role of Social Workers in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
A Complete Guide to Missouri Home Health Care Insurance
.jpg)
Missouri Alliance for Home Care Fall Risk Assessment Process
.jpg)
How to Improve the Quality of Life in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Professional Home Care Assistance in Missouri
.jpg)
Why Choose Genesis Home Care Campbell Missouri?
.jpg)
Discover Missouri Home Care Insurance Plans for Your Needs

Phoenix Home Care and Hospice Services in Independence, MO
.jpg)
Top Missouri Home State Health Care Programs for Families

How To Become A Home Health Care Provider In Missouri?
.jpg)
Why the Missouri Primary Care Health Home Initiative Matters?
.jpg)
How to Address Elder Abuse in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Impact of Medicare Changes on Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
The Importance of Nutritional Programs in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Develop a Fall Prevention Program in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
How to Choose the Best Senior Care Home in Kirkwood, MO
.jpg)
Does Medicaid Pay For Home Health Care In Missouri?
.jpg)
Home Health Care for Seniors in Howard County Missouri
.jpg)
The Psychological Impact of Moving to a Nursing Home
.jpg)
How to Create a Personalized Care Plan in Nursing Homes?
.jpg)
Explore Home Care Business for Sale in Missouri
.jpg)
Essential Tips for Choosing a Nursing Home in Missouri
.jpg)
Veterans Home Care Services in St. Louis Missouri
.jpg)
How to Qualify for Medicare Home Health Care in Missouri?
.jpg)
How To Start A Private Duty Home Care Business In Missouri
.jpg)
Why Choose Integrity Home Care in Joplin, Missouri?
.jpg)
Finding the Best Home Health Care Agencies in Missouri
.jpg)
How to Manage Chronic Illnesses in Nursing Homes?
.jpg)
Home Health Care in Springfield IL
.jpg)
At Home Care in Hannibal, Missouri
.jpg)
How to Ensure Safety and Security in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
Know Your Legal Rights as a Nursing Home Resident
.jpg)
The Impact of COVID-19 on Nursing Home Care
.jpg)
Starting A Home Health Care Business In Missouri
.jpg)
Top-Rated Phoenix Home Care Columbia Missouri
.jpg)
Exploring Top Missouri Nursing Home Care Communities
.jpg)
In-Home Care in Missouri
.jpg)
Best 24-Hour Home Care Options in Missouri
.jpg)
Home Health Care Services in West St. Louis, Missouri
.jpg)
Top Companion Care Services at Home in Missouri
.jpg)
The Role of Occupational Therapy in Nursing Homes
.jpg)
The Role of Missouri Home Care Association in Care Excellence
.jpg)
Senior Home Care Missouri
.jpg)
Preferred Care at Home in Greater Kansas City, Missouri

Integrity Home Health Care Springfield Missouri
.jpg)
What Are the Easy Baked Recipes for Seniors?
.jpg)
What Are the Best Vitamins for Dementia?
.jpg)
What is Vocational Rehabilitations?
.jpg)
Affordable Caregiver St. Joseph MO Services
.jpg)
3 Types of Missouri Home Care
.jpg)
Guidelines for Caring for a Cancer Patient at Home
.jpg)
Find the Best Home Health Nurse in Missouri
.jpg)
What Are the Senior Activities at Home?
.jpg)
How to Maintain Family Connections in Nursing Homes?
.jpg)
How to Find Private Nursing Agency Near You?
.jpg)
Steps to Obtain Your Missouri Home Care License
.jpg)
What is Caregiver Jobs in Connecticut?
.jpg)
Accessing At-Home Care in Missouri
.jpg)
Comprehensive In-Home Health Care Services in Missouri
.jpg)
The Benefits of Proactive Home Care in Missouri
.jpg)
Top Missouri In-Home Senior Care Services for Your Loved Ones
.jpg)
How to Qualify for Missouri Medicaid for Nursing Home Care?
.jpg)
How to Start a Residential Care Home in Missouri?
.jpg)
Reliable Home Health Care St. Louis MO Services
.jpg)
How to Choose the Right Nursing Home for Your Loved One?
.jpg)
Personal Care Home in Missouri
.jpg)
What are Supportive Care Innovations?
.jpg)
Top Phoenix Home Health Care in Columbia, Missouri
.jpg)
Comprehensive Guide to Live-In Home Care in Missouri
.jpg)
How Phoenix Home Care Supports Families in Jefferson City
.jpg)
Compassionate Respite Home Care Services in Missouri
.jpg)
Affordable Home Health Care in Columbia MO
.jpg)
Reliable Home Care Services Across Missouri
.jpg)
Challenges in Accessing Home Health Care Services
.jpg)
Missouri Home Health Care
.jpg)
How to Access Home Health Care in Los Angeles?
.jpg)
What is Palliative Care at Home?
.jpg)
What Is the Best Vitamin for Alzheimers Patients?
.jpg)
What Is Elderly In-Home Care?
.jpg)
How Do I Get Medicare to Pay for Home Care?
.jpg)
Best Strategies For Your Health Advantage
.jpg)
Top 2 Benefits of Supportive Care Assessments
.jpg)
Does Hospice Cover 24-Hour Care at Home?
.jpg)
Why Choose Home Health Care Joplin MO?
.jpg)
What are Holistic Approaches to Home Health?
.jpg)
Top At Home Care Services in Springfield MO
.jpg)
How To Find Home Health Physical Therapy Near You?
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits Of Online Caregiver Jobs
.jpg)
Benefits of Private Home Care in St. Louis
.jpg)
What Is Home Nursing Care?
.jpg)
Benefits of Advantage Home Health Services
.jpg)
How to Find Community Health Centers?
.jpg)
What Are Home Health Aide Agencies?
.jpg)
Does Food Stamps Count as Income for Mortgage?
.jpg)
Top 9 Healthy Living Benefits
.jpg)
Services Offered by Home Care of Mid Missouri
.jpg)
Comprehensive Guide to Home Care Assistance St. Louis
.jpg)
How Much Is the Weekly Pay for Home Health Care?
.jpg)
How to Find Volunteer Yard Work for Seniors Near you?
.jpg)
Top 3 Types of Disability Service Providers
.jpg)
In-Dept Guide to Aging and In-Home Services
.jpg)
How To Choose The Right Home Health Aide Agency in NJ?

What Are Daily Pay Agencies?
.jpg)
What Industry Is Caregiving?
.jpg)
Comprehensive Guide to Home Health Aide Jobs Hiring
.jpg)
A Complete Guide To Golden Discounts for Seniors
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits of In-Home Health Care
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits of Family Resource Home Care
.jpg)
How to Find a Care Planning Consultants?
.jpg)
Best Tips To Discuss Home Care with Aging Parents
.jpg)
A Complete Guide to Disability Care Management
.jpg)
Can I Afford a Home Care Worker?
.jpg)
What is Adult Family Living Program?
.jpg)
Who are Direct Support Professionals?
.jpg)
What is Assisted Transportation?
.jpg)
How to Find Personal Care Assistant Jobs?

Top 3 Benefits of Having a Home Care Agency License
.jpg)
Who Can Benefit from Advantage Home Care?
.jpg)
What Are the Easy Recipes for Seniors at Home?
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits of Community Living Services
.jpg)
Is there a Discounts for People Over 50?
.jpg)
What Are the 50 Year Old Benefits?
.jpg)
What is Home Attendant Care?
.jpg)
Key Components of Comprehensive Senior Health Services
.jpg)
How to Obtain a Missouri Non-Medical Home Care License?
.jpg)
Top 5 Disability Advocacy Groups
.jpg)
What is Occupational Therapy?

A Comprehensive Guide to a Private Home Care Services

What Is The Average Family Caregiver Pay Rate?
.jpg)
The Importance Of Shower Aids for the Elderly
.jpg)
What is Home Day Care Insurance?
.jpg)
A Guide To Non-Medical Home Care Business Insurance
.jpg)
What is Private Pay Home Care?
.jpg)
Role of Caregivers in Home Health
.jpg)
What is Care at Home Agency?
.jpg)
What is Palliative Care for the Elderly?
.jpg)
What are Accessible Housing Solutions?

What are 5 Qualities of a Good Caregiver?
.jpg)
Importance of Non-Medical Home Care Services
.jpg)
How To Embrace Getting Older?
.jpg)
Importance of Long-Term Care Planning
.jpg)
What Is Friends and Family Home Care?
.jpg)
How to Choose the Right Elderly Respite Care Option?
.jpg)
Strategies for Effective Chronic Illness Management
.jpg)
Comprehensive Guide to NHTD Waiver Program Benefits
.jpg)
What is Advanced Home Care?
.jpg)
Importance of Effective Healthcare Navigation
.jpg)
A Complete Guide To IHSS Jobs
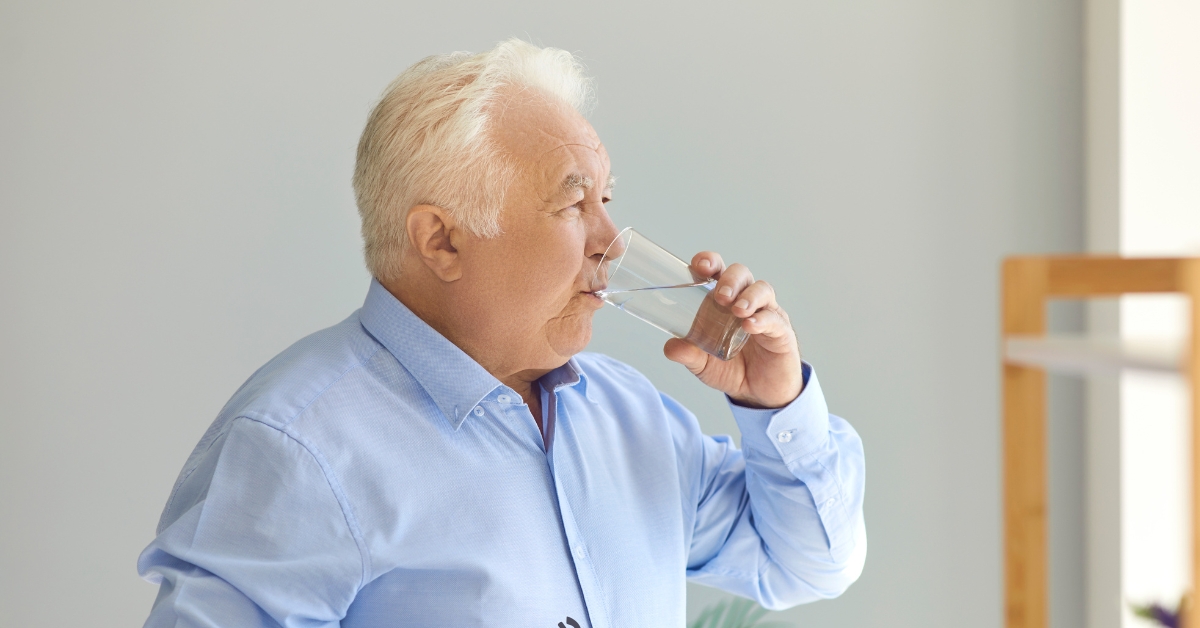

How Much Water Should a 90 Year Old Drink Daily?
.jpg)
Importance of Accessing Behavioral Health Services
.jpg)
How Long Does it Take to Get Approved for IHSS?
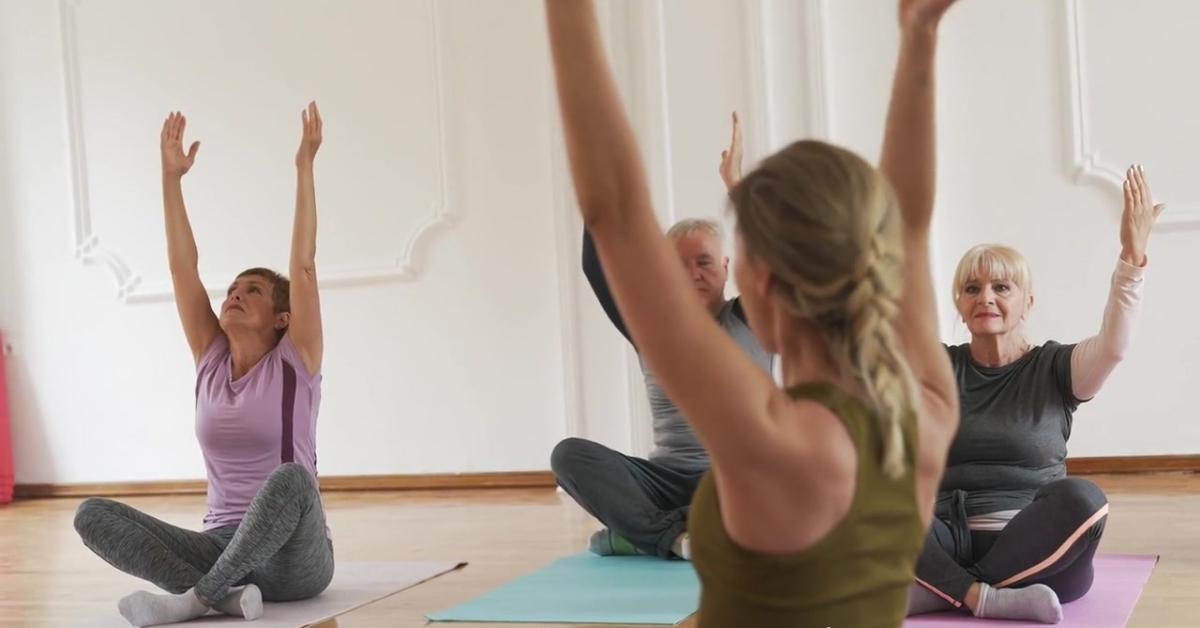

The Benefits of Yoga for Seniors in Missouri
.jpg)
An In- Depth Guide to Emergency Medicaid in Missouri
.jpg)
Private Care for Elderly at Home
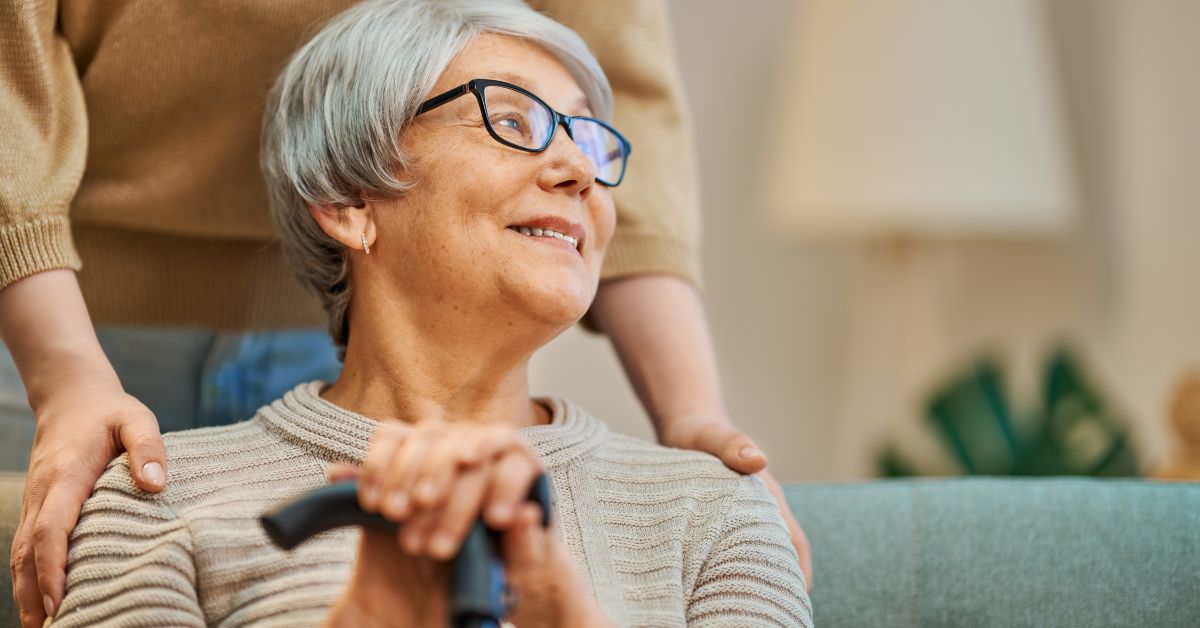

What is A Freedom Care?
.jpg)
How to Apply for IHSS Services in San Diego?
.jpg)
Comprehensive Social Services for Seniors
.jpg)
The Importance of Palliative Care Information
.jpg)
Home Modifications in NY
.jpg)
Top 4 Key Functions of Managed Care Organizations
.jpg)
Top 4 Benefits of At-Home Care
.jpg)
Who Can Benefit from Independent Living Support?
.jpg)
Importance of IHSS Qualifications
.jpg)
What Are the Key Family Caregiver Resources Available?
.jpg)
What is Preferred Home Care?
.jpg)
How To Find Home Care Jobs Near You?
.jpg)
Comprehensive Checklist for Medicaid Waiver Eligibility
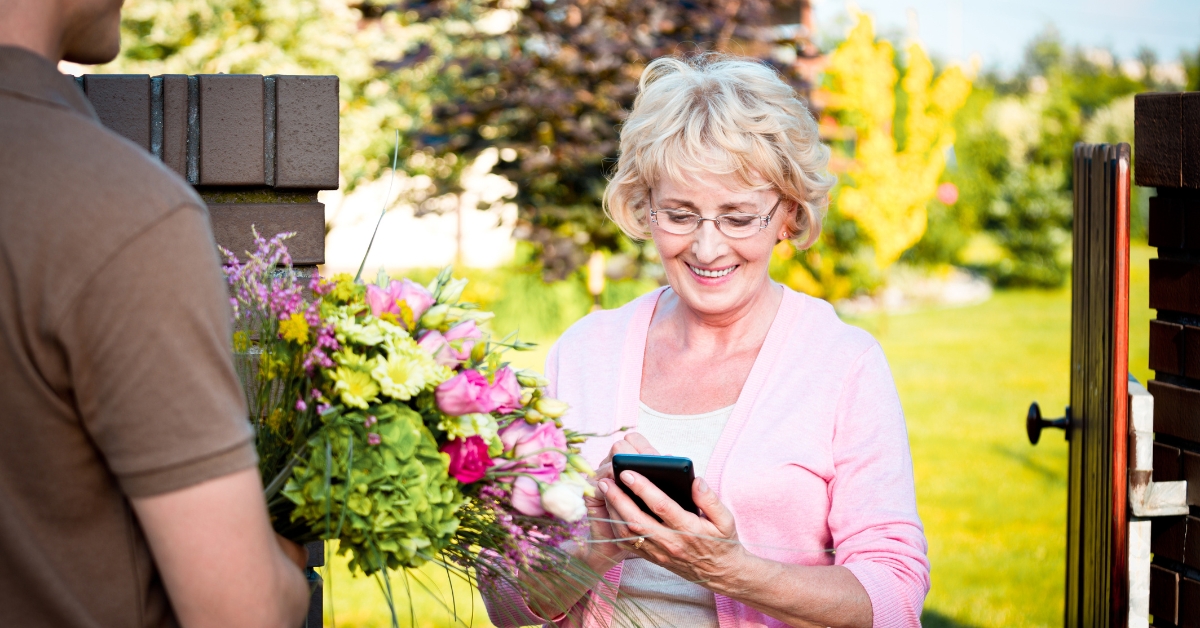

What Is Home Care Delivered?
.jpg)
What are Private Home Care Agencies?
.jpg)
What is IHSS Visalia?
.jpg)
What is a CDPAP Agency?
.jpg)
What are Home Health Aide Services?
.jpg)
How To Choose the Best Caregiver Training Program?
.jpg)
How to Choose the Right Personal Care Agency?
.jpg)
Top 3 Types of Assistive Technology Resources
.jpg)
Importance of Home Health Care Service Insurance
.jpg)
In-Dept Guide for Medicaid Home Care in NY
.jpg)
Essential Aging in Place Products
.jpg)
Comprehensive Guide to Nursing Home Alternatives
.jpg)
Top 6 Best Exercises for Crepey Arms
.jpg)
Best Strategies for Getting Rid of "Old Lady Arms"
.jpg)
How to Pay for Nursing Home Care with Social Security?
.jpg)
How Much Does In-Home Child Care Cost Per Hour?
.jpg)
What is 24-Hour Care?
.jpg)
Aging in Place Solutions
.jpg)
Introduction to IHSS Recipient Application Form
.jpg)
How to Find Gastroenterologist that Accepts Medicaid?
.jpg)
3 Tips for Finding Affordable Senior Housing in Missouri
.jpg)
How To Choose the Right Senior Care Assistance?
.jpg)
Overview of IHSS in Salinas, CA
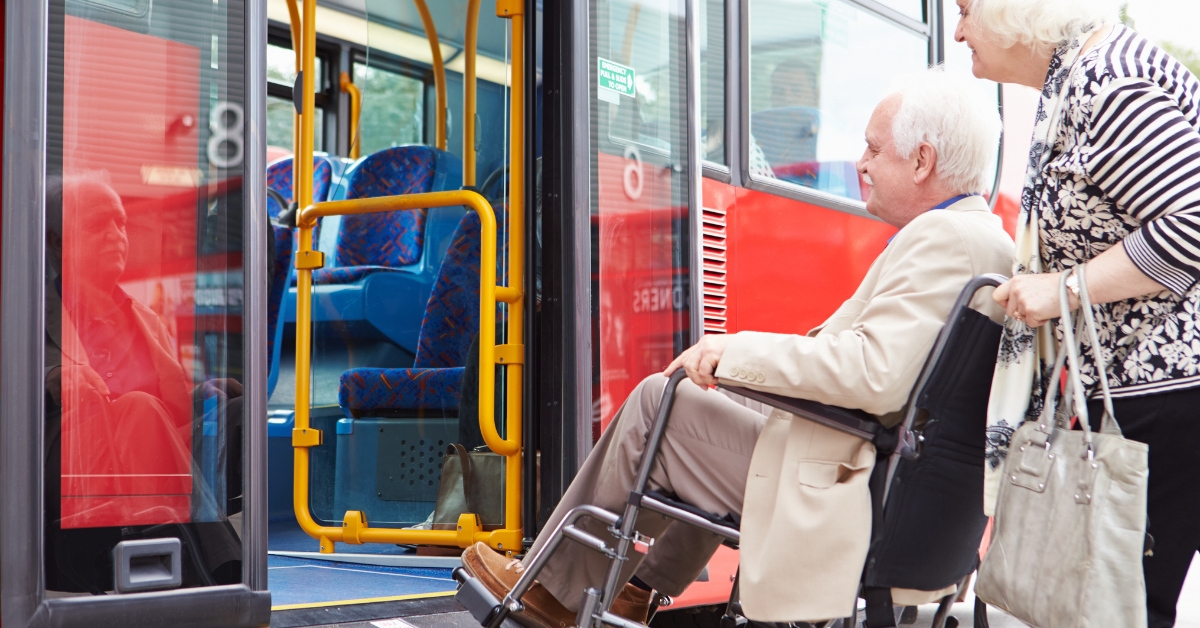

3 Types of Senior Transportation Services
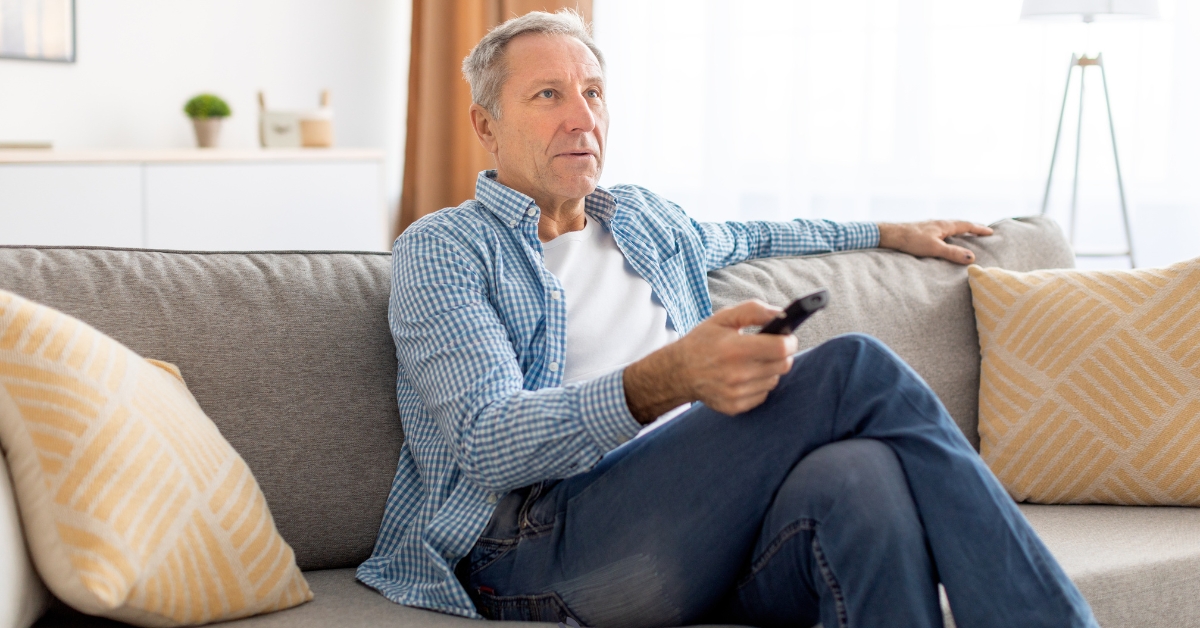

5 Benefits of Cable TV for Senior Citizens
.jpg)
The Importance of the Medicaid Card in Missouri
.jpg)
4 Types of Home Care Licenses
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits Of Patient-Centered Care
.jpg)
Finding Respite Care Near You
.jpg)
What Are Caregiver Support Groups?
.jpg)
National Family Caregiver Support Program
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits of Mobility for Seniors at Home
.jpg)
Top 6 Effective Exercises for Flabby Arms Over 50
.jpg)
The Ultimate Guide to Finding CDPAP Agencies Near You
.jpg)
Best Affordable Home Care Options
.jpg)
What is Hospice Home Care?
.jpg)
What are the Legal Considerations in Home Care?
.jpg)
Understanding Medicaid Application Help
.jpg)
In-Depth Guide on Respecting Cultural Beliefs in Home Care
.jpg)
The Best Strategies for Addressing Caregiver Guilt
.jpg)
Who Can Benefit from the CDPAP Program?
.jpg)
Top 4 Benefits of Chronic Pain Management at Home
.jpg)
Understanding Holistic Wellness for Seniors
.jpg)
What is Nutrition Education for Seniors?
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits of Integrating Complementary Therapies
.jpg)
Effective Support for Autism in Home Care
.jpg)
How to Find Private Pay Home Care Near You?
.jpg)
Missouri Disability Parking Permit Renewal Online
.jpg)
In-Depth Guide on Recognizing Elder Abuse in Home Care
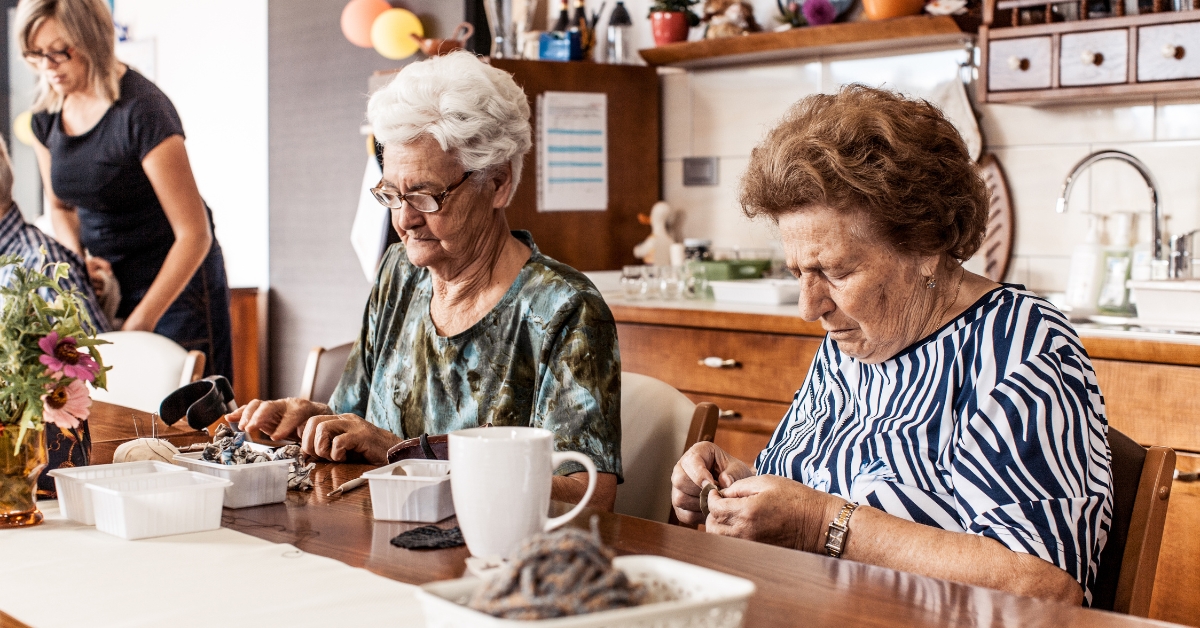

The Ultimate Guide for Finding the Best Senior Centers NY
.jpg)
Does Medicaid Cover Dementia Care?
.jpg)
How to Find Occupational Therapy Near You?
.jpg)
What is CDPAP?
.jpg)
When Should Someone With Dementia Go Into a Care Home?
.jpg)
Top 9 Benefits of In-Home Nursing
.jpg)
A Complete Guide of Finding Home Health Care Services Near You
.jpg)
A Complete Guide to Stress Reduction in Home Care
.jpg)
8 Most Common Responsibilities of Dementia Caregivers
.jpg)
What is Cultural Competence in Care?
.jpg)
A Comprehensive Guide to Home Nursing Care
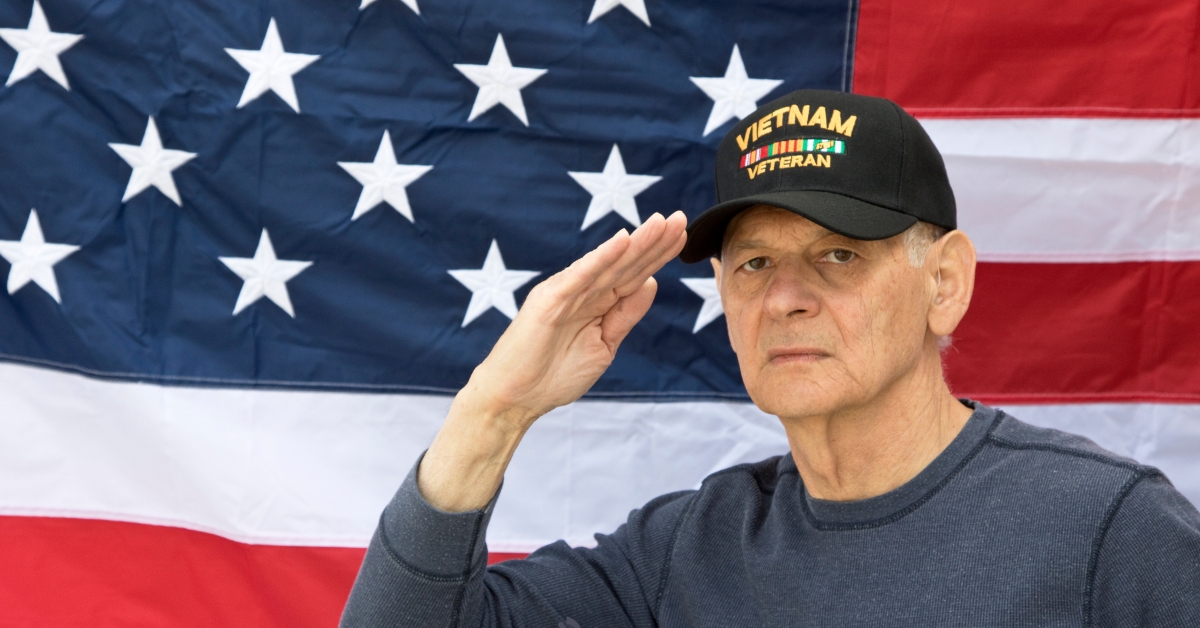

Who Is Eligible for the Veterans Home Care Program?
.jpg)
In-Depth Guide to Home Care for Stroke Survivors
.jpg)
A Complete Guide to Medicare and Medicaid for Home Care
.jpg)
How to Improve Mental Health in Elderly?
.jpg)
Essential Nutrition for Chronic Illnesses

5 Benefits of Listening Podcasts for Women Over 60
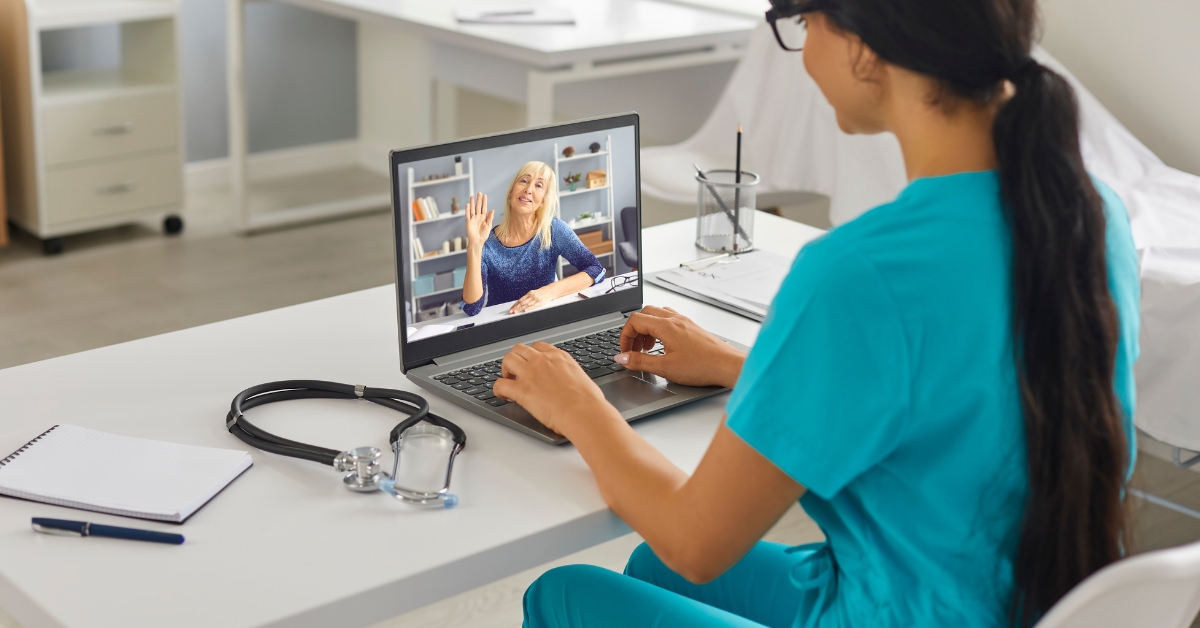
Best Telehealth Options for Home Care
.jpg)
Top 6 Tips For Acing The Home Health Aide Test
.jpg)
Understanding Cognitive Stimulation in Home Care
.jpg)
Best Caregiver Appreciation Quotes

The Complete Guide to Senior Housing Options in Missouri
.jpg)
In Home Physical Therapy Cost
.jpg)
Coping with Chronic Illness at Home
.jpg)
How To Find Fitness for Seniors Near You?
.jpg)
Ultimate Guide on Creating Safe Homes for Visual Impairments
.jpg)
What is Family Dynamics in Home Care?
.jpg)
Helping the Elderly with Technology
.jpg)
A Complete Guide to Palliative Care in Home Health
.jpg)
5 Sit-Down Games for Senior Citizens
.jpg)
Personal Care Services Missouri
.jpg)
6 Social Activities for Seniors
.jpg)
A Complete Guide To Dementia Care Plan
.jpg)
What Factors Affects End of Life Care Costs?
.jpg)
How Much Does Medicare Pay for Home Health Care Per Hour?
.jpg)
Understanding Mental Health Support in Home Care
.jpg)
A Complete Guide on Finding the Right Nursing Services
.jpg)
Ultimate Travel Tips with Home Care
.jpg)
Occupational Therapy vs Physical Therapy
.jpg)
An Essential Guide to Sleep Quality in Seniors
.jpg)
Top 4 Benefits of Caregiver Stress Management
.jpg)
In-Depth Guide on Choosing Personal Care Assistants
.jpg)
Ultimate Personal Hygiene Tips for Seniors
.jpg)
Does Private Insurance Cover Home Health Care?
.jpg)
Top 3 Emotional Impact of Home Care
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits of Alzheimer's Care at Home
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits of Mindfulness Practices at Home
.jpg)
A Comprehensive Guide on Coping with Grief in Home Care
.jpg)
Top 3 Types of Adaptive Equipment for Independence
.jpg)
Who Qualifies for Disability Benefits Missouri?
.jpg)
5 Benefits of Good Sleep Hygiene for Seniors

The 6 Benefits of End of Life Care at Home
.jpg)
How Much Does Memory Care Cost?
.jpg)
What are the Technology Solutions in Home Health?
.jpg)
Does Medicare Cover Home Health Care for Dementia?
.jpg)
Top 4 Benefits of Socialization for Homebound Seniors
.jpg)
Understanding Safe Home Environments for Senior Care
.jpg)
Top 7 Benefits of Pet Ownership for Seniors
.jpg)
How to Reduce Loneliness in the Elderly?
.jpg)
What is Memory Enhancement in Home Care?
.jpg)
What Licenses do I Need to Start a Home Health Care Business?
.jpg)
Comprehensive Guide to End of Life Care for Elderly
.jpg)
What is CDPAP Stand for?
.jpg)
Top 10 Benefits of Respite Care for Family Caregivers
.jpg)
Does Medicare Cover Dementia Care?
.jpg)
In-Depth Guide on Financial Planning for Home Care
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits of Animal Therapy in Home Care
.jpg)
Does Medicare Pay for Home Health Care?
.jpg)
How to Manage Medications at Home?
.jpg)
What is End-of-Life Care Planning?
.jpg)
Top Strategies in Addressing Social Isolation
.jpg)
After Surgery Home Care Cost
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits of Cultural Competency Training
.jpg)
In-Depth Guide to Nutrition for Malnutrition
.jpg)
NYS Handicap Parking Permit Renewal

What Is A Primary Caregiver?
.jpg)
Elderly Nutrition Program
.jpg)
A Complete Guide for Physical Therapy at Home for Seniors
.jpg)
A Comprehensive Guide To Elderly Nutritional Needs
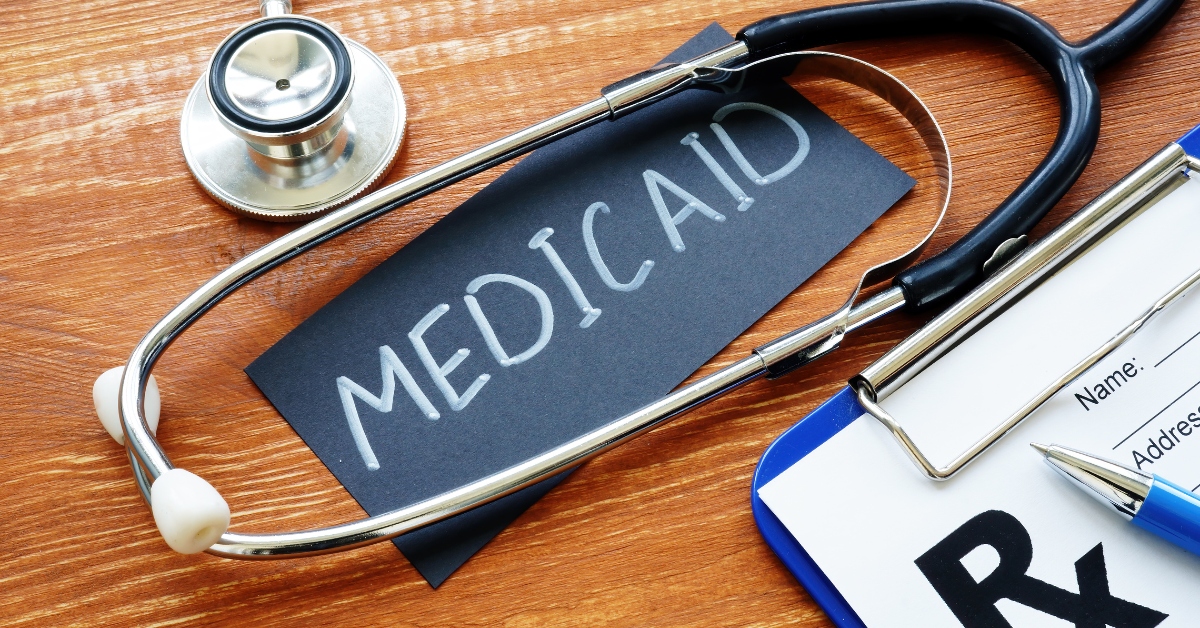
What Are Medicaid Cards?
.jpg)
The Best Taking Care for Parents Quotes
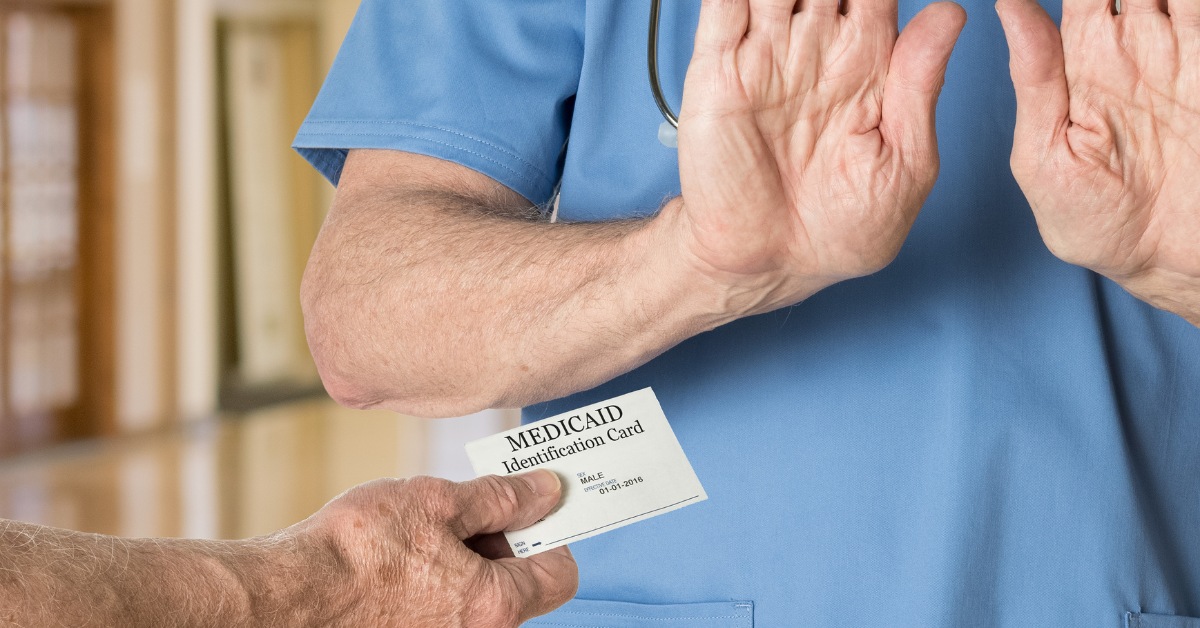

A Complete Guide On Medicaid Waiver Services
.jpg)
Senior Living Apartments Based on Income
.jpg)
What is the Most Common Mental Illness in the Elderly?
.jpg)
Best 2 Tips for Effective Music and Art Therapy at Home

The Comprehensive Guide to Self Help for the Elderly
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits of Pet Therapy at Home
.jpg)
Things Old People Do
.jpg)
Home Care Financial Assistance Programs

Aging And Sleep: How Does Growing Old Affect Sleep?
.jpg)
Home Safety for Elderly

Client Spotlight: Catherine’s Story
.jpg)
The 4 Stages of Pneumonia in the Elderly
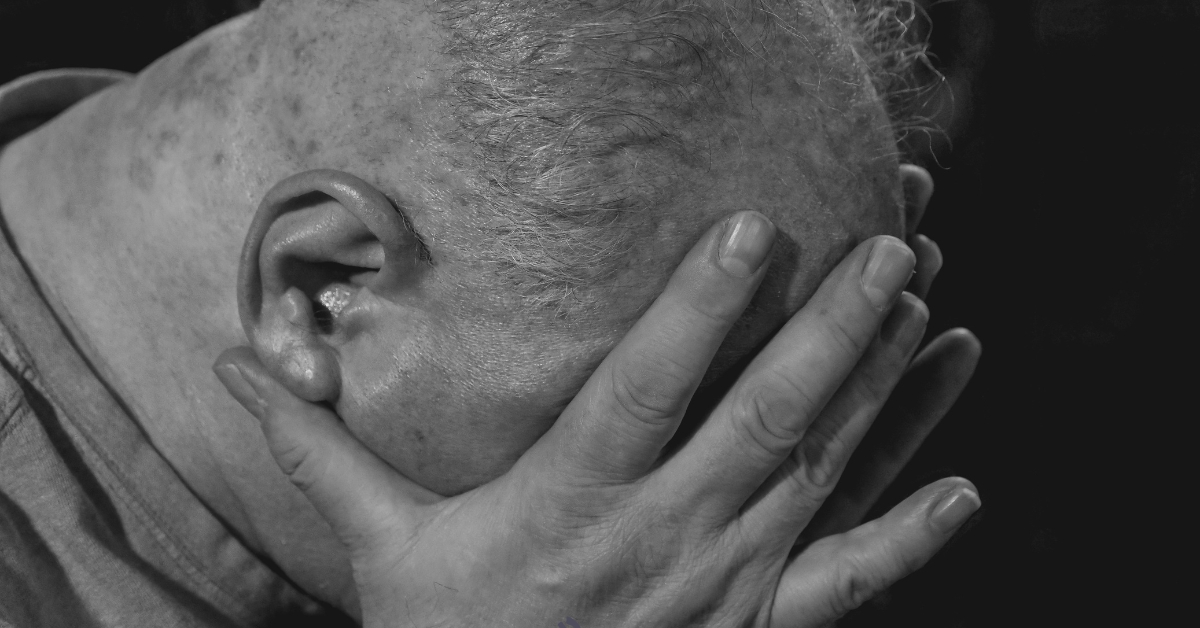
Top 6 Factors Contributing to Anxiety in Elderly at Night
.jpg)
Why Home Health Care is Important?
.jpg)
What is Home Helpers Home Care?

A Complete Guide to Finding Caregiver Jobs Near You
.jpg)
Top 9 Free Stuff for Seniors Over 60

Are Dementia Patients Aware of their Condition?

Top 12 Easy Meals for Seniors to Prepare

How to Stop Dementia Patients from Wandering at Night?

Top 5 Benefits of Senior Centers in Buffalo

When Are You Considered Elderly?

What are Caregiver Contracts?

How to Find Best Memory Care Near You?
.jpg)
What is an Elder Law Attorney?
.jpg)
Care for Veterans at Home
.jpg)
Understanding End of Life Care Ethical Issues
.jpg)
8 Services Offered by Low Cost Cleaning Services for Seniors Near You

What is Domiciliary Care?

9 Best Recipes for the Elderly
.jpg)
How Much Do Elderly Caregivers Get Paid?

Top 4 Benefits of Yard Cleanup for Seniors
.jpg)
A Complete Guide to Dementia Care at Home

A Complete Guide of Designing a 7-day Meal Plan for Elderly
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits Of Assisted Living Facilities
.jpg)
Complete Guide to the Cost of Senior Living Communities

The Ultimate Guide for Social Security Caregiver Pay in Nevada
.jpg)
What Is Assisted Living?
.jpg)
Assisted Living vs Long Term Care

How to Deal with Angry Dementia Parent?
.jpg)
What is Dementia Care?

What is the Normal Heart Rate for 80 Year-Old Woman?

What is Memory Care?

Seniors and Technology
.jpg)
Assisted Living vs Nursing Home
.jpg)
What is a Geriatric Care Manager?
.jpg)
4 Best Types Of Health Insurance for Senior Citizens
.jpg)
What is Geriatric Care?
.jpg)
Top 3 Tips For Finding A Job for Senior Citizens

The Ultimate Guide for Finding Alzheimer's Care Near You
.jpg)
6 Benefits of Rides for Seniors to Medical Appointments
.jpg)
3 Safest Sleep Aid for the Elderly
.jpg)
Assisted Living vs Memory Care
.jpg)
Do People With Alzheimer's Know they Have It?
.jpg)
The Best Toilet Aids for Elderly
.jpg)
What Is Home Health Care for Alzheimer’s Patients?
.jpg)
What Are Elder Care Solutions?
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits Of Certified Geriatric Care Management
.jpg)
Top 6 Advantages Of In-Home Senior Care
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits Of Respite Care Services
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits Of Pet Care Assistance for Senior Citizens
.jpg)
Does Medicare Cover Nursing Home Care for Dementia?

How to Apply for the Senior Food Allowance Card?
.jpg)
The Best Sleep Aid for the Elderly

Paying for Home Care with Social Security in Missouri
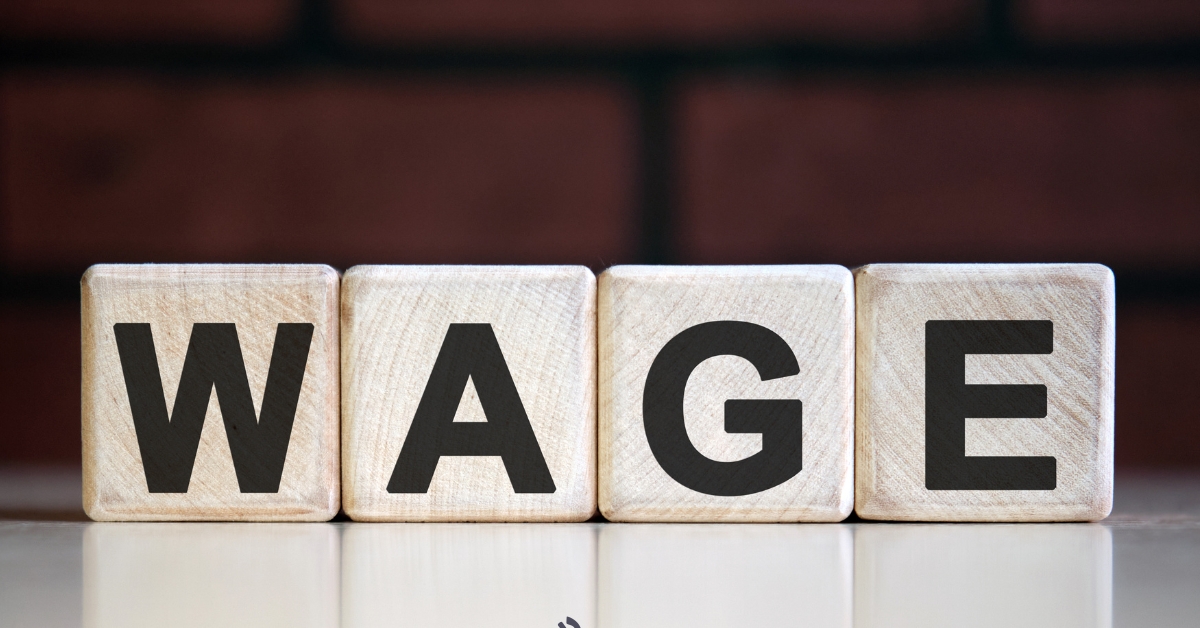
How to Evaluate Private Pay Home Care Rates?
.jpg)
Best 3 Types Of Walking Aids for the Elderly
.jpg)
What Is Dementia Home Care?
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits Of Retirement Independent Living Communities
.jpg)
Top 4 Benefits Of Compression Stocking Aid for Elderly
.jpg)
Best 3 Tips For Managing In-Home Dementia Care Costs
.jpg)
3 Top-Rated Options for Geriatric Home Care
.jpg)
When Should an Alzheimers Patients Go To a Nursing Home?
.jpg)
Top 8 Benefits Of Joining A Dementia Caregiver Support Group
.jpg)
How To Find Caregiver Support in Missouri?
.jpg)
Exploring the Average Cost of In-Home Senior Care
.jpg)
What Is Elderly Care?
.jpg)
What Is Senior Home Assistance?
.jpg)
What Are Elderly Personal Care Services?
.jpg)
What Are Elderly Day Care Services?
.jpg)
Home Health Care for Mentally Disabled Adults

Top 4 Healthy Food for Seniors
.jpg)
Memory Care Home Solutions for Seniors
.jpg)
A Comprehensive Guide To Grants for Elderly Care Services
.jpg)
Who Pays for Hospice Care at Home?
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits of Compassionate Alzheimer’s Care
.jpg)
Elderly Exercise Benefits: Top 3 Ways Seniors Can Improve Their Health
.jpg)
At What Age Are You Considered A Senior Citizen?
.jpg)
What Does ABA Stand For?
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits Of Nurses Next Door Home Care Services
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits Of Choosing Elastic Waist Jeans
.jpg)
How Much Do Home Care Nurses Make?
.jpg)
5 Types of Senior Legal Services
.jpg)
How to Qualify for Home Health Care?
.jpg)
Best Options for Elderly Care at Home
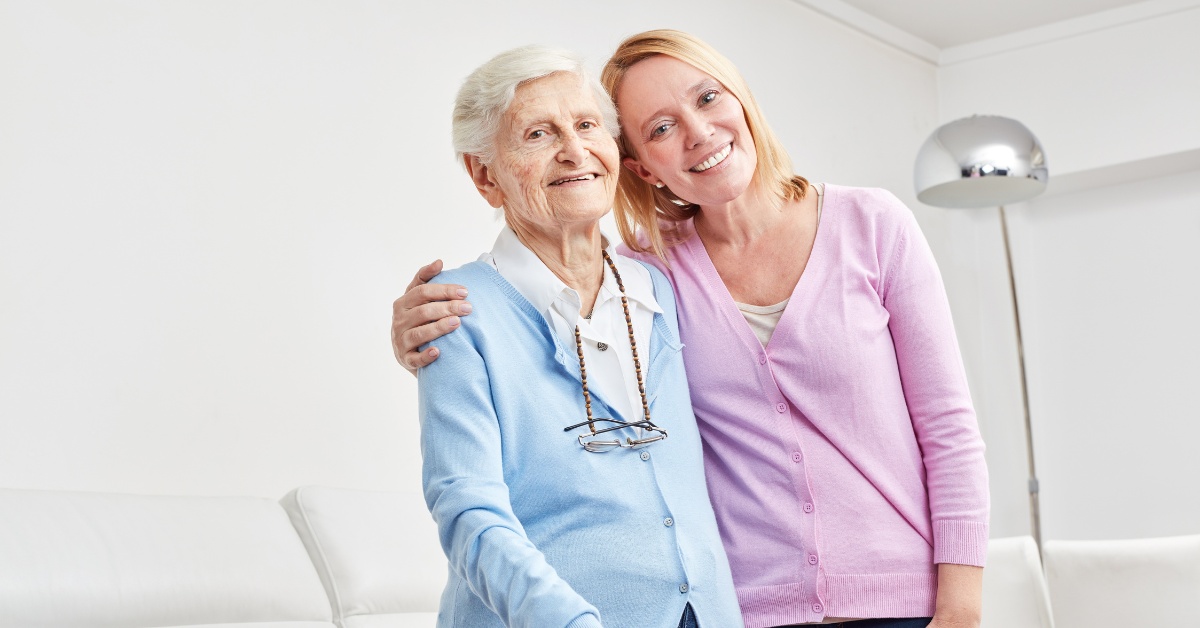

How To Get Paid To Care For A Family Member?
.jpg)
What is Home Caring?
.jpg)
Top 5 Benefits of In-Home Care Services for Disabled
.jpg)
What Happens when Medicare Stops Paying for Nursing Home Care?
.jpg)
Best Home Care Agencies in New York
.jpg)
What Is The Difference Between Caregiver And Live in Caregiver?
.jpg)
Best Elderly Transportation Services
.jpg)
Best Safety Tips For Home Care
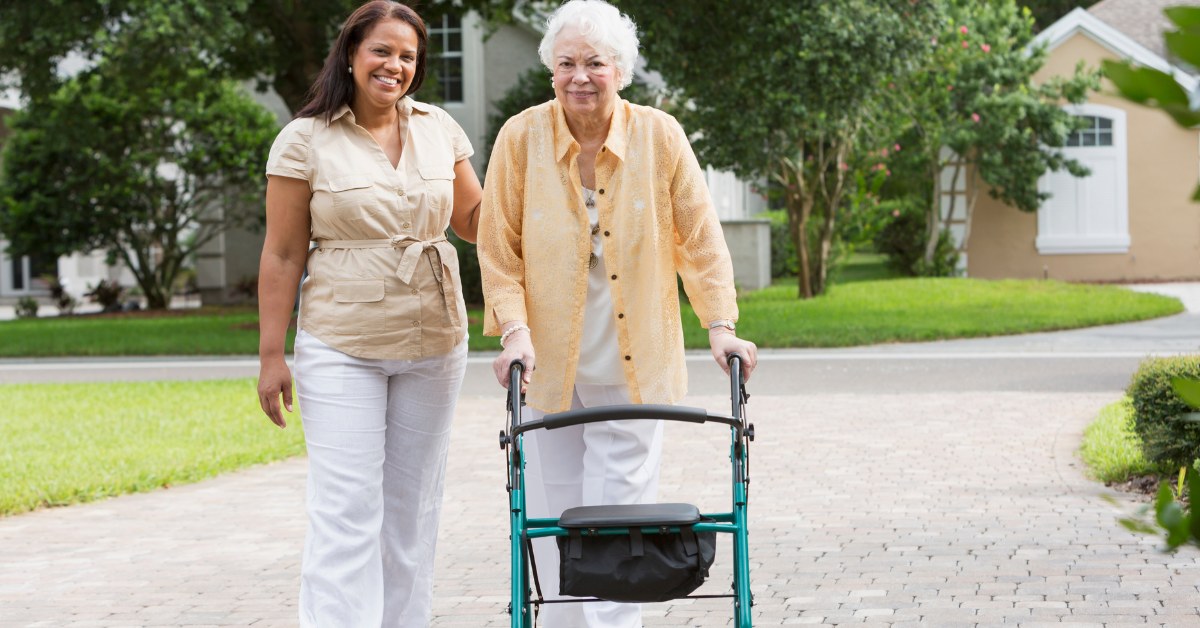

What are 4 The Types of Caregivers?
.jpg)
What Is Bathing Assistance for Elderly?
.jpg)
How Much Do Nursing Home Social Workers Get Paid in New York?
.jpg)
What Does A Home Health Aide Do?
.jpg)
6 Best Home Care Services Covered by Medicare This 2024
.jpg)
How Much Do Family Members Get Paid for Caregiving?
.jpg)
How Much Is In Home Child Care Per Hour Near Missouri?
.jpg)
How Many Hours Can A Home Health Aide Work?
.jpg)
Professional Caregivers St. Louis
.jpg)
6 Primary Activities of Daily Living
.jpg)
Who Qualifies for Home Health Care?
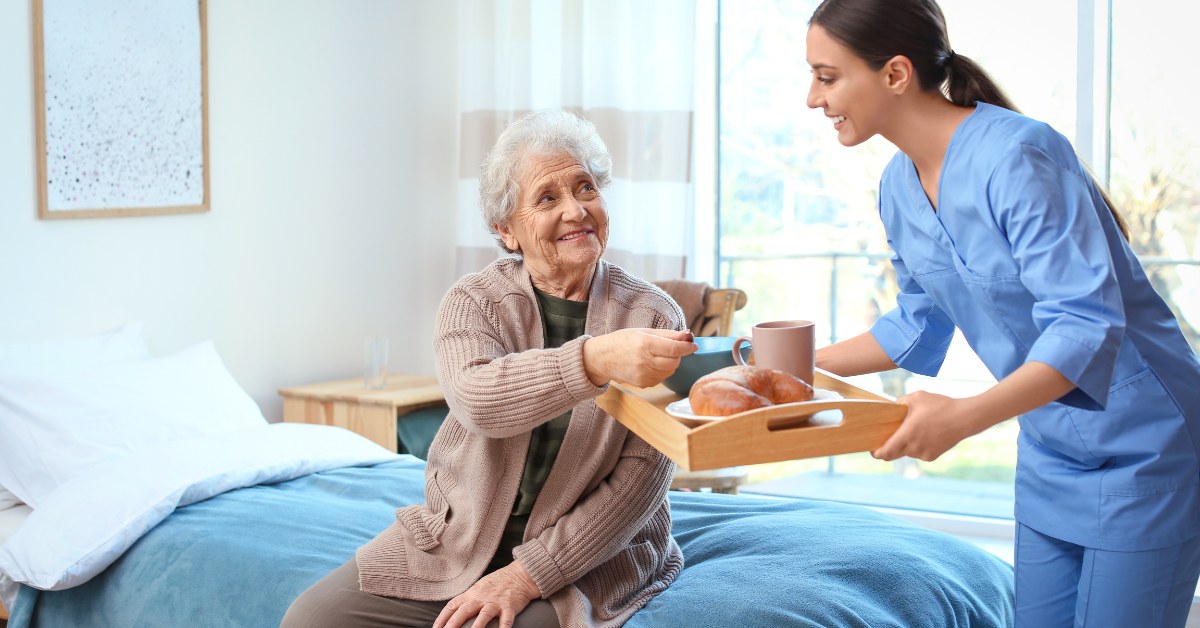

What Is The Average Cost of Home Care?
.jpg)
Requirements For Home Care Covered by Medicaid
.jpg)
Home Care vs Respite Care
.jpg)
What Defines A Home Caregiver?
.jpg)
Does Social Security Pay You To Take Care Of A Family Member?
.jpg)
What Are The 5 Categories Of Caring?
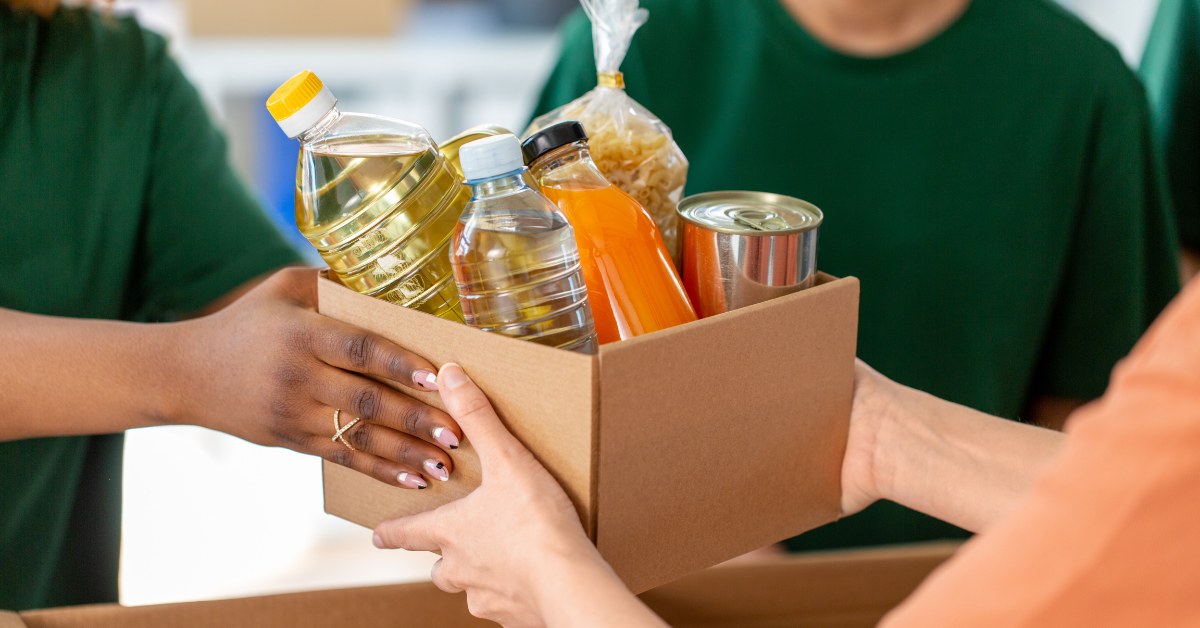

If I Make 1800 A Month Can I Get Food Stamps?
.jpg)
How Do I Get Paid To Be A Caregiver?
.jpg)
Top Causes Of Failure To Thrive in Adults
.jpg)
How to Prevent Your Seniors from Falling?

Key Insights from Parkinson’s Statistics
.jpg)
How To Find Compassionate Caregivers?

What is Missouri Fair Pay For Home Care?
.jpg)
4 Types Of Home Health Solutions

What is Home Care?

What Is The Maximum Hours For Home Care In Missouri?

What States Pay Caregivers the Most?
.jpg)
What Are Consumer Directed Services?
.jpg)
How to Get Certified Home Health Aide?
.jpg)
What Are The 3 Types of Care?

What is the Rate for a Caregiver in Missouri?
.jpg)
Does Home Care Require a Background Check?
.jpg)
How Much Does Home Care Pay in Missouri?
.jpg)
What are Consumer Directed Services In Missouri?
.jpg)
Which is Better Caregiver or Caretaker?
.jpg)
What’s Another Name For Caregiver?
.jpg)
How To Find Home Instead Senior Care Locations?

HomeTeam receives BBB Accreditation
How Do I Get Medicaid To Pay For Home Care?
.jpg)
What Is A Caregiver?

Ten Questions To Ask When Choosing A Home Care Provider
.jpg)
What Is Home Care Nursing?
.jpg)
Top 5 Myths About Home Care

Top 7 Key Features Of Home Care Application

What Are Assisted Living Statistics?
.jpg)
How To Find A Reliable Health Care Agency?
.jpg)
What Are The 6 Areas of Care?
.jpg)
A Complete Guide To Home Care Vaccine Mandate

Who Qualifies for Home Health Care Services?
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits Of Geriatric Primary Care
.jpg)
Home Care for Drug/Alcohol Addicts

Home Care Industry Statistics & Facts
.jpg)
Preferred Home Health Care & Nursing Services
.jpg)
How to Become Home Health Aide?
.jpg)
What’s The Difference Between A Home Care and A Caregiver?

How Much Does Home Care Cost in Missouri?
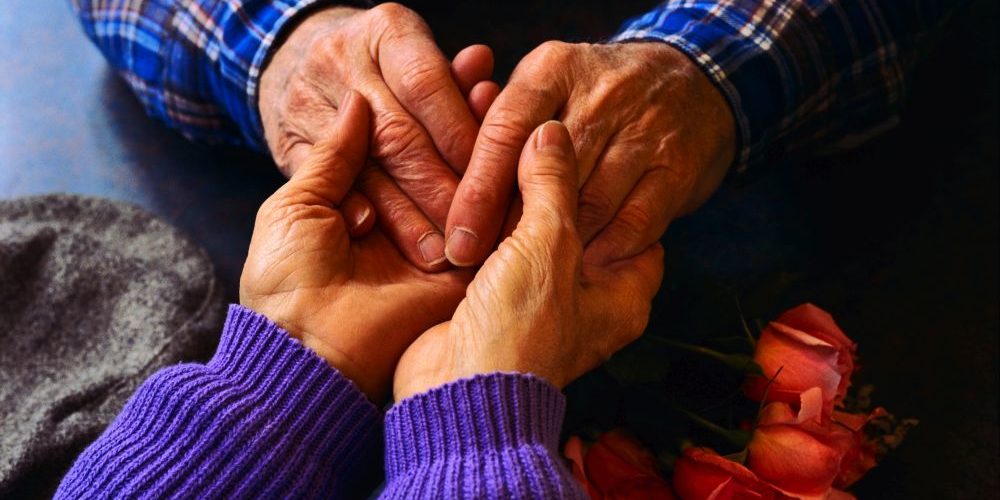

Paying for Home Care: Some Options
.jpg)
How To Become A Caregiver?

Home Care vs Personal Care

Most Common Missouri Slang
.jpg)
How To Treat Diarrhea In The Elderly?

Who is Eligible for Home Care in Missouri?
.jpg)
Recommended Tips For Taking Care Of Elderly Parents

How Long Will Medicare Pay For Home Care?

Best Caregivers Quotes

Home Care Vs Long Term Care

The Best Guide to Meet Caregiver Requirements

Will Medicaid Pay For 24-hour Home Care?
.jpg)
9 Effective Arm Exercises for Flabby Arms
.jpg)
How Often Grandparents Should See Their Grandchildren?
.jpg)
Home Care vs Nursing Home
.jpg)
Best Recliners For Elderly
.jpg)
What Are Dementia Statistics?

Does Medicaid Cover Home Care?

What Are Hospice Care Statistics?
.jpg)
When Did Home Care Start?
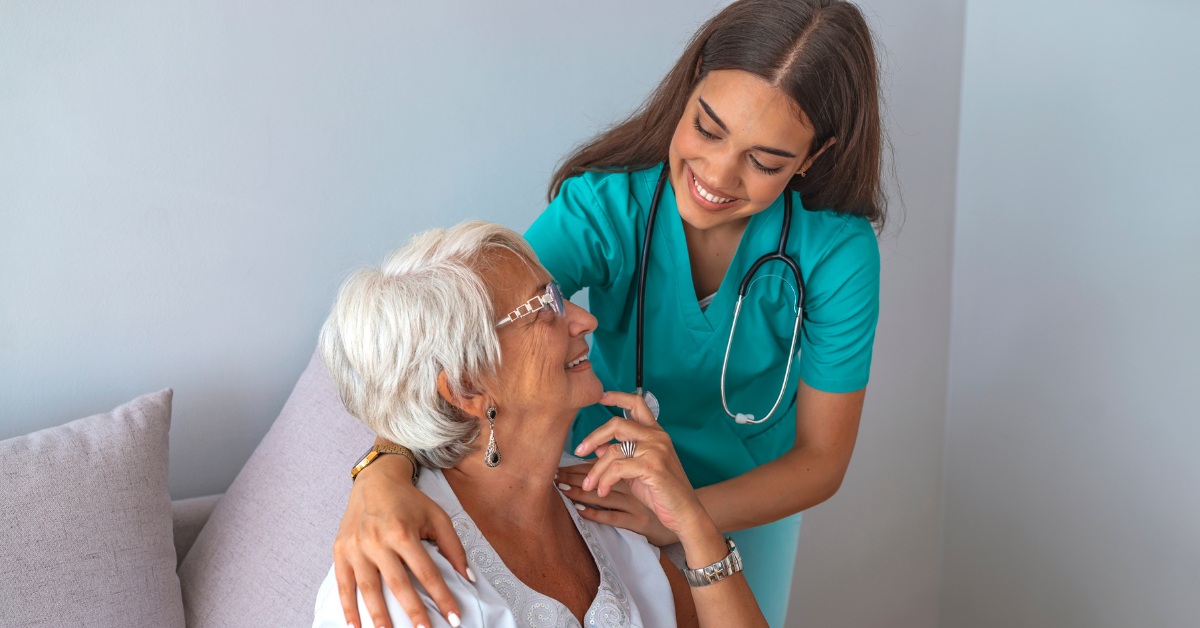

Top 3 Programs For Medicaid Assisted Living
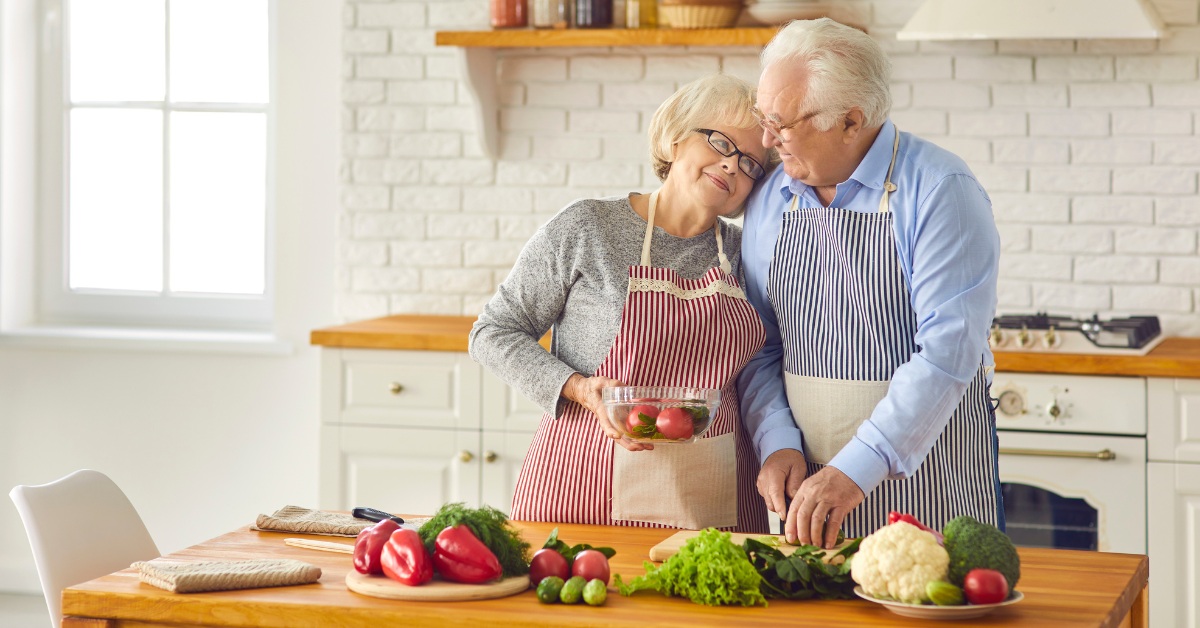

The Best Recipes for Elderly Parents
.jpg)
Exploring The Average Cost of Home Care
.jpg)
What Is The Most Common Home Care Service?
.jpg)
Can a Family Member Get Paid to be a Caregiver in NY?

The Role of Regular Floor Sweeping in Preventing Falls

Transportation Services: Helping Seniors Stay Connected

Errand Assistance: Supporting Senior Independence

The Role of Registered Nurses in Medication Setup at Home

Laundry Services: Ensuring Fresh and Clean Clothing

HomeTeam's Role in Self-Directed Care Coordination

Waste Management: Regular Trash Removal Services

Eligibility Requirements for Medicaid's Consumer Directed Services

Air Quality: Importance of Dusting and Vacuuming
.jpg)
Best Guide on Addressing Incontinence with Dignity
.jpg)
Top 5 Ways on Celebrating Milestones in Home Care
.jpg)
What Are Disability Rights Advocacy?
.jpg)
What are Elderly Companion Services?
.jpg)
Top 6 Benefits of Respite Care Programs
.jpg)
Top 7 Benefits of Daily Routines for Seniors
.jpg)
A Complete Guide on Supporting Independence at Home
.jpg)
Your Complete Hospital to Home Care Transition Guide
.jpg)
Aging in Place: Home Adaptations

The Importance of Medication Management
.jpg)
Does Long Term Health Insurance Cover in Home Care?
.jpg)
Importance of Home Care for Seniors
.jpg)
A Complete Guide to Occupational Therapy at Home
.jpg)
Understanding Mental Health Support at Home
.jpg)
How Often Should You do Physical Therapy at Home?
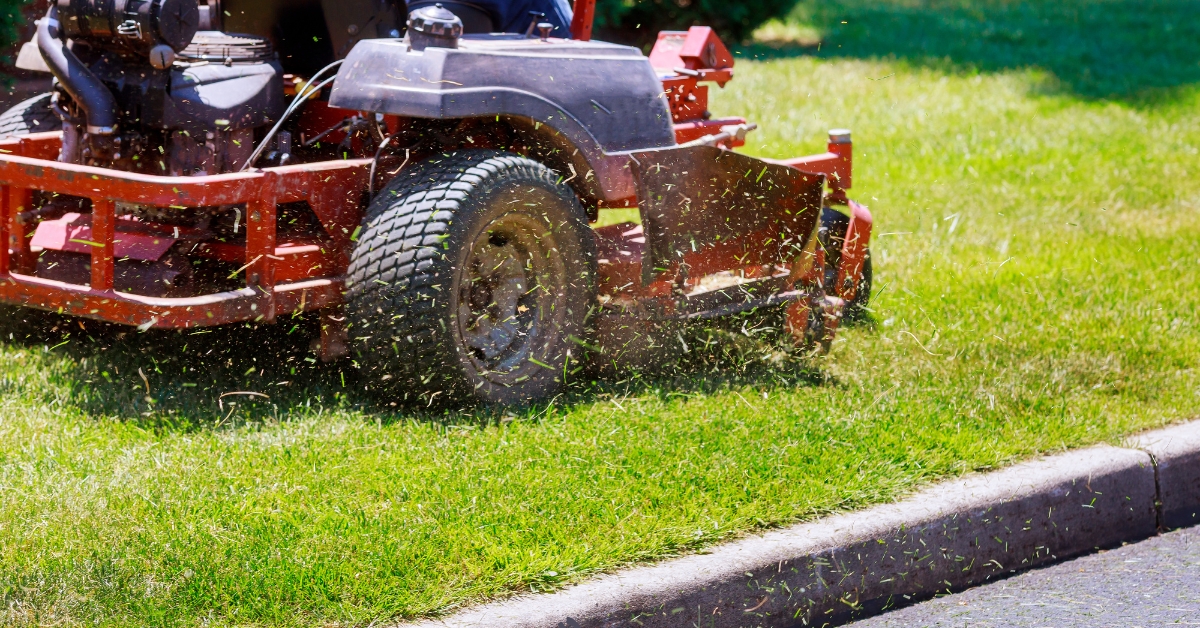

3 Tips in Yard Work Help for Seniors
.jpg)
Understanding Sleep Disorders in Seniors
.jpg)
In-Depth Guide on Managing Chronic Conditions at Home
.jpg)
What is Private Pay?
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits of Telemedicine in Home Care
.jpg)
Top 6 Exercise Benefits for Seniors
.jpg)
Best Support for Traumatic Brain Injuries
.jpg)
The Importance of Communication
.jpg)
Your Ultimate Guide on Preventing Falls for Seniors
.jpg)
A Complete Guide on Coping with Caregiver Burnout
.jpg)
How Much Does Private Home Care Cost?
.jpg)
In-Depth Guide to Home Modifications for Disabilities
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits of Integrating Nutrition for Wellness

What Insurance Covers in In-Home Care?
.jpg)
Top 3 Strategies for Supporting Family Caregivers
.jpg)
How to Apply for Medicaid in NC?
.jpg)
Ultimate Tips for Daily Living with Home Care
.jpg)
How Much Does the VA Pay for In-Home care?
.jpg)
A Complete Guide to Home Safety for Aging in Place
.jpg)
How to have Dental Care for Homebound Seniors?
.jpg)
How Much Does Private Home Care Cost Per Hour?
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits of Residential Care Facilities

Identifying Activities of Daily Living for Care Planning

Clothing Maintenance: Ironing and Mending Services

A Comprehensive Guide to Personal Care Services Offered by HomeTeam

Trash Removal: An Overlooked but Essential Home Care Service

Keeping the Home Clean: Essential Housekeeping Tasks

How to teach children with autism to accept changes in routines

The Role of Home Healthcare in Managing Diabetes

Understanding the Difference Between Skilled Nursing and Home Care

How Home Team Services Address Chronic Pain Management

The Financial Benefits of In-Home Care vs. Assisted Living

How to Encourage Seniors to Adopt Healthy Sleep Habits

How to Customize Therapy Goals for In-Home Recovery

How to Recognize Signs of Caregiver Stress in Families

The Importance of Reliable Transportation for Seniors

The Role of Pain Management Techniques in Home Therapy

The Role of Nutritional Counseling in In-Home Healthcare Plans

How to Choose Between Short-Term and Long-Term Home Care

The Benefits of Peer Support in Home Healthcare Programs

The Importance of Communication Between Caregivers and Families

How Home Team Services Help Manage Postpartum Recovery

The Benefits of Consistent Caregiver Assignments in Home Care

How to Address Behavioral Challenges in Pediatric Home Therapy

The Benefits of Home-Based Therapy Services for Seniors

The Role of Senior Advocacy in Home Care Services

The Benefits of Regular Care Plan Reviews for Seniors

The Role of Cognitive Therapy in In-Home Care Plans

The Benefits of Companionship for Seniors Receiving Home Care

How to Encourage Seniors to Embrace Healthy Lifestyle Changes

The Benefits of Combining Therapies in In-Home Care Plans

How Home Team Services Personalize Care for Senior Patients

The Benefits of Regular Assessments in Home Healthcare Plans

The Benefits of Regular Assessments in Home Healthcare Plans
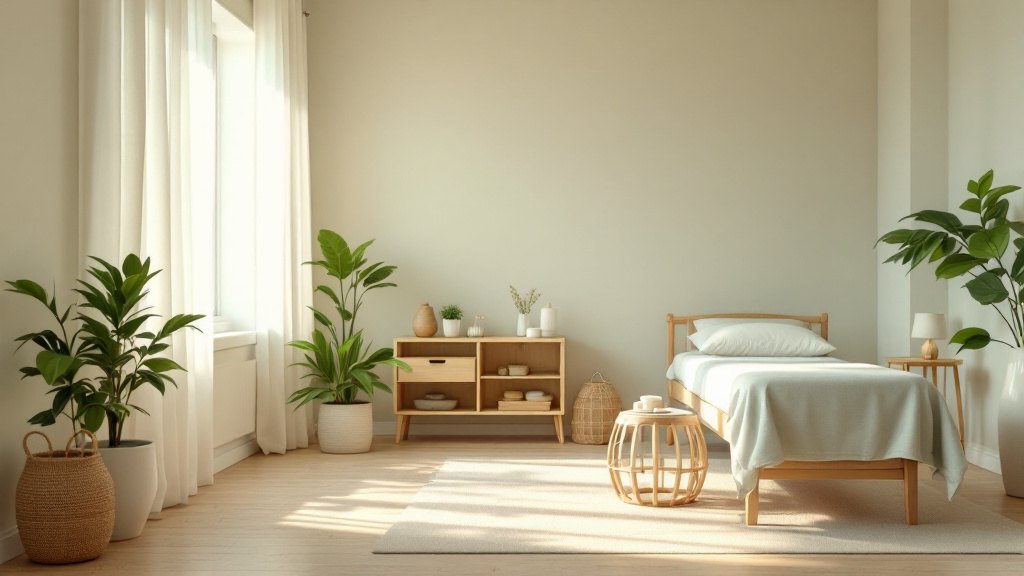

The Importance of Balance and Coordination Training in Home Therapy

The Importance of Proper Documentation in Home Care Services

How to Discuss Home Care Options with Aging Parents

The Role of Education in Empowering Home Health Patients

The Benefits of In-Home Physical Therapy for Seniors

The Role of Home Therapy in Post-Stroke Recovery

How Home Team Services Ensure Continuity of Care

How Home Care Improves the Quality of Life for Seniors

The Importance of Occupational Therapy in Daily Living Skills

How Home Team Services Provide Holistic Patient Care

The Importance of Strong Communication in Home Care Services

The Role of In-Home Rehabilitation After Orthopedic Surgery

How to Manage Transportation Challenges for Aging Parents

How to Address Common Challenges in In-Home Healthcare

The Importance of Personalized Care Plans for Seniors

How Home Team Services Provide Support for Palliative Care Patients
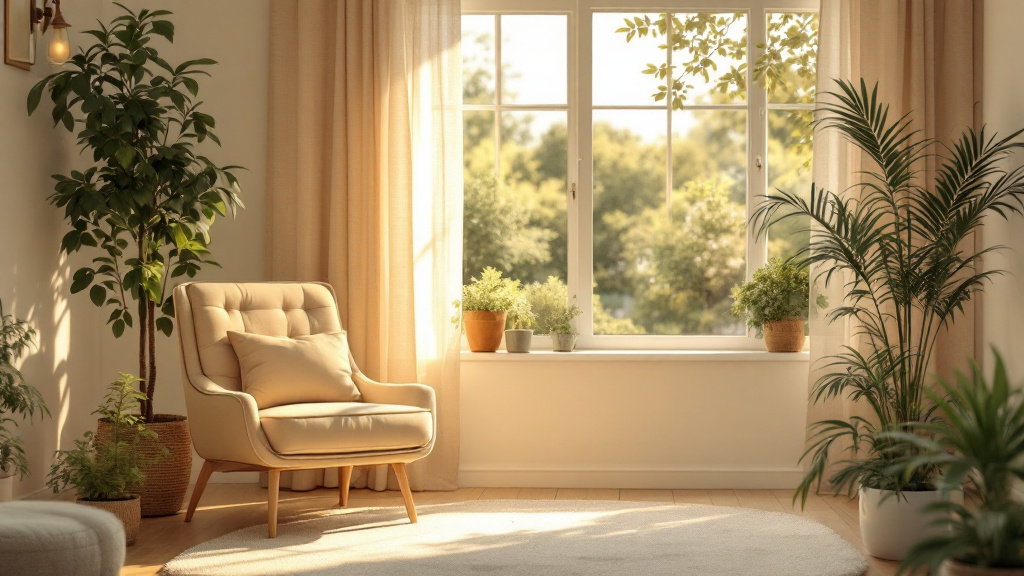

The Benefits of Having a Caregiver Companion for Seniors
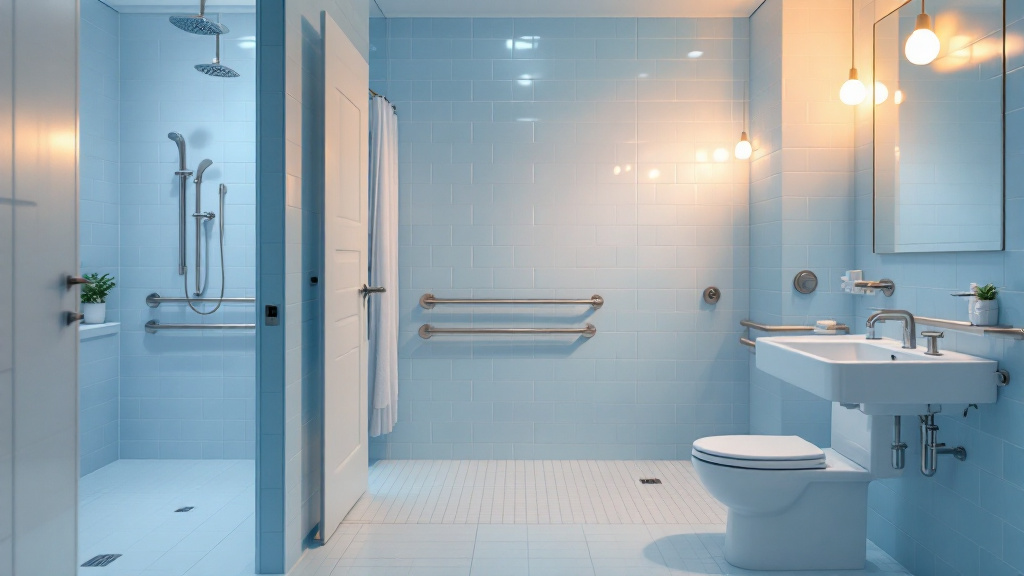

How to Create a Safe Bathroom for Seniors at Home

How to Help Seniors Transition to Using Mobility Aids

The Role of Pet Therapy in Senior Well-being
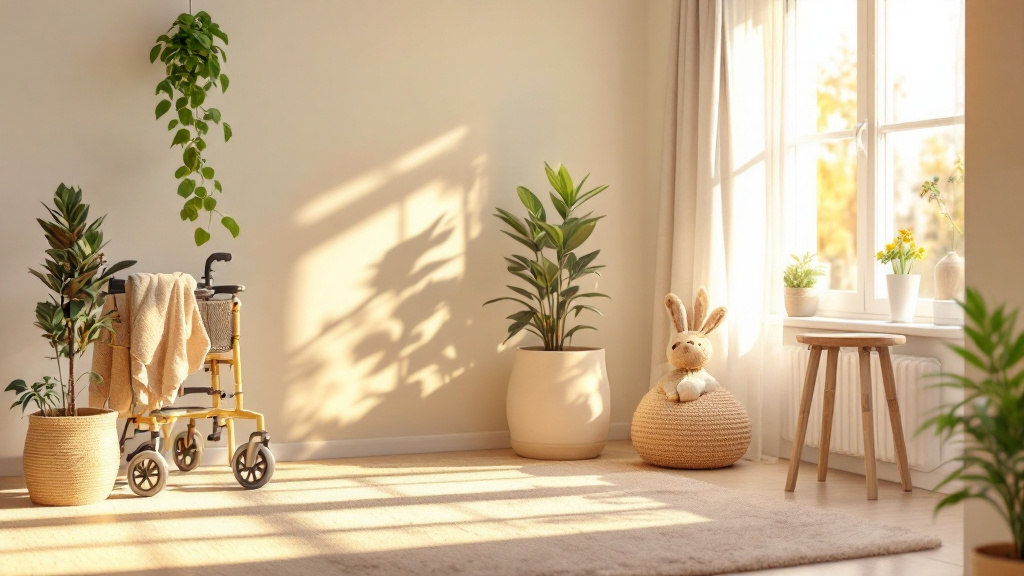

The Benefits of Mobility Training for Homebound Patients

The Role of Recreational Activities in Senior Home Care

The Importance of Sleep in Healing and Recovery at Home

How Home Team Services Address Mental Health in the Home Setting

The Importance of Emotional Support in Home Health Services

The Role of Technology in Modern In-Home Care

Benefits of 24/7 Live-In Care for Seniors

The Benefits of Senior Care for Couples at Home
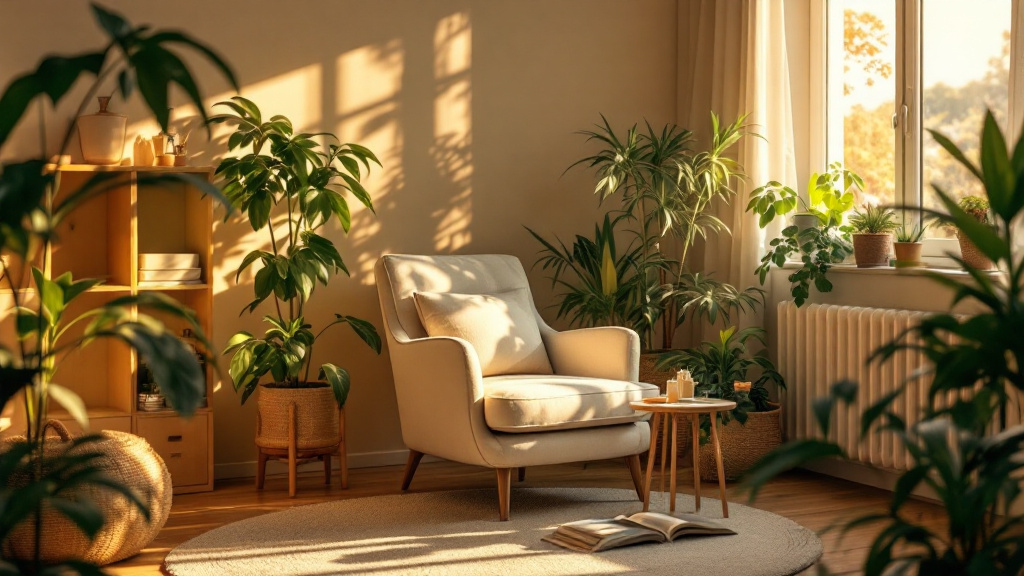

Understanding Hospice and Palliative Care Services at Home

The benefits of inclusive recreational activities

How to support transitions to new schools or therapists

The impact of ABA therapy on non-verbal children

The benefits of community integration for individuals with autism

How to address food aversions and expand diet options

How to foster independence in children with autism through ABA therapy

The role of functional behavior assessments in developing effective treatment plans

How to navigate insurance coverage for ABA therapy services

The benefits of telehealth options for in-home ABA therapy

How to use token economy systems to encourage positive behavior

How to address bullying concerns with children with autism

How to address bullying concerns with children with autism

How to support siblings of children with autism in the home

How to choose the right in-home ABA therapy provider

The role of humor and playfulness in building trust during therapy
.jpg)
When Will I Receive My Ebt Card After Being Approved?
.jpg)
What Old People Do for Fun?
.jpg)
Top 3 Benefits of CDPAP Caregiver Requirements
.jpg)
A Complete Guide To Home Care St. Louis

How long will Medicaid Pay for Home Care?
.jpg)
3 Types of Insurance Coverage for Home Care
.jpg)
How To Live Longer As A Senior?
.jpg)
What States Pay Family Caregivers?
.jpg)
Home Care Vs Assisted Living

The Most Common Home Care Covered by Insurance
.jpg)
What Are The Highest Paying Home Care Agencies?
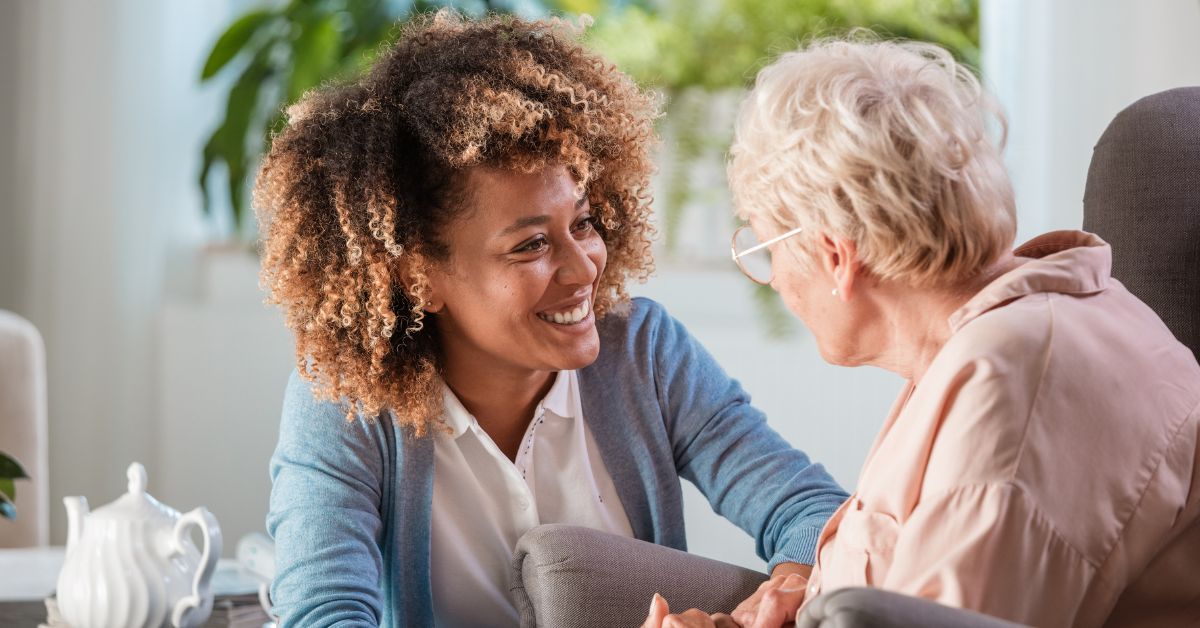

CDPAP vs Home Care
.jpg)
Free Home Repairs for Senior Citizens

How to address challenges related to puberty and adolescence

Strategies for teaching self-regulation skills to children

The role of therapy in teaching financial literacy skills

The importance of teaching children with autism to handle disappointment

How to use social media as a resource for autism support

The role of social stories in teaching new skills

The importance of understanding co-occurring conditions in autism

The importance of teaching safety and awareness in public settings

The benefits of combining therapy techniques for holistic development

How to create effective reinforcement systems at home

The role of ABA therapy in developing emotional intelligence

How to handle regression in learned skills at home

How to manage sibling dynamics in families with a child with autism

How to promote self-care for parents of children with autism

The Role of Technology in Enhancing In-Home Care Services

The Role of Advocacy in Navigating the CDS System

Why In-Home Care is More Affordable Than Many Families Realize

How Home Team's Caregivers Provide Comprehensive Support
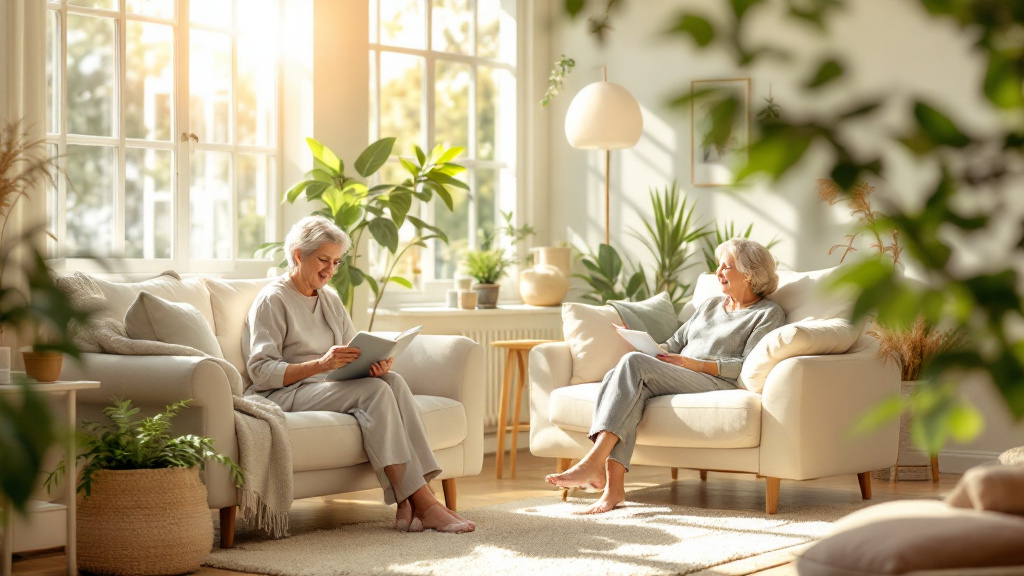

How CDS Programs Empower Individuals to Lead Independent Lives

How to Maximize the Benefits of CDS for You and Your Family

How CDS Programs Empower Individuals to Lead Independent Lives
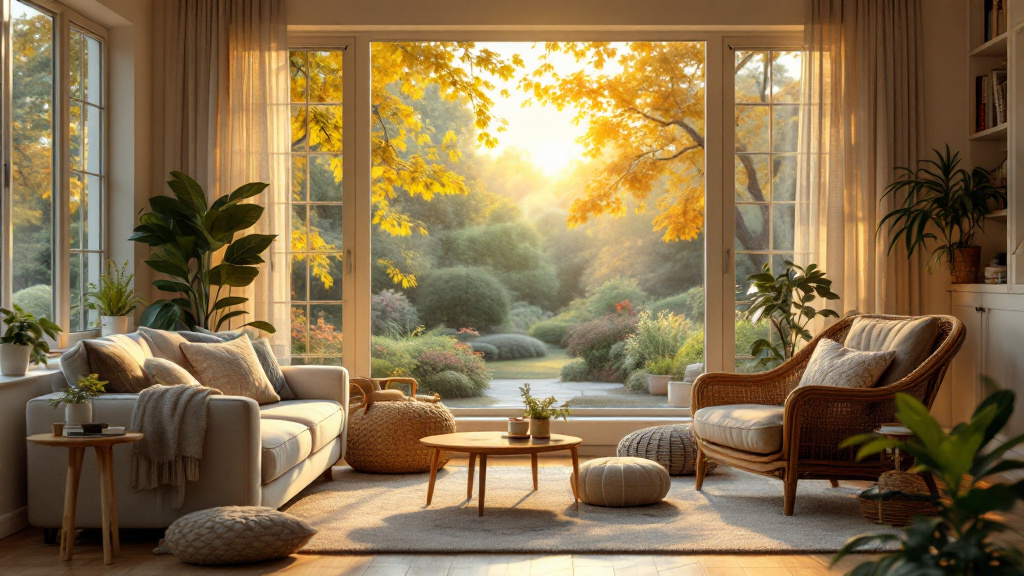

Why In-Home Care is the Best Choice for Individuals with Dementia

How to Build a Strong Relationship with Your In-Home Caregiver

Why In-Home Care is Ideal for Individuals Recovering from Surgery

How to Access Consumer Directed Services Without Hassle

The Role of Light Housekeeping in Creating a Healthy Home Environment

How to Find the Right Balance Between Independence and Support

What to Expect When Enrolling in a Consumer Directed Services Program

How to Avoid Caregiver Burnout with the Right Support

How to Create a Safe and Comfortable Space for Caregiving Activities

Why In-Home Care Services are the Best Option for Aging in Place

How to Choose the Right Caregiver for Your In-Home Care Needs

Why Home Team's Services Are Highly Recommended by Families

How to Ensure a Smooth Start to Your In-Home Care Journey
The Role of Personalization in Achieving Positive Care Outcomes
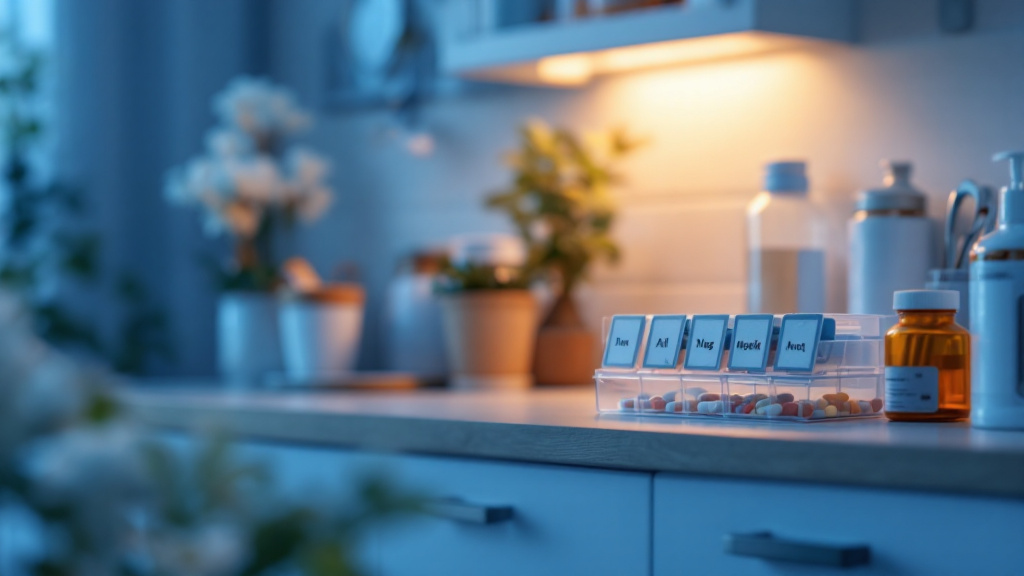

How to Manage Medications Effectively with the Help of In-Home Care

The Importance of Personalized Care Plans in Consumer Directed Services

The Benefits of Hiring a Trusted Agency for In-Home Care Services

Why Companion Care is Key to Combatting Loneliness Among Seniors

Why CDS Programs Are Ideal for Individuals with Long-Term Care Needs

Why Personal Care Services Are Essential for Aging in Place

How to Build a Successful Partnership with Your Caregiver

How CDS Programs Promote Dignity and Independence

How Home Team Helps Clients Access the Care They Need Most

The Role of Training and Support for Family Caregivers in CDS

How CDS Programs Reduce Stress for Families and Clients

The Importance of Open Communication in the Caregiving Process

Understanding the Role of Caregivers in the CDS Program

How to Handle the Challenges of Caregiving with Support from Home Team

Why In-Home Care is a Safer Alternative to Assisted Living Facilities


























